Competitive video gaming has transformed from basement hobby to legitimate high school sport over the past decade. What began as informal after-school gatherings has evolved into structured programs with dedicated coaches, regular practice schedules, competitive leagues, scholarship opportunities, and official recognition alongside traditional athletics. For schools exploring how to serve students with diverse interests while building college-ready skills, esports programs offer compelling opportunities that blend competition, teamwork, technology proficiency, and inclusive participation.
High school esports represents organized competitive gaming where students compete in team-based or individual video game competitions against other schools. These programs mirror traditional athletic structures with tryouts, regular practices, coaches providing strategic guidance, league competitions throughout seasons, championship tournaments, and post-season recognition. Games like League of Legends, Rocket League, Overwatch, Super Smash Bros., Valorant, and dozens of other titles provide competitive platforms where students develop tactical thinking, communication skills, and performance under pressure.
This comprehensive guide examines every dimension of high school esports—how programs operate structurally, what benefits students gain beyond gaming skills, how schools recognize competitive gaming achievements appropriately, and how modern digital recognition displays ensure esports competitors receive acknowledgment equal to their contributions and accomplishments.
Understanding High School Esports Programs
Esports programs in high schools provide structured competitive gaming opportunities organized similarly to traditional athletic teams. Students participate in sanctioned competitions, develop skills through coaching and practice, and represent their schools in interscholastic competition.
What Makes Esports Different from Casual Gaming
The distinction between casual gaming and competitive esports parallels the difference between shooting hoops recreationally and playing organized basketball. Esports involves structured practice, strategic preparation, team coordination, performance analysis, and competitive tournaments with meaningful stakes.

Competitive esports requires deep game knowledge including mechanics, strategies, meta-game understanding, and tactical adaptations. Players study opponent tendencies, analyze match replays, practice specific scenarios, and develop team coordination requiring communication precision that casual gaming never demands. The competitive pressure, accountability to teammates, and representation of school identity create experiences fundamentally different from recreational play.
According to the National Federation of State High School Associations (NFHS), high school esports participation has grown from fewer than 1,000 schools in 2018 to over 8,500 schools nationwide by 2026, demonstrating the rapid mainstream acceptance of competitive gaming as a legitimate school activity.
How Esports Programs Are Structured
Most high school esports programs follow organizational models similar to traditional athletics, adapted for the unique requirements of competitive gaming.
Team Organization:
Programs typically field multiple teams across different game titles rather than a single unified squad. A school might simultaneously support League of Legends, Rocket League, Valorant, Super Smash Bros., and Overwatch teams—each with separate rosters, practice schedules, and competition calendars. This multi-game approach accommodates varied student interests while maximizing participation opportunities.
Team sizes vary by game requirements. League of Legends and Valorant teams need five active players plus substitutes, while Super Smash Bros. competitions involve individual players representing their schools. Most programs roster 10-15 students per game to ensure adequate substitutes, practice partners, and coverage for absences.
Coaching and Supervision:
Quality programs employ coaches who understand both competitive gaming and adolescent development. Coaches might be teachers with gaming knowledge, professional esports coaches hired specifically for expertise, or community volunteers vetted through standard school procedures. Effective coaches provide strategic guidance, teach communication skills, analyze gameplay for improvement areas, and maintain appropriate behavioral standards.
Some schools struggle finding qualified coaching talent given esports’ relatively recent emergence. Solutions include professional development training through organizations like the North America Scholastic Esports Federation (NASEF), hiring specialist coaches who support multiple teams across games, or partnering with local gaming organizations providing coaching resources.
Practice Schedules:
Competitive teams practice 3-5 times weekly, typically for 1-2 hours per session. Practice structures blend individual skill development, team strategy refinement, scrimmages against other schools, replay analysis, and meta-game study examining professional competition trends.

Unlike traditional sports requiring specific facilities, esports practices occur in computer labs, dedicated esports facilities, or remotely from home with team communication through Discord or similar platforms. This flexibility offers accessibility advantages while creating supervision challenges schools must address thoughtfully.
Competitive Leagues and Tournaments
High school esports competitions occur through multiple organizational structures serving different competitive levels and student interests.
Major High School Esports Organizations:
PlayVS: The largest high school esports platform, partnered with NFHS to provide sanctioned competitions across 20+ game titles. PlayVS manages team registration, scheduling, match hosting, and standings tracking for state championships mirroring traditional sports governance.
North America Scholastic Esports Federation (NASEF): Nonprofit organization emphasizing educational aspects of esports through curriculum integration, college pathways, and inclusive participation beyond elite competition. NASEF runs seasonal leagues with less emphasis on exclusivity than win-at-all-costs competition.
High School Esports League (HSEL): Independent organization hosting competitions, tournaments, and championships with significant prize pools and scholarship opportunities for top performers.
Game-Specific Organizations: Publishers like Riot Games (League of Legends), Epic Games (Fortnite), and others run official scholastic programs with developer support, professional-grade competition infrastructure, and connections to collegiate and professional pathways.
Competition formats vary by organization and game. Regular season matches occur weekly throughout fall, winter, or spring seasons. Teams accumulate wins determining playoff seeding, culminating in state or national championship tournaments. Some competitions occur entirely online through game clients, while others feature in-person LAN events where teams compete at physical venues for championship finals.
Popular Game Titles in High School Competition
Different games appeal to varied student interests while developing distinct skill sets and offering unique competitive experiences.
Team-Based Strategy Games:
League of Legends: The most popular esports title globally, this multiplayer online battle arena (MOBA) requires five-player teams executing coordinated strategies, resource management, and tactical decision-making over 30-40 minute matches.
Valorant: Tactical first-person shooter combining precise aim with strategic ability usage, where five-player teams alternate between attacking and defending objectives requiring communication precision and adaptability.
Overwatch: Hero-based team shooter where players select from diverse characters with unique abilities, requiring team composition strategy, role specialization, and adaptive tactics.
Individual Competition Games:
Super Smash Bros. Ultimate: Fighting game where players compete one-on-one in tournaments, showcasing mechanical skill, game knowledge, and psychological pressure management.
Rocket League: Vehicle-based soccer combining precise car control with team coordination in fast-paced matches accessible to varied skill levels while maintaining high competitive ceilings.
Sports Simulation Games:
NBA 2K: Basketball simulation allowing students who love sports but may not make traditional athletic teams to compete through gaming expertise.
FIFA/EA Sports FC: Soccer simulation providing similar opportunities for sports enthusiasts channeling passion through competitive gaming.
Game selection balances competitive viability, student interest, age-appropriateness, spectator accessibility, and avoiding titles with excessive violence or mature content inconsistent with educational environments. Most programs avoid first-person shooters with realistic military combat, focusing instead on stylized or fantasy-themed competitions appropriate for school sponsorship.
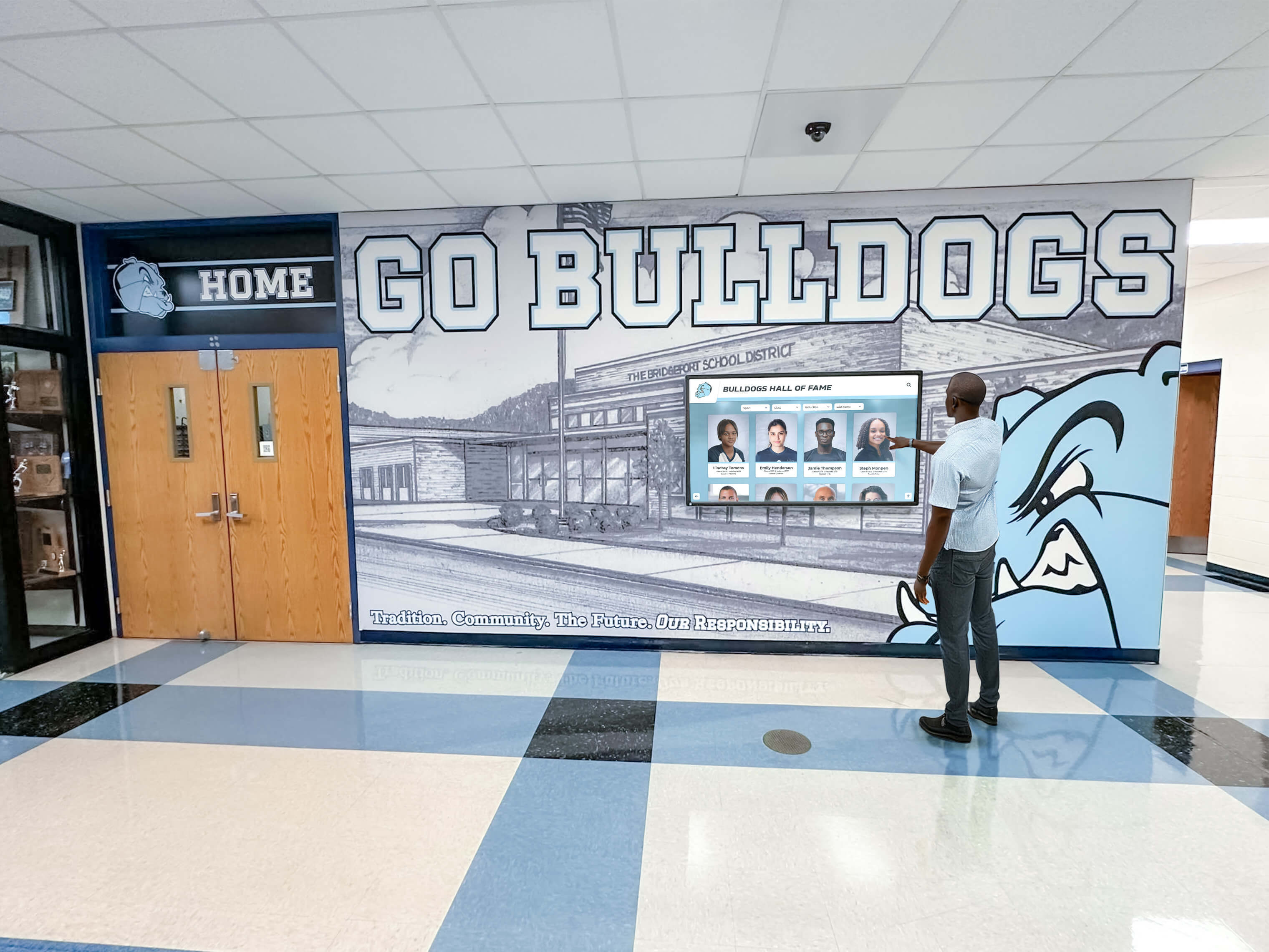

Benefits of High School Esports Programs
Beyond entertainment value, competitive esports develops transferable skills, creates inclusive participation opportunities, and supports college and career pathways increasingly relevant in technology-driven economies.
