Children facing extended hospital stays confront challenges beyond physical illness—isolation from friends and normal routines, anxiety about medical procedures, boredom during recovery periods, and loss of control over daily activities. Healthcare administrators and Child Life specialists increasingly recognize that addressing these psychological and emotional dimensions proves as critical to healing as medical interventions themselves. Video games at children’s hospitals have emerged as powerful therapeutic tools transforming how pediatric facilities support patients through technology that engages, distracts, and celebrates achievement during difficult circumstances.
The therapeutic gaming movement in pediatric healthcare has expanded dramatically from experimental programs at a handful of institutions to comprehensive initiatives at nearly 200 hospital partners worldwide. Specialized gaming technology specialists now occupy dedicated positions at major children’s hospitals, integrating video games strategically into treatment plans, rehabilitation protocols, and patient experience enhancement. These programs deliver measurable improvements in anxiety reduction, pain management, physical rehabilitation outcomes, and overall patient satisfaction during hospitalization.
Intent: Demonstrate Therapeutic Gaming Value and Recognition Opportunities
This guide examines how children's hospitals implement therapeutic gaming programs—exploring equipment selections, therapeutic benefits, specialist roles, and recognition systems celebrating patient achievements during recovery. Healthcare administrators developing patient experience initiatives, Child Life departments evaluating technology investments, and facilities managers implementing pediatric programs will discover how video games deliver clinical value extending far beyond entertainment while creating opportunities to honor resilience and milestone accomplishments.
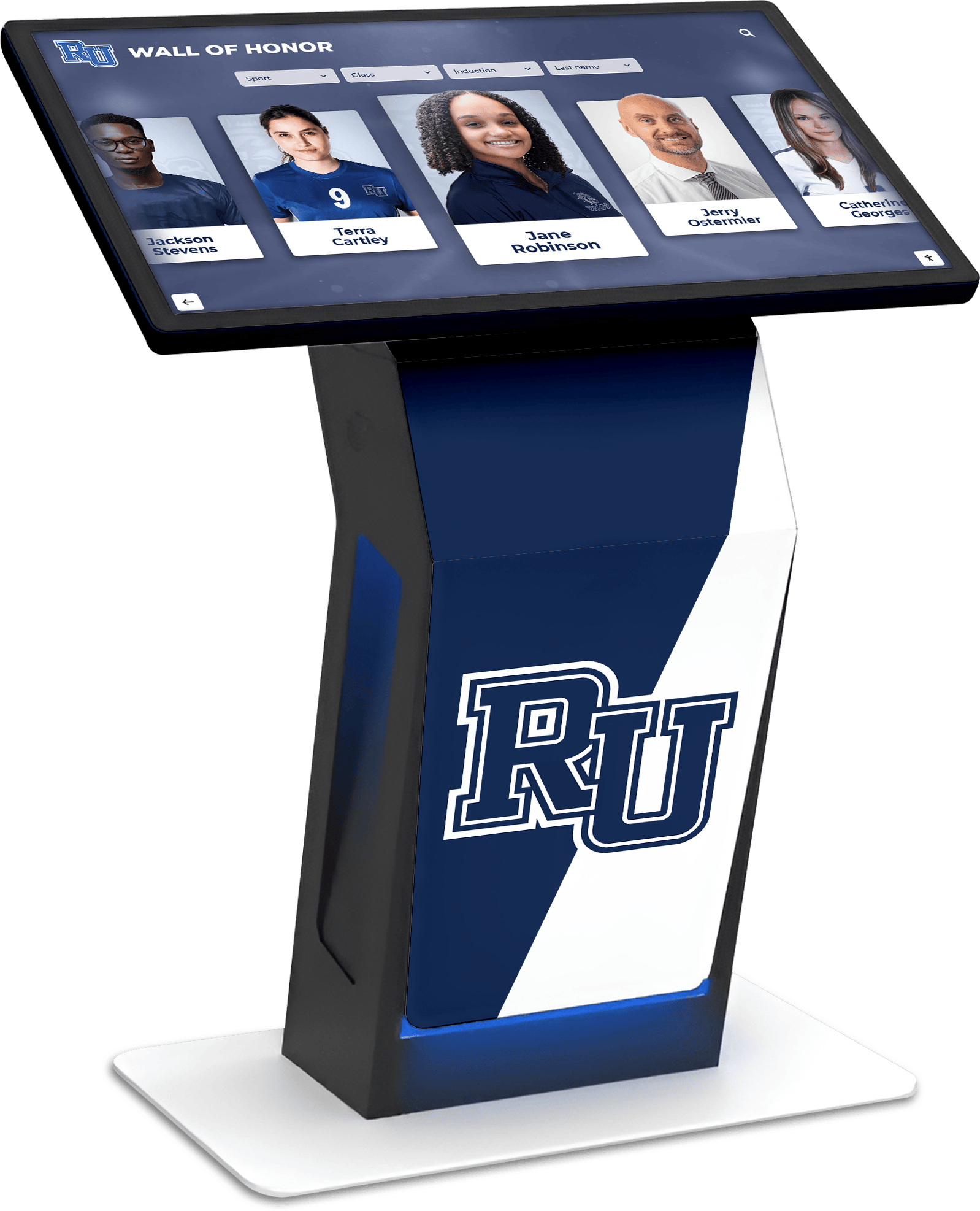
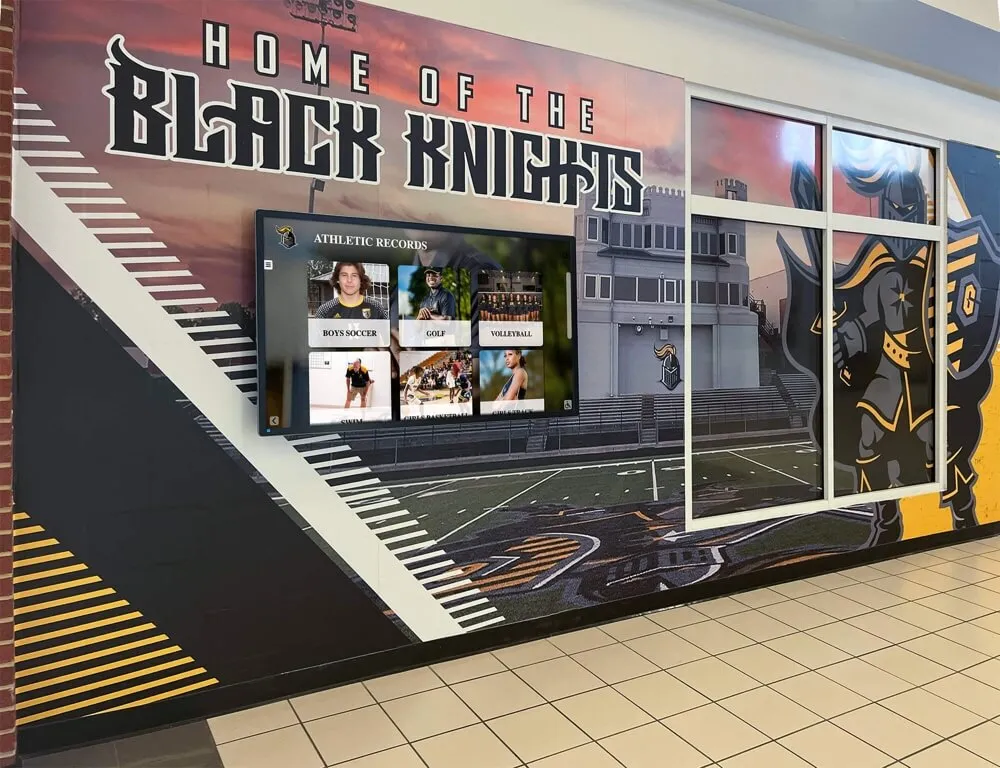
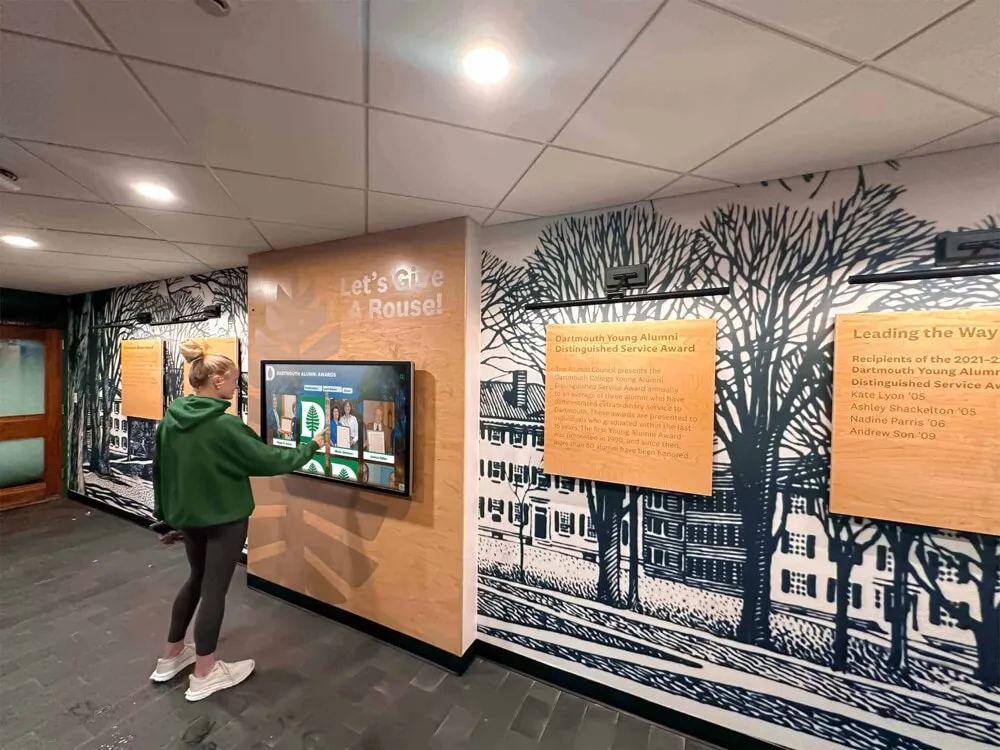
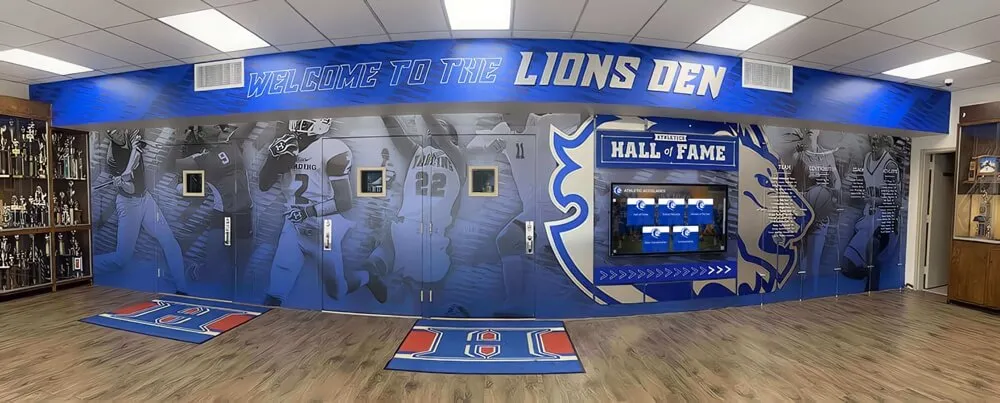
Digital recognition platforms like Rocket Alumni Solutions provide healthcare facilities with tools celebrating patient achievements, milestones, and recovery victories through interactive displays that honor courage and perseverance during challenging circumstances—applying the same technology that preserves athletic and academic achievement to recognize pediatric patients' extraordinary journeys.
The Rise of Therapeutic Gaming in Pediatric Healthcare
Video games entered children’s hospitals initially through charitable donations and volunteer efforts rather than strategic clinical integration. Organizations like Child’s Play Charity, founded in 2003, pioneered providing gaming equipment to pediatric facilities, recognizing that hospitalized children needed access to normalizing activities connecting them to childhood experiences outside medical contexts.
From Charitable Gifts to Clinical Programs
Early gaming initiatives focused primarily on entertainment value—providing distraction during long hospital stays through donated game consoles placed in patient rooms or common areas. While these efforts delivered meaningful comfort, they operated independently from medical care rather than integrating with treatment approaches.
The transformation occurred as healthcare professionals observed tangible therapeutic benefits extending beyond simple entertainment. Patients using video games demonstrated reduced anxiety before procedures, reported lower pain levels during uncomfortable treatments, showed improved mood and cooperation with medical staff, maintained better engagement with physical rehabilitation exercises, and experienced less social isolation through multiplayer gaming connections.
These observations prompted children’s hospitals to formalize therapeutic gaming through dedicated specialist positions, strategic equipment investments, integration with rehabilitation protocols, and measurable outcomes tracking. According to research published in the Children’s Hospital Association analysis, therapeutic gaming specialists began formally working around 2018 when approximately five people occupied such roles nationwide—a number that has since grown to an estimated 60 worldwide as programs expand.