Academic and Cognitive Skill Development
Competitive gaming requires intellectual capabilities directly transferable to academic success and professional performance.
Strategic Thinking and Problem-Solving:
Esports demands rapid analysis of complex situations, pattern recognition, prediction of opponent behaviors, and strategic adaptation based on changing conditions. These cognitive processes mirror skills required in mathematics, science, business strategy, and countless professional contexts. Research from the University of California, Irvine found that competitive gaming improves problem-solving speed, strategic planning capabilities, and multi-tasking efficiency.
Communication and Teamwork:
Team-based esports requires constant verbal communication coordinating tactics, sharing information about opponent positions, calling plays, and providing encouragement under pressure. Effective teams develop communication clarity, conflict resolution skills, and shared mental models enabling synchronized action—capabilities valuable in collaborative academic projects and workplace team environments.
Unlike some traditional sports where only certain positions require extensive communication, esports demands that every player continuously contribute to team information flow. This universal communication requirement ensures all participants develop verbal coordination skills rather than some players primarily executing physical tasks with minimal verbal interaction.
Digital Literacy and Technology Skills:
Participating in esports naturally develops technological competency increasingly essential for career success. Students gain familiarity with computer hardware, troubleshooting technical issues, using communication platforms, managing online accounts, understanding network connectivity, and navigating digital competition infrastructure. These practical technology skills complement academic computer education with hands-on application developing genuine proficiency.
According to the International Society for Technology in Education (ISTE), esports participation correlates with improved digital citizenship understanding, online safety awareness, and responsible technology use as students navigate competitive gaming’s social and ethical dimensions.
Social and Emotional Benefits
Esports creates community connections and emotional growth opportunities particularly valuable for students who may not thrive in traditional extracurricular activities.
Inclusive Participation Opportunities:
Traditional athletics create inherent participation barriers through physical requirements, size considerations, and competitive pyramid structures where only elite performers earn playing time. Esports offers more accessible entry points where students with varied physical abilities can compete on equal footing based purely on skill, strategy, and dedication.

This inclusivity proves particularly significant for students with physical disabilities who face limited options in traditional athletics. Competitive gaming removes physical barriers while maintaining all the teamwork, competition, and school representation opportunities that make athletics valuable. Programs report strong participation from female students, underrepresented minorities, and students with disabilities who historically faced access limitations in traditional athletic contexts.
Research from the Positive Coaching Alliance found that schools with esports programs show increased overall student engagement in school activities, with over 60% of esports participants reporting that gaming teams represented their first involvement in competitive school activities.
Social Belonging and School Connection:
Adolescents need peer communities where they feel valued and connected. For students passionate about gaming but uninterested in traditional activities, esports provides that crucial social belonging. Team membership creates regular social interaction, shared challenges building camaraderie, and common interests facilitating friendships that might not develop otherwise.
Coaches consistently report that students involved in esports demonstrate improved school attendance, better grades due to eligibility requirements, and stronger connections to school communities. The identity as team representative creates investment in school reputation and pride in institutional affiliation similar to traditional athletic participation.
College and Career Pathway Development
Esports participation increasingly connects to tangible post-secondary opportunities including scholarships, collegiate competition, and career pathways in gaming and technology industries.
Collegiate Esports Scholarships:
Over 200 colleges and universities now offer varsity esports programs with scholarship support for competitive gamers. Schools like the University of California, Irvine, Ohio State University, and hundreds of others recruit talented high school players offering scholarship packages sometimes reaching full tuition value for elite performers.
According to the National Association of Collegiate Esports (NACE), member institutions distributed over $16 million in esports scholarships during the 2025-2026 academic year—creating genuine college access pathways for students who excel in competitive gaming. These opportunities particularly benefit students from families with limited college financial resources who might otherwise struggle accessing higher education.
Beyond direct esports scholarships, competitive gaming experience strengthens college applications by demonstrating commitment, teamwork, leadership, and diverse interests. Admissions officers increasingly value esports participation as evidence of modern skill development and digital proficiency relevant to contemporary educational contexts.
Career Pathways in Gaming and Technology:
The global gaming industry generates over $200 billion annually, creating diverse career opportunities extending far beyond professional player positions. Esports participation exposes students to careers in game design, software development, broadcast production, marketing, event management, data analytics, coaching, and countless other professional pathways.
Students passionate about gaming often channel that interest into computer science education, digital media studies, business programs focused on entertainment industries, or communication degrees emphasizing broadcast and content creation. High school esports provides concrete experience and industry exposure informing career exploration during critical developmental periods when students establish professional directions.

According to career development research from NASEF, over 40% of high school esports participants pursue STEM majors in college—significantly higher than general student populations—suggesting gaming interest effectively channels students toward high-demand technical fields.
How Schools Recognize Esports Achievements
As esports programs mature and gain acceptance, schools increasingly recognize competitive gaming accomplishments through ceremonies, awards, and permanent displays paralleling traditional athletic recognition.
Awards and Recognition Categories
Quality esports programs celebrate diverse achievements ensuring varied contributions receive appropriate acknowledgment.
Individual Performance Recognition:
- Most Valuable Player (MVP) Awards: Recognizing exceptional individual performances throughout seasons based on statistics, impact in critical matches, and consistent excellence.
- All-Conference and All-State Selections: League organizations select top performers across positions and games for prestigious honors paralleling traditional athletic all-star recognition.
- Game-Specific Excellence Awards: Recognition for leading statistics in particular games, such as highest KDA (kill/death/assist) ratios in MOBAs, best save percentages in Rocket League goalkeepers, or tournament performance consistency.
- Most Improved Player: Acknowledging students who demonstrate remarkable growth throughout seasons, celebrating development and dedication beyond absolute performance levels.
Team Achievement Recognition:
- Conference Championships: Teams winning regular season competitions in their leagues receive championship recognition comparable to traditional sports conference titles.
- State Championship Recognition: PlayVS state champions and equivalent achievements through other organizations deserve prominent celebration as peak competitive accomplishments.
- National Tournament Qualifications: Teams reaching national championship events represent exceptional achievement warranting permanent recognition regardless of final placement.
- Season Records and Milestones: Undefeated seasons, longest winning streaks, and program records provide recognition opportunities celebrating collective team excellence.
Character and Contribution Awards:
- Sportsmanship Awards: Recognizing students who exemplify positive competitive behavior, respectful opponent treatment, and gracious performance under pressure or disappointment.
- Leadership Recognition: Team captains, players who mentor newer teammates, and students advancing program culture deserve acknowledgment for contributions beyond personal performance.
- Academic Excellence Awards: Students maintaining high GPAs while competing in esports demonstrate balanced priorities worthy of special recognition.
- Community Builder Recognition: Students organizing team activities, managing social media presence, or supporting team cohesion through positive influence.

Traditional Recognition Methods for Esports
Schools apply familiar recognition approaches from traditional athletics adapted for competitive gaming contexts.
End-of-Season Banquets:
Esports teams increasingly host formal banquet events celebrating season accomplishments, presenting individual awards, recognizing senior contributions, and honoring team achievements. Similar to athletic banquet celebrations, these events provide formal recognition opportunities bringing together players, families, coaches, and school administrators celebrating students appropriately.
Well-executed banquets include highlight video presentations showcasing season moments, coach speeches recognizing individual contributions, formal award presentations with physical trophies or plaques, senior recognition honoring graduating players, and guest speakers from collegiate programs or gaming industry discussing opportunities and pathways.
School Assembly Recognition:
Esports achievements deserve acknowledgment during school-wide assemblies alongside traditional athletic accomplishments. Announcing championship victories, recognizing all-conference selections, and introducing esports teams during assembly programs validates gaming competition as legitimate school activity deserving community celebration.
Assembly recognition proves particularly important for establishing esports credibility among students unfamiliar with competitive gaming. Visible school-wide acknowledgment signals institutional support, helps normalize esports participation, and encourages broader student consideration of gaming teams as viable activity options.
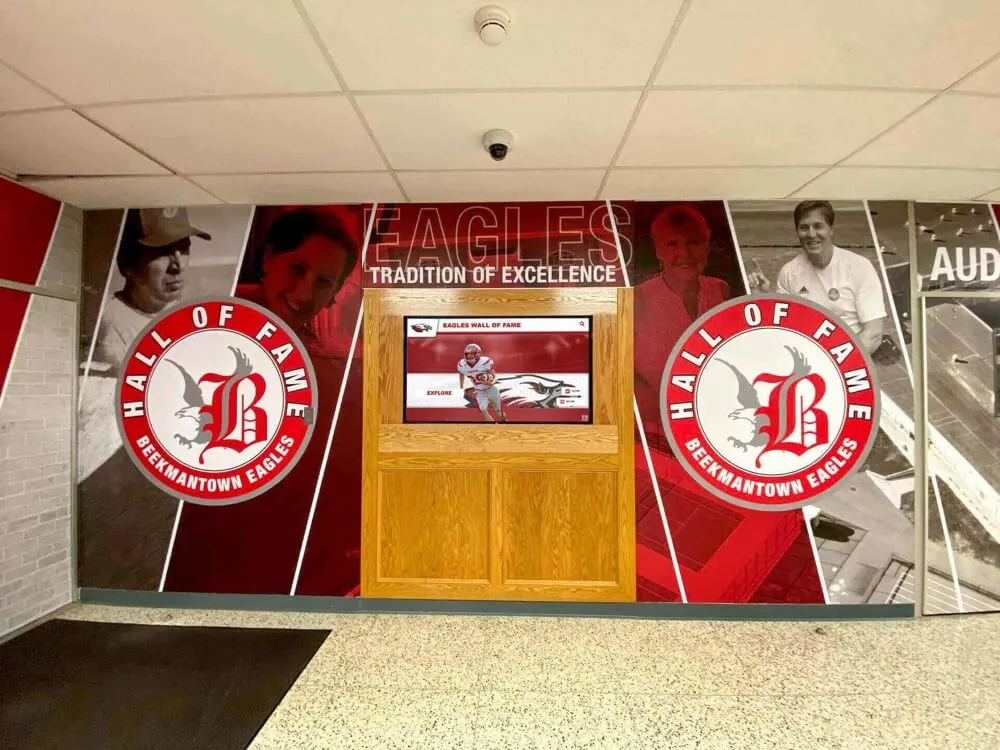
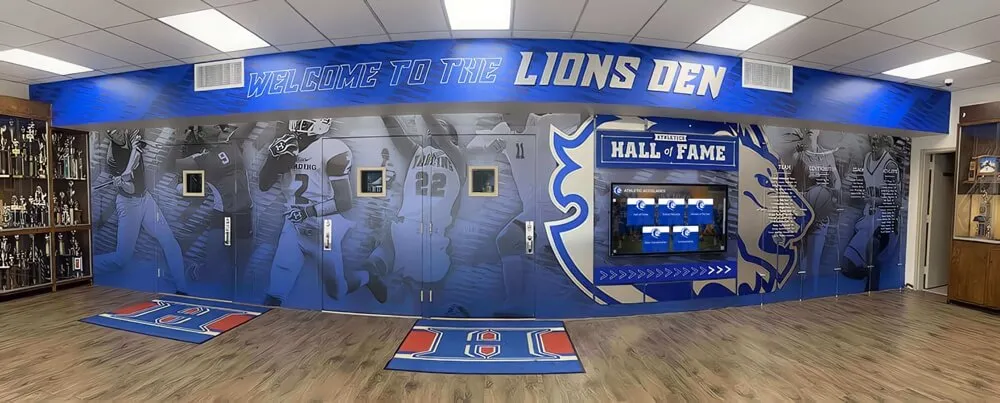
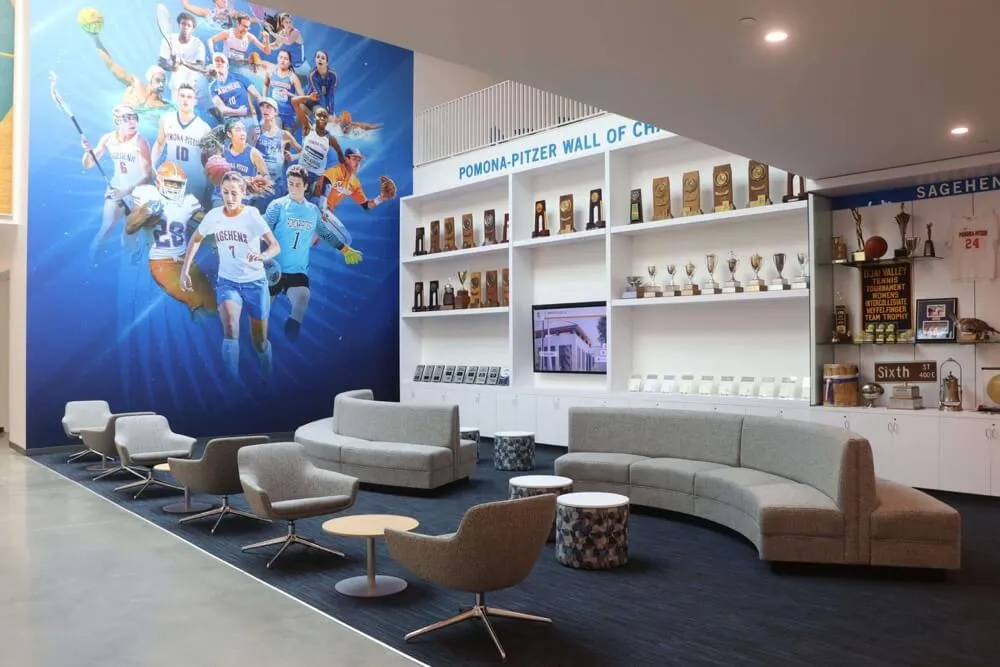
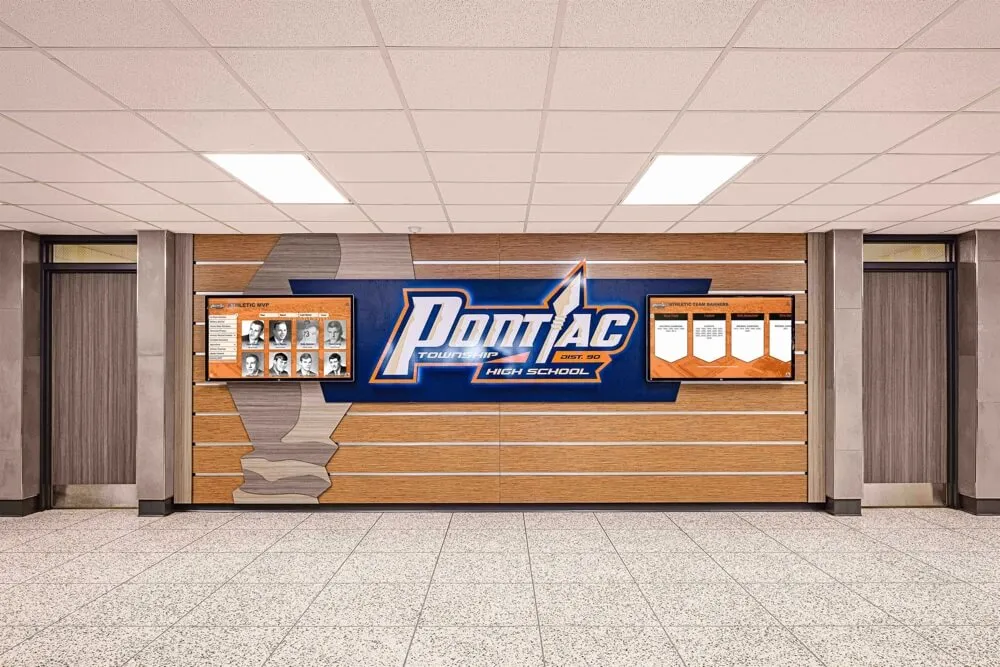
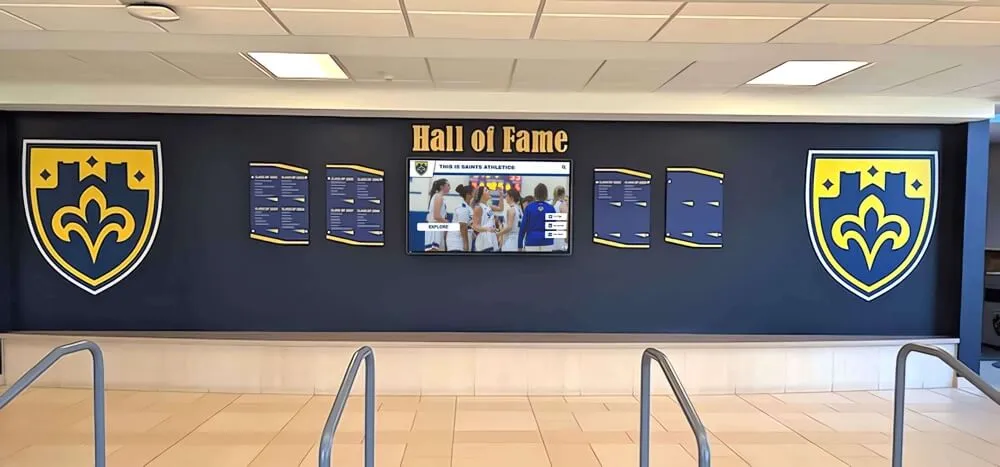
Championship Banners and Physical Displays:
State championship banners, conference title recognition, and tournament placement displays in school facilities provide permanent visible acknowledgment of esports achievements. While traditional trophy cases may not perfectly accommodate gaming achievements, schools increasingly dedicate display space ensuring esports receives physical recognition comparable to other competitive activities.