Seattle Children’s Leadership in Therapeutic Gaming
Seattle Children’s Hospital emerged as a pioneering institution developing comprehensive therapeutic gaming programs that other facilities now emulate. Their Therapeutic Gaming Program, operating since 2018, integrates gaming specialists directly into clinical teams rather than positioning games as isolated recreational activities.
The Seattle Children’s approach demonstrates how therapeutic gaming programs function optimally: gaming specialists assess individual patient needs, preferences, and limitations; collaborate with medical teams to identify therapeutic opportunities; select games strategically based on therapeutic goals rather than entertainment value alone; partner with physical and occupational therapists incorporating gaming into rehabilitation; and document outcomes measuring program effectiveness systematically.
This clinical integration distinguishes therapeutic gaming from recreational play. When Seattle Children’s describes their program, they emphasize using gaming tools to supplement medical progress through active games promoting movement and healing, with specialists frequently partnering with rehabilitation therapists. Video games become therapeutic modalities delivering specific clinical outcomes rather than simply entertainment options filling idle time.
National Program Expansion and Standardization
Mary Bridge Children’s Hospital launched what they describe as the nation’s first second-generation pediatric gaming program in 2023, building on lessons learned from pioneering institutions while advancing therapeutic gaming practices. According to Mary Bridge’s program description, their approach “levels up hospital stays” by strategically deploying gaming technology across patient care contexts.
Second-generation programs benefit from established best practices around equipment selection meeting infection control requirements, workflow integration enabling gaming specialists to reach patients efficiently, outcomes measurement demonstrating clinical value, and staff training helping medical teams understand gaming’s therapeutic applications. These standardized approaches enable newer programs to deliver immediate value rather than developing protocols experimentally.
Child’s Play Charity has evolved from equipment donation to capacity building, now supporting 49 gaming technology specialist positions and providing resources like The Therapeutic Video Game Guide helping hospitals implement programs effectively. This infrastructure development signals therapeutic gaming’s transition from experimental innovation to standard pediatric care practice.
Therapeutic Benefits: How Gaming Supports Healing
Research increasingly documents specific mechanisms through which video games deliver therapeutic value beyond general entertainment or distraction. Understanding these benefits helps healthcare administrators justify program investments while guiding implementation strategies maximizing clinical impact.
Anxiety Reduction and Psychological Comfort
Hospitalization creates profound anxiety for pediatric patients—fear of painful procedures, uncertainty about diagnoses and treatments, loss of familiar environments and routines, and concerns about missing school and social activities. Video games provide psychological refuge through multiple mechanisms that research continues to validate.
A comprehensive study published in JAMA Pediatrics and highlighted by Johns Hopkins Medicine reviewed research from 2011 through March 2026, concluding that video games can provide “novel tools to help improve children’s mental health—particularly for ADHD and depression.” While this research examined general populations rather than exclusively hospitalized children, the findings support therapeutic gaming’s mental health benefits.
Video games reduce anxiety through predictable structure during unpredictable circumstances. Hospitalized children lose control over basic daily decisions—when they eat, sleep, receive visitors, or move freely. Games restore agency through meaningful choices affecting virtual outcomes, providing psychological control when external circumstances feel overwhelming.
Gaming also redirects cognitive focus away from anxious preoccupation. According to therapeutic gaming specialists, games selected to match patient capabilities and interests create absorbing experiences where children concentrate on gameplay challenges rather than ruminating about medical conditions or upcoming procedures. This cognitive redirection proves particularly valuable before anxiety-provoking events like surgeries or difficult treatments.

Pain Management and Distraction Therapy
Video games function as effective distraction therapy during painful or uncomfortable medical procedures. The interactive nature of gaming demands active attention—processing visual information, making rapid decisions, coordinating physical responses—consuming cognitive resources that would otherwise focus on pain perception.
Research on distraction therapy demonstrates that engaging activities reduce perceived pain intensity more effectively than passive entertainment. Video games provide ideal distraction characteristics: continuous engagement requiring sustained attention, progressive difficulty maintaining optimal challenge, immediate feedback creating absorbing flow states, and interactive control demanding active participation.
Therapeutic gaming specialists strategically deploy games during specific clinical contexts—administering chemotherapy or lengthy infusions, performing wound care or dressing changes, conducting physical therapy exercises, and waiting periods before procedures when anxiety peaks. Gaming transforms these challenging moments from purely negative experiences into opportunities for achievement and engagement.