Modern Digital Recognition for Esports
Digital recognition platforms offer particularly appropriate solutions for esports achievements given gaming’s technological nature and the limitations of traditional physical displays for showcasing digital competition results.
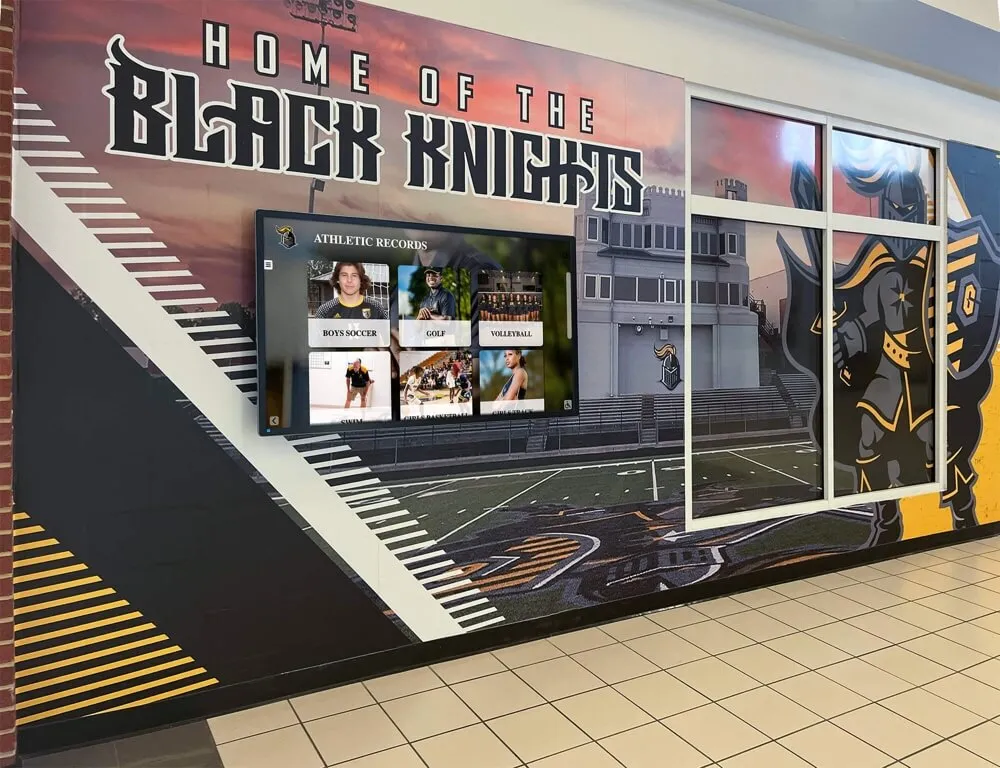
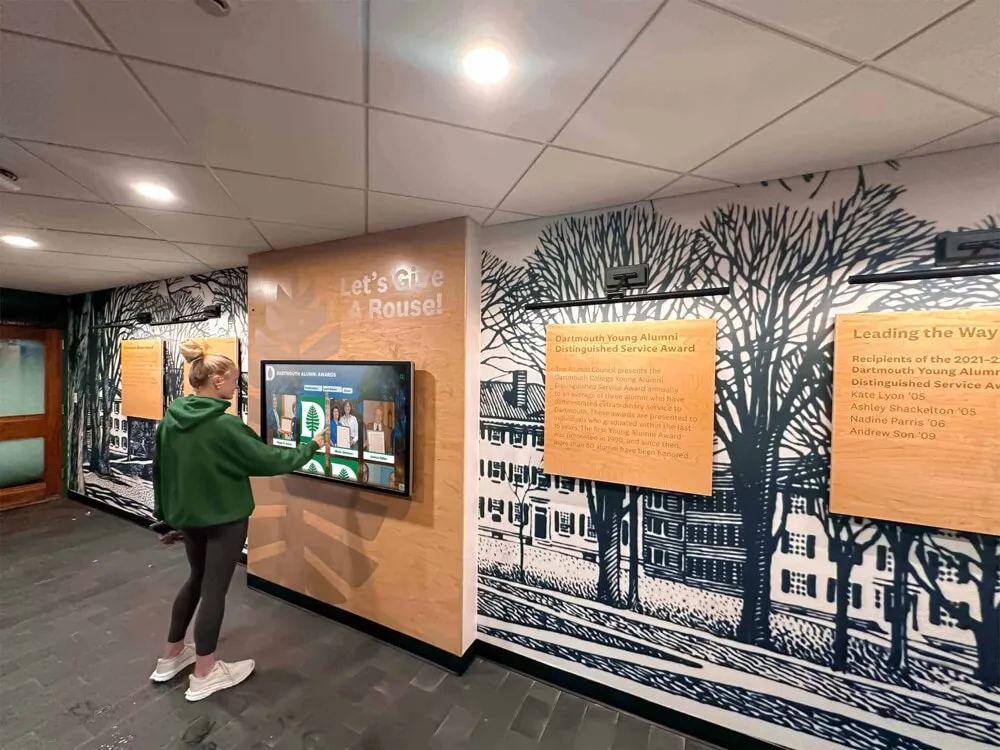
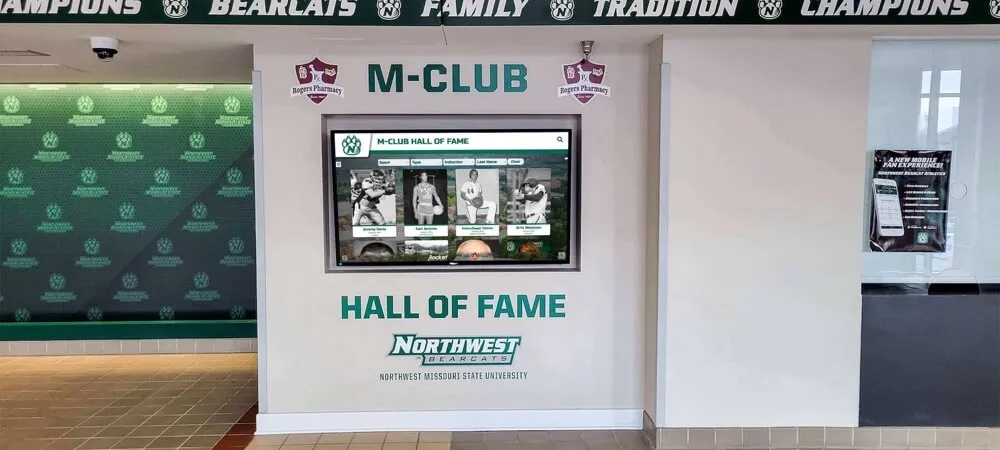
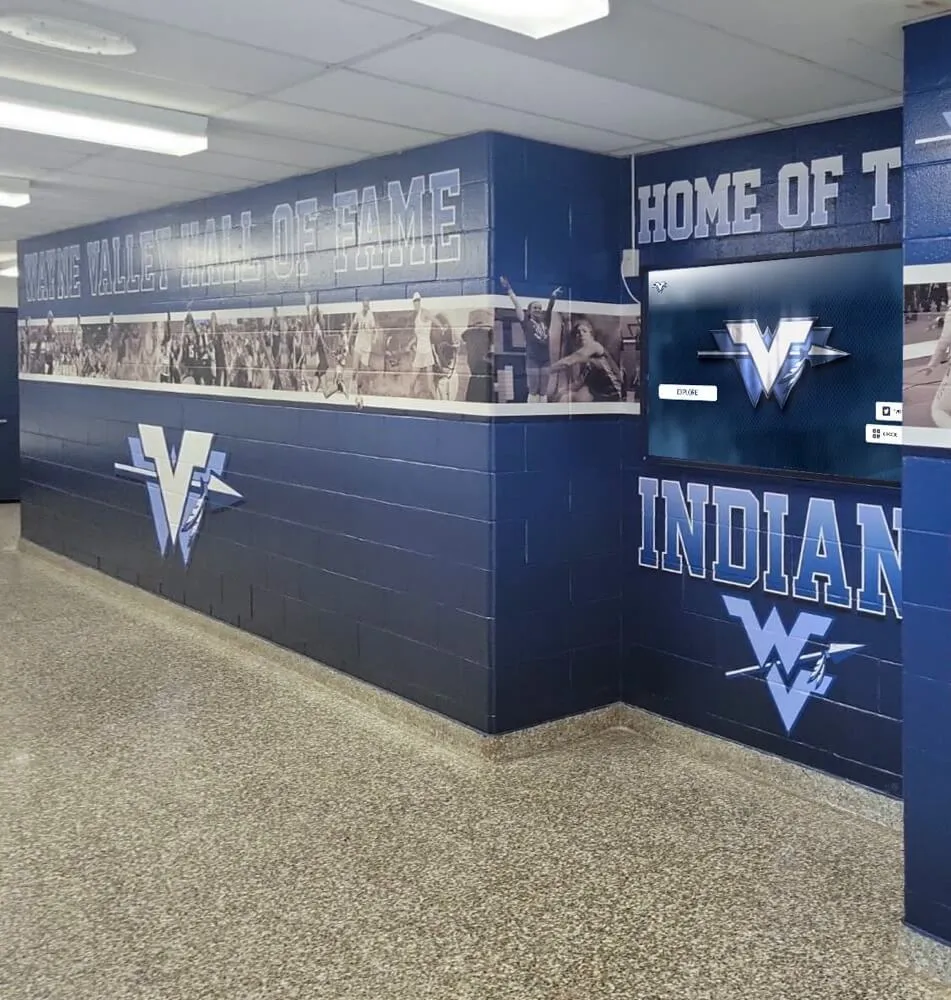
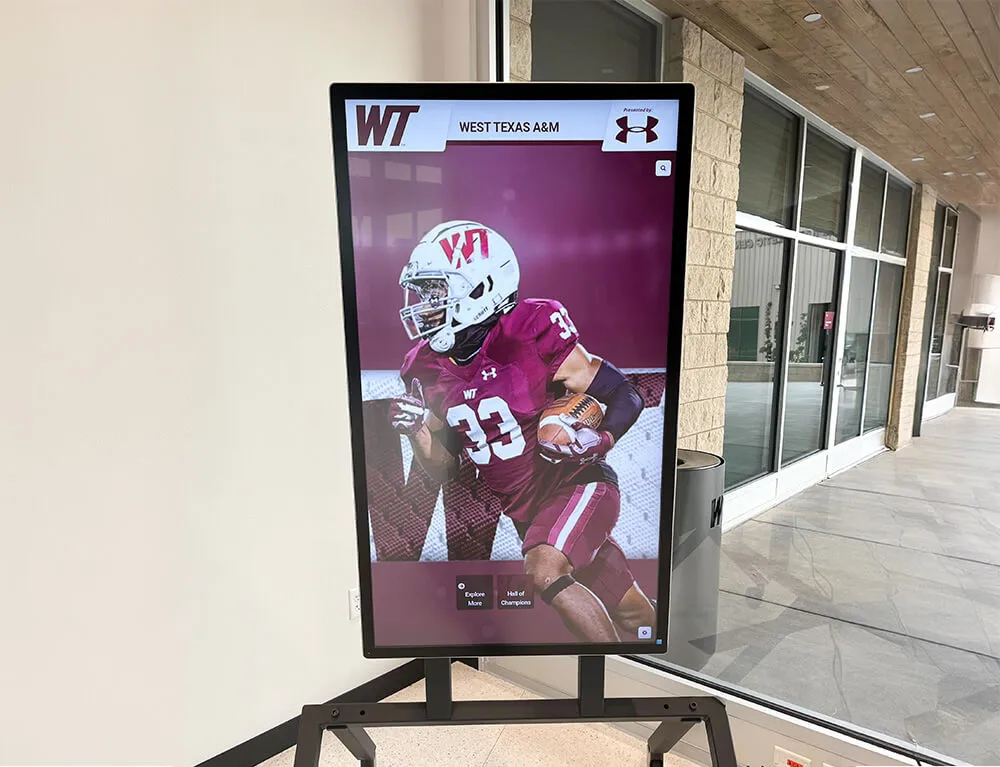
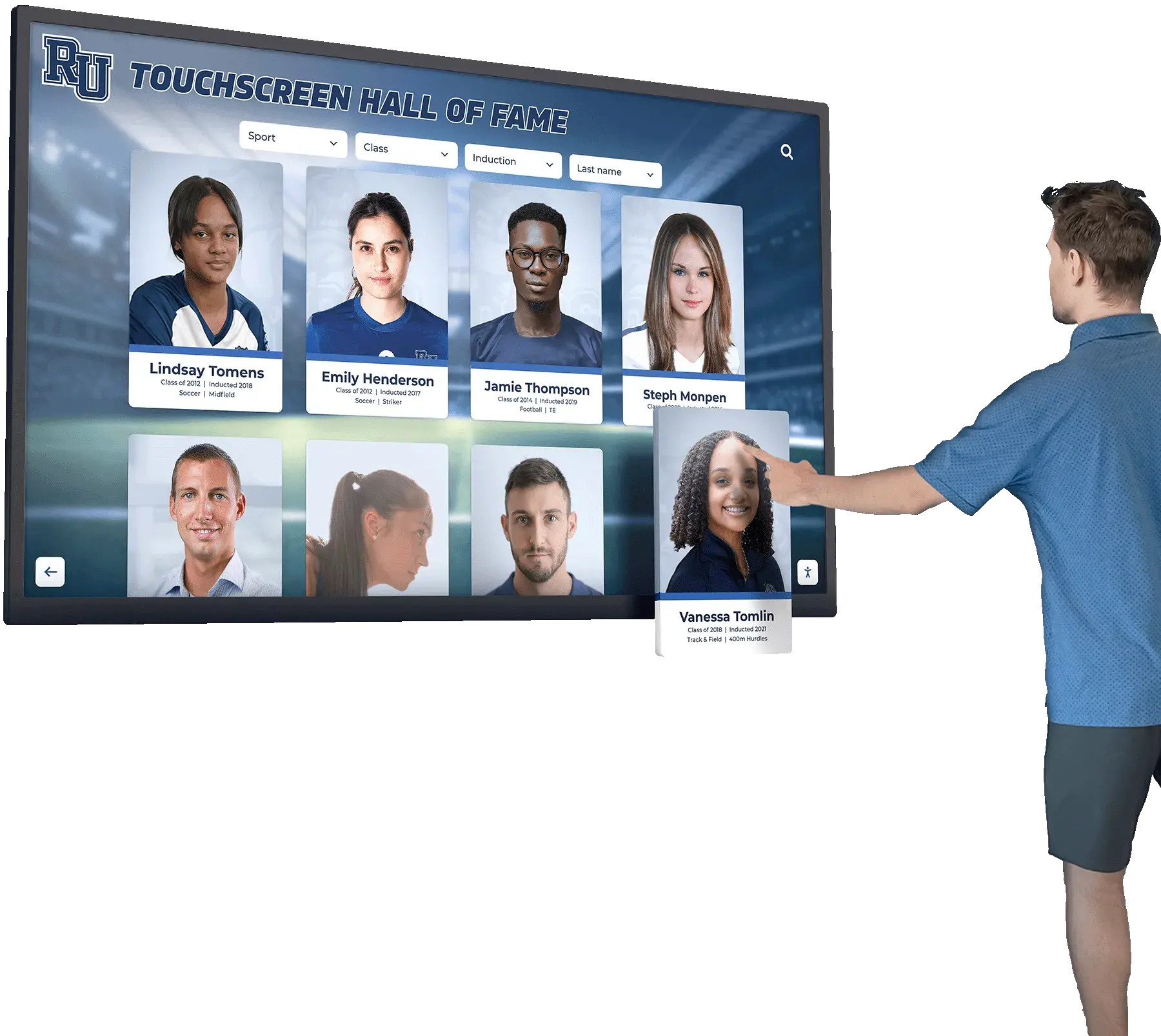
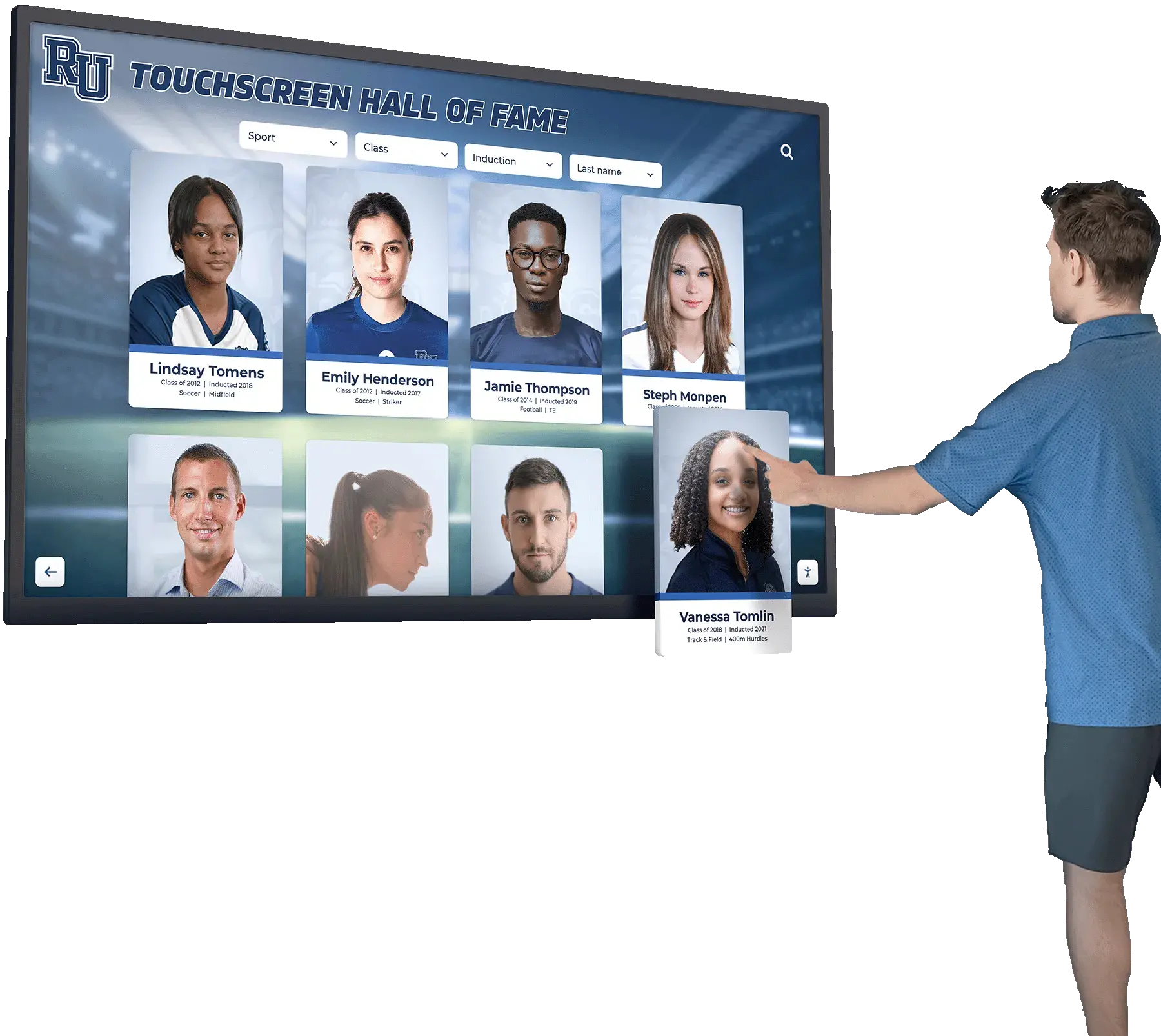
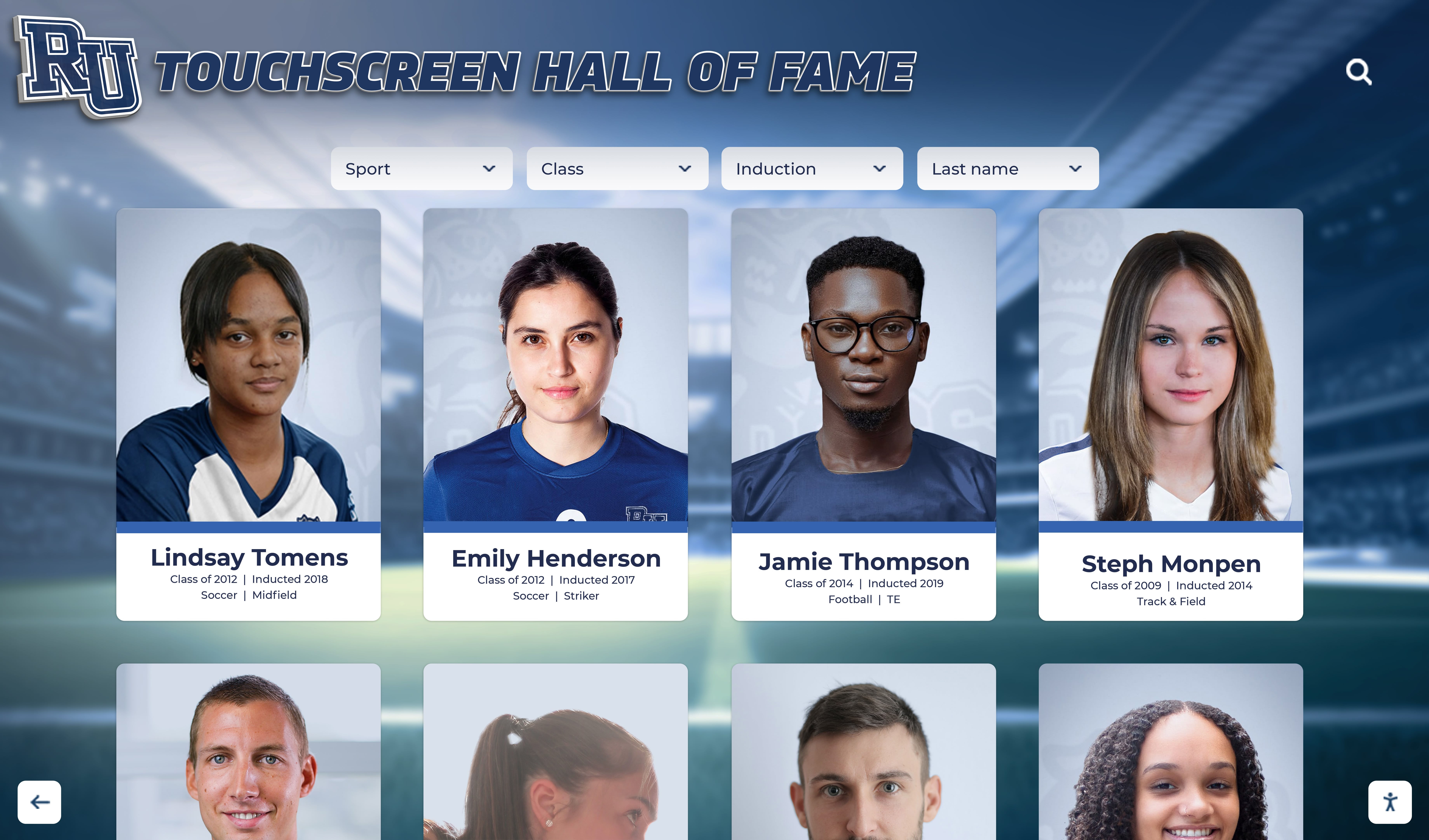
Interactive Touchscreen Displays:
Digital recognition systems provide ideal platforms for celebrating esports accomplishments through rich multimedia content impossible with traditional physical plaques. Touchscreen displays can showcase player profiles with comprehensive statistics, highlight video clips from championship matches, team rosters with individual photographs, season records and tournament brackets, championship recognition across multiple years, and detailed achievement histories preserving program legacy permanently.
Unlike physical trophy cases with finite space, digital platforms accommodate unlimited esports recognition without forcing choices about which achievements deserve permanent display. Every state championship, all-conference selection, and significant team accomplishment receives comprehensive acknowledgment without space constraints limiting recognition scope.
Interactive functionality allows students, families, and visitors to explore esports achievements through intuitive search, filter by game title or season, compare historical performance trends, and discover detailed stories behind competitive accomplishments—engagement impossible with static physical displays.
Integration with Traditional Athletic Recognition:
Modern recognition platforms enable schools to seamlessly integrate esports alongside traditional athletics, academics, arts, and other achievements within unified systems. This integration demonstrates that institutions value diverse excellence forms equally rather than creating segregated recognition suggesting esports represents lesser accomplishment.
Solutions like Rocket Alumni Solutions provide purpose-built recognition platforms accommodating athletics, esports, academics, arts, community service, and unlimited achievement categories from single unified systems. Schools using these platforms report that integrated recognition helps legitimize esports participation while ensuring gaming achievements receive display prominence equivalent to their significance and effort required.