Physical Rehabilitation and Motor Skill Development
Active gaming technology—motion controllers, virtual reality systems, and augmented reality applications—provides powerful physical rehabilitation tools that make therapeutic exercises feel like play rather than work. According to hospital program descriptions, gaming specialists frequently partner with physical and occupational therapists incorporating gaming into rehabilitation protocols.
Patients recovering from surgeries, injuries, or conditions affecting mobility often resist traditional physical therapy due to discomfort, boredom, or lack of motivation. Video games addressing the same therapeutic goals through gameplay dramatically improve compliance and engagement. Children perform prescribed movements repeatedly through gaming when they would resist equivalent traditional exercises.
Virtual reality systems prove particularly valuable for rehabilitation. VR applications can require specific movements for gameplay success, provide immediate visual feedback showing movement quality, gamify repetitive exercises through progression systems, and distract from discomfort during therapeutic activities. Children’s Hospital Colorado describes using virtual reality to transform patient care across multiple therapeutic applications.

Fine motor skill development through traditional gaming controllers benefits patients recovering from hand injuries, neurological conditions affecting coordination, or developmental delays. The precise movements required for gaming success provide therapeutic exercise within engaging contexts that maintain patient motivation across treatment duration.
Social Connection and Community Building
Extended hospitalization isolates children from normal social networks—missing school activities, separated from friends and siblings, confined to medical environments with limited peer interaction. Video games provide vital social connection opportunities addressing this isolation dimension.
Multiplayer gaming enables hospitalized children to maintain relationships with friends outside hospitals through online play, connecting existing social networks despite physical separation. Children play familiar games with school friends, maintaining normalcy and continuity during disruptive circumstances.
Gaming also facilitates new social connections within hospitals. Patients play together in common areas or connect through hospital networks, creating communities among children sharing similar experiences. These peer connections prove particularly valuable for children with rare conditions who rarely encounter others facing comparable challenges.
Therapeutic gaming specialists sometimes organize tournaments, competitions, or collaborative gaming events creating structured social opportunities. These activities provide positive experiences contrasting with medical procedures while building community among patients, families, and hospital staff.
Cognitive Engagement and Educational Continuity
Hospitalization disrupts education as children miss school during extended stays or frequent admissions. Educational gaming provides opportunities maintaining academic engagement during medical treatment, preventing children from falling behind peers academically.
Strategy games, puzzle games, and educational titles specifically designed for learning provide cognitive stimulation matching various developmental levels and subject areas. Gaming specialists collaborate with hospital educators selecting games aligning with patients’ grade levels and learning needs.
Beyond formal educational content, most games develop valuable cognitive skills—problem-solving and strategic thinking, reading comprehension and information processing, mathematical reasoning and resource management, and spatial reasoning and pattern recognition. These cognitive benefits occur through engaging gameplay rather than explicit instruction, making learning feel recreational rather than academic.
Gaming Equipment and Technology for Pediatric Facilities
Implementing therapeutic gaming programs requires careful equipment selection balancing clinical requirements, budgetary constraints, and patient needs. Understanding available technology options helps healthcare administrators make informed investments delivering maximum therapeutic value.
Mobile Gaming Carts: The GO Kart Model
Gamers Outreach pioneered mobile gaming cart design through their GO Kart program, creating equipment specifically addressing pediatric healthcare environments. According to Gamers Outreach’s mission description, GO Karts feature medical-grade gaming kiosks equipped with monitors, current-generation video game consoles, and controllers—all powered by a single plug for portability.
Mobile cart advantages prove essential in hospital contexts. Gaming specialists transport equipment between patient rooms serving bedridden or immunocompromised children unable to visit common areas. Carts move easily for thorough cleaning between patients meeting strict infection control requirements. Equipment concentrates in compact configurations minimizing space demands in crowded patient rooms.
The 2026 VTuber Summer Slam fundraiser raised $740,843 fulfilling 200 GO Karts for hospitals, while Spooktacular Streamathon 2026 raised $402,182 helping fulfill 68 GO Karts and 4 Save Point Machines. These significant fundraising totals demonstrate both strong community support for pediatric gaming and substantial equipment costs requiring external funding support.

Infection Control and Medical-Grade Equipment
Hospital equipment faces stringent requirements beyond consumer electronics standards. Medical-grade gaming equipment must accommodate frequent disinfection without damage, feature smooth surfaces without crevices harboring pathogens, use antimicrobial materials resisting bacterial growth, and meet safety standards for electrical equipment in medical environments.