Web Accessibility for Remote Engagement:
Digital recognition platforms with web accessibility enable esports participants to share achievements through social networks, connect with collegiate recruiting programs, and maintain ongoing engagement with accomplishments long after graduation. This extended reach proves particularly valuable for esports given gaming’s online nature and digital-native participant expectations for web-based content access.
Alumni competing professionally or continuing gaming careers at collegiate levels can point recruiters, sponsors, or professional contacts to permanent recognition records documenting high school accomplishments, tournament performances, and competitive credentials—creating tangible value beyond emotional acknowledgment alone.
Addressing Common Concerns About High School Esports
Despite growing acceptance, some stakeholders maintain reservations about gaming programs requiring thoughtful responses addressing legitimate concerns while advocating for inclusive activity offerings.
Concern: Screen Time and Health Implications
Critics worry that school-sponsored esports encourages excessive screen time contributing to health issues including obesity, vision problems, and sedentary lifestyle development.
Balanced Response:
Quality esports programs incorporate health education addressing physical wellness explicitly. Responsible programs include stretching exercises preventing repetitive strain injuries, posture education minimizing back and neck problems, vision break protocols reducing eye strain, and overall wellness curricula discussing balanced lifestyle integration with gaming participation.
Research from the American Academy of Pediatrics suggests that structured competitive activity—even screen-based—provides superior outcomes compared to unstructured solo gaming. Supervised team practice with coaching, specific time boundaries, and skill development focus represents fundamentally different activity than unsupervised recreational gaming without limits or purpose.
Additionally, many students passionate about gaming spend substantial time playing regardless of school program existence. Channeling that interest into structured supervised activity with positive peer communities, adult mentorship, and health education provides better outcomes than leaving gaming purely as unmonitored leisure activity.
Concern: Violent Content and Inappropriate Games
Some stakeholders express concern about schools sponsoring competitive gaming potentially involving violent or age-inappropriate content.
Balanced Response:
Responsible esports programs establish clear game selection criteria prioritizing age-appropriate titles consistent with educational contexts. Most high school programs avoid realistic military shooters or games with graphic violence, focusing instead on fantasy-themed MOBAs, stylized shooters, sports simulations, racing games, and fighting games with cartoon aesthetics.
Organizations like PlayVS and NASEF maintain approved game lists vetted for age-appropriateness, excluding titles with ESRB ratings above Teen, extreme violence, or content inconsistent with educational settings. Schools maintain final authority over game participation, allowing districts to exclude specific titles if community standards warrant more conservative approaches.
The gaming industry has evolved significantly, with many competitive titles designed intentionally for broad audiences including younger players. Games like Rocket League, Super Smash Bros., and sports simulations contain zero questionable content while providing legitimate competitive platforms developing valuable skills.
Concern: Distraction from Academics
Critics worry esports participation diverts time and attention from academic priorities, potentially harming educational performance for struggling students.
Balanced Response:
Well-structured esports programs establish academic eligibility requirements paralleling traditional athletics. Most programs require minimum GPA thresholds (typically 2.0-2.5) for participation, regular grade monitoring ensuring academic standing maintenance, and mandatory benching for students falling below standards until improvement occurs.
Research data consistently shows that students participating in extracurricular activities—including esports—demonstrate better academic performance compared to non-participants. The National Center for Education Statistics found that extracurricular participation correlates with higher GPAs, improved attendance, better graduation rates, and enhanced college enrollment across all activity types including esports.
Similar to recognizing academic excellence alongside athletic achievement, esports programs create academic accountability structures helping maintain educational focus while providing valued participation opportunities motivating school engagement for students who might otherwise remain disconnected from institutional communities.
Concern: Limited Transferable Skills Compared to Traditional Sports
Skeptics question whether esports develops capabilities comparable to traditional athletic participation, suggesting physical sports provide superior character development and life skill training.
Balanced Response:
While esports lacks cardiovascular fitness development inherent to physical sports, competitive gaming builds numerous transferable skills highly relevant to contemporary career and life success. Communication under pressure, strategic thinking, rapid decision-making, team coordination, resilience following setbacks, competitive drive, and technology proficiency all emerge through quality esports participation.
The question shouldn’t be whether esports provides identical benefits to traditional athletics—different activities naturally develop different capabilities. Rather, schools should ask whether esports provides sufficient value justifying institutional support and whether programming serves students who might not otherwise participate in school activities.
For students with physical limitations, those uninterested in traditional sports, or populations historically underrepresented in athletics, esports creates participation pathways fostering school connection, developing valuable skills, and providing competitive experiences that might not occur otherwise. According to student engagement research, schools offering diverse activity options including esports show higher overall participation rates compared to institutions maintaining limited traditional programming.
Starting an Esports Program in Your School
Schools interested in launching esports programs face practical considerations regarding facilities, funding, league affiliations, and program management requiring systematic planning approaches.
Facility and Equipment Requirements
Unlike traditional sports requiring specialized facilities, esports programs adapt to varied space and technology configurations based on available resources.
Space Options:
- Computer Labs: Many schools launch programs using existing computer labs after school hours, requiring zero additional facility investment while leveraging equipment already available.
- Dedicated Esports Rooms: Some schools create specialized gaming spaces with optimized equipment, comfortable seating, streaming capabilities, and team collaboration areas when budgets and facilities allow investment.
- Hybrid Approaches: Students might practice remotely from home during some sessions while gathering for team practices, strategy sessions, and match competitions requiring in-person coordination.
Technology Requirements:
Minimum specifications vary by game requirements. Competitive titles like Rocket League and sports simulations run adequately on modest systems, while intensive games like Valorant or League of Legends require more capable hardware. Most programs aim for gaming PCs with mid-range graphics cards, solid-state storage, quality monitors with adequate refresh rates, comfortable gaming mice and keyboards, and reliable headsets enabling clear communication.
Schools typically invest $800-$1,500 per gaming station when purchasing new equipment, though many programs launch using existing computers or donated hardware from community partners. Used equipment markets, education technology grants, and corporate partnerships often provide affordable equipment access enabling program launches without prohibitive initial investments.
Network Infrastructure:
Reliable high-speed internet represents critical infrastructure for competitive online gaming. Schools should verify adequate bandwidth supporting multiple simultaneous game clients, coordinate with IT departments ensuring gaming traffic receives sufficient network priority, address firewall configurations that might block game clients or communication platforms, and establish backup connectivity contingencies preventing match forfeits due to technical failures.
Program Funding and Budget Considerations
Esports programs require funding for equipment, league fees, coaching stipends, and operational expenses similar to traditional athletic costs.
Typical Startup Costs:
- Equipment purchase or upgrade: $5,000-$15,000 for 10-player setup
- League registration fees: $500-$1,000 annually per organization
- Coaching stipends: $1,000-$5,000 annually depending on responsibilities
- Team jerseys and apparel: $500-$1,500 for branded clothing
- Tournament travel if attending in-person events: Variable based on participation

Funding Sources:
- Activity Fees: Many schools fund esports through standard activity fees similar to other extracurricular programs
- Booster Organizations: Parent groups and community supporters increasingly establish esports booster clubs raising funds through donations and events
- Corporate Sponsorships: Technology companies, gaming hardware manufacturers, and local businesses often support school programs through equipment donations or financial sponsorship
- Title IX Athletic Budget: Some schools classify esports within athletic department budgets, accessing established funding streams
- Grant Programs: Education technology grants, STEM initiative funding, and gaming industry education programs provide application-based funding opportunities
Many programs launch with modest budgets under $10,000 annually, scaling investment as participation grows and community support develops. The relatively low cost compared to traditional sports like football or hockey makes esports financially accessible for schools with limited athletic budgets.
League Selection and Competition Structure
Schools must select competitive organizations aligned with program goals, student interests, and institutional priorities.
PlayVS Partnership:
Most schools partner primarily with PlayVS given their NFHS sanctioning providing state championship recognition paralleling traditional athletic state titles. PlayVS handles scheduling, match hosting, technical support, and championship tournament organization with standardized processes schools understand from traditional sports experience.
Supplementary Leagues:
Programs often participate in multiple organizations simultaneously. Students might compete in PlayVS for state championships while also participating in NASEF programming emphasizing curriculum integration and HSEL tournaments offering scholarship prizes. This multi-league approach maximizes competitive opportunities and serves diverse student interests within single programs.
Game Selection:
Survey student interest determining which games generate sufficient participation supporting competitive teams. Balance student preferences against age-appropriateness, competitive infrastructure availability, spectator accessibility, and coaching expertise when making game selections. Most programs begin with 2-4 games, expanding offerings as programs mature and participation grows.
Coaching and Program Management
Quality coaching represents critical success factors determining whether programs thrive or struggle with behavioral issues and poor competitive results.
Coach Qualifications:
- Game knowledge and strategic understanding sufficient to provide meaningful tactical guidance
- Adolescent development expertise managing student wellbeing, conflict resolution, and emotional challenges
- Communication skills clearly explaining concepts, providing constructive feedback, and facilitating team discussions
- Technology proficiency navigating gaming platforms, competition infrastructure, and communication tools
- Commitment to positive culture emphasizing growth, learning, sportsmanship, and balanced priorities
Schools without staff possessing gaming expertise might recruit community volunteers, hire specialized esports coaches, or invest in professional development training existing educators. Organizations like NASEF provide coaching certification programs building educational esports expertise among teachers and coaches.

Program Policies:
Establish clear behavioral expectations, communication protocols, eligibility requirements, and participation standards from program inception. Address bullying and harassment explicitly, define appropriate communication during competition, establish social media guidelines, clarify academic eligibility standards, and define consequences for policy violations ensuring accountability.
The Future of High School Esports
Competitive gaming in secondary education continues evolving rapidly as mainstream acceptance grows, infrastructure matures, and pathways to collegiate and professional opportunities expand.
Continued Growth and Mainstream Acceptance
Esports participation will continue expanding as younger students who grew up gaming reach high school age expecting competitive opportunities. Demographic trends suggest gaming represents normal leisure activity for contemporary adolescents rather than niche hobby, making school-sponsored competition natural programming extension.
State athletic associations increasingly provide official oversight similar to traditional sports governance. While some states maintain esports within activities associations rather than athletic governance, the trend moves toward greater institutional recognition and standardized competition structures paralleling established sports.
Career and Educational Pathway Development
Collegiate esports programs will continue expanding as universities recognize gaming’s appeal for student recruitment and scholarship opportunities. Beyond elite gaming scholarships, competitive esports experience strengthens applications across various academic programs including computer science, game design, digital media, business, and communications.
The gaming industry’s continued growth creates expanding career opportunities extending far beyond professional player positions. High school programs providing industry exposure and skill development will increasingly function as career and technical education pathways preparing students for technology and media professions.
Technology Integration and Facility Investment
Schools will increasingly invest in purpose-built esports facilities reflecting program importance and serving recruitment advantages attracting prospective families. Dedicated gaming rooms with professional-grade equipment, streaming capabilities, spectator areas, and integrated technology systems will become common in schools with established programs and adequate facility resources.
According to education facility planning research, over 30% of high schools undergoing major renovations or new construction in 2025-2026 included dedicated esports spaces in facility designs—demonstrating gaming’s permanent integration into school programming rather than temporary trend.
Recognition Technology Evolution
As esports matures, recognition approaches will evolve beyond traditional trophy cases toward interactive digital displays particularly suited to gaming achievement documentation. Digital platforms can showcase match highlights, player statistics, championship brackets, team evolution across seasons, and comprehensive recognition histories impossible with physical displays alone.
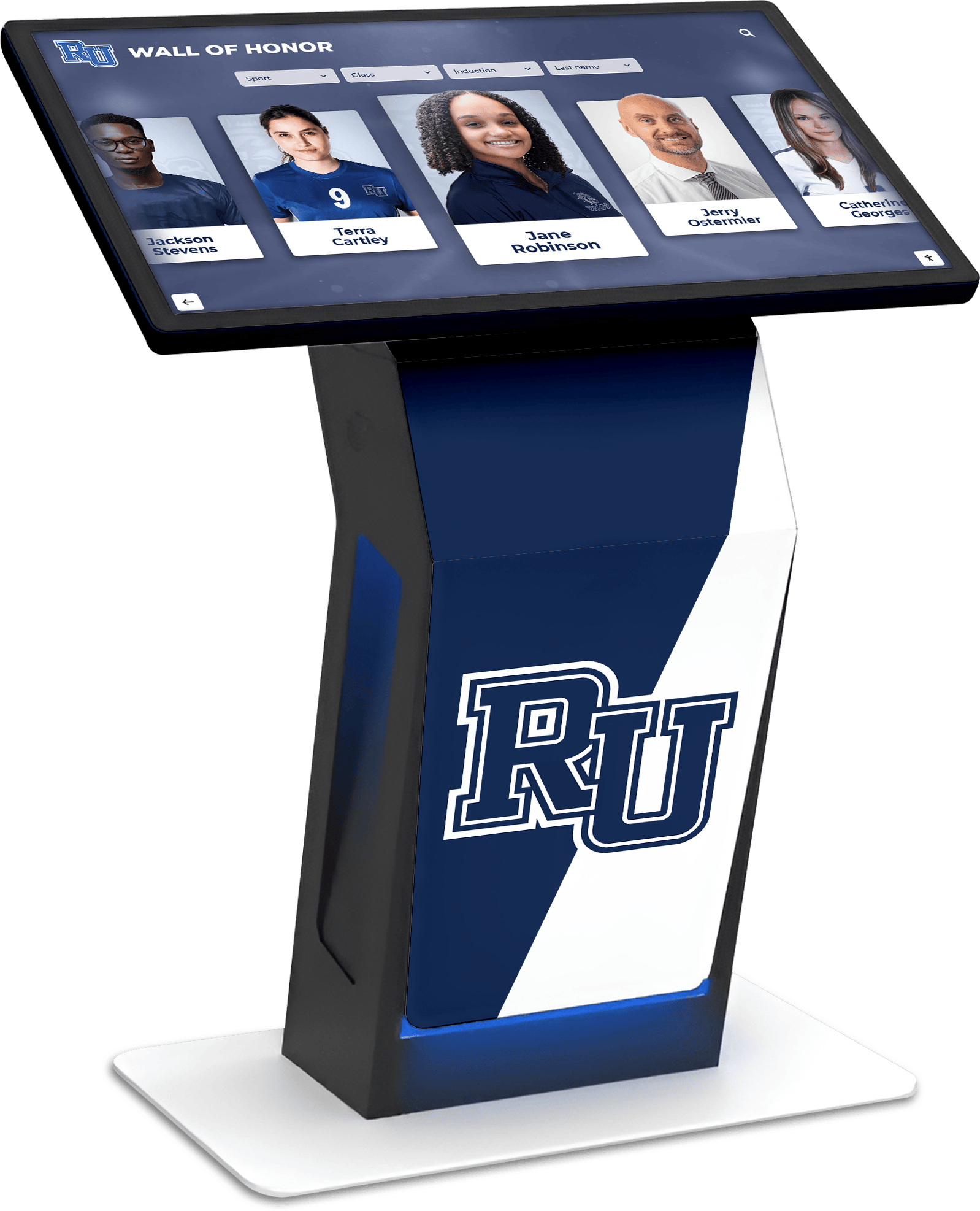

Modern recognition systems enable schools to celebrate esports alongside traditional athletics, academics, arts, and all achievement categories within unified platforms demonstrating that institutions value diverse excellence equally. This integrated recognition approach helps normalize esports participation while ensuring gaming achievements receive prominence equivalent to their significance.
Celebrating Esports Excellence Through Comprehensive Recognition
High school esports represents legitimate competitive activity developing valuable skills, creating inclusive participation opportunities, and connecting students to college and career pathways in technology and gaming industries. As programs mature and gain mainstream acceptance, recognition approaches must evolve ensuring esports achievements receive acknowledgment proportionate to effort invested and excellence demonstrated.
Traditional recognition methods including banquets, awards ceremonies, and championship banners provide familiar frameworks adapted appropriately for competitive gaming contexts. However, digital recognition platforms offer particularly compelling solutions for esports documentation given gaming’s technological nature and the capabilities of interactive displays for showcasing multimedia content, comprehensive statistics, and historical achievement preservation.
Quality recognition programs celebrate diverse achievements across individual performance, team accomplishments, character demonstration, and community contribution. They integrate esports alongside traditional recognition categories demonstrating institutional values embracing varied excellence forms. Most importantly, effective recognition validates student dedication, honors competitive achievement appropriately, preserves program history permanently, and signals that schools value all students regardless of which competitive platforms showcase their talents.
Ready to create recognition systems celebrating esports alongside all school achievements? Rocket Alumni Solutions provides purpose-built digital recognition platforms designed specifically for educational institutions, offering intuitive content management, comprehensive achievement documentation across unlimited categories, engaging interactive displays, web accessibility extending recognition globally, and proven approaches helping schools build inclusive excellence cultures where every student sees their contributions valued appropriately.
Your esports competitors achieve remarkable accomplishments through strategic thinking, team coordination, competitive excellence, and dedication paralleling traditional athletic participation. Modern recognition programs ensure these achievements receive celebration that inspires continued excellence, validates diverse talents, creates lasting institutional pride, and builds school communities where all students feel valued for their contributions regardless of which competitive arenas showcase their capabilities.
High school esports represents more than gaming—it’s structured competition developing transferable skills, inclusive activity engaging diverse student populations, college preparation creating tangible opportunities, and community building connecting students meaningfully to their schools. When schools support esports thoughtfully and recognize achievements appropriately, they demonstrate commitment to serving all students while preparing them for success in increasingly digital futures where gaming literacy, technology proficiency, and online collaboration represent essential capabilities rather than recreational diversions.