Starlight Gaming Stations represent another specialized medical gaming solution. Starlight’s gaming equipment meets strict infection safety protocols, comes pre-loaded with age-appropriate games rated E10+ or below, and offers streaming capabilities, parental controls, and dedicated technical support. These purpose-built systems address clinical requirements that consumer gaming equipment cannot meet.
Equipment selection significantly impacts program sustainability. Consumer electronics breaking down under intensive use and frequent cleaning create maintenance burdens and service interruptions. Medical-grade equipment designed specifically for clinical environments delivers reliability justifying higher initial investments through reduced replacement costs and consistent availability.
Diverse Platform Selection for Patient Needs
Comprehensive therapeutic gaming programs deploy multiple gaming platforms addressing varied patient needs, preferences, and therapeutic applications rather than standardizing on single systems.
Console Gaming Systems: Traditional gaming consoles (PlayStation, Xbox, Nintendo Switch) provide extensive game libraries covering diverse genres and interests. Consoles support multiplayer gaming enabling social connection, work with various controller adaptations for accessibility, and offer familiar experiences matching what patients use at home.
Virtual Reality Systems: VR technology delivers immersive rehabilitation applications and profound distraction during uncomfortable procedures. VR proves particularly effective for pain management, enabling patients to “escape” hospital environments through engaging virtual experiences. However, VR requires careful patient screening—motion sickness concerns, infection control for headsets requiring facial contact, and appropriateness for various age groups limit universal deployment.
Tablet and Mobile Gaming: Portable devices provide gaming access for patients with mobility limitations or those requiring bedside isolation. Tablets offer touch-screen interfaces requiring minimal physical capability, extensive casual game libraries, and simple sanitization. These devices work well for younger children and patients with limited gaming experience.
PC Gaming Systems: Computer-based gaming enables specialized therapeutic applications, educational gaming, and titles unavailable on consoles. Adaptive input devices for patients with physical limitations integrate more easily with PC systems. Some hospitals deploy PC gaming primarily for rehabilitation applications requiring specific software.
Accessibility Adaptations and Inclusive Gaming
Pediatric hospitals serve children with diverse physical capabilities requiring adaptive gaming technologies ensuring all patients can access therapeutic gaming benefits regardless of disabilities or limitations.
Adaptive controllers like Xbox Adaptive Controller provide customizable input systems accommodating various physical abilities. These devices feature large programmable buttons, multiple input connection options, and mounting systems enabling stable positioning for patients with limited mobility. Adaptive technology transforms gaming from activities some patients cannot access into inclusive experiences available to all.
One-handed controllers, mouth-operated controllers, eye-tracking systems, and voice-command gaming expand access further for patients with severe physical limitations. Therapeutic gaming programs should maintain adaptive equipment inventory ensuring specialists can match technology to individual patient capabilities rather than excluding children unable to use standard controllers.
The Therapeutic Gaming Specialist Role
Successful pediatric gaming programs depend on dedicated specialists who understand both gaming and therapeutic applications. These professionals bridge entertainment technology and clinical care, ensuring games deliver maximum therapeutic value rather than functioning as mere distractions.
Position Development and Professionalization
Therapeutic gaming specialist positions emerged organically as hospitals recognized that effective gaming programs required more than equipment donations. Child Life specialists traditionally responsible for developmental and emotional support during hospitalization needed gaming expertise complementing their clinical training. Simultaneously, gaming enthusiasts lacked clinical knowledge integrating games therapeutically.
Therapeutic gaming specialists typically combine gaming knowledge with child development understanding, clinical awareness of pediatric conditions and treatments, technology troubleshooting and equipment maintenance capabilities, and interpersonal skills building rapport with anxious patients. Some specialists enter healthcare from gaming backgrounds, while others expand Child Life training with gaming expertise.
The role’s professionalization accelerated as pioneers like Seattle Children’s demonstrated measurable outcomes justifying dedicated positions. According to CHRISTUS Children’s program description, their “Gaming Guy” plays video games with patients specifically to improve emotional wellbeing and reduce hospitalization stress—a position that would have seemed frivolous before therapeutic gaming’s clinical validation.
Daily Responsibilities and Patient Interaction
Therapeutic gaming specialists typically follow structured workflows maximizing patient reach and clinical impact. Daily responsibilities include rounding on patient floors identifying candidates for gaming interventions, collaborating with medical teams understanding treatment schedules and patient conditions, assessing individual patient interests, capabilities, and therapeutic needs, selecting appropriate games and equipment matching patient profiles, facilitating gaming sessions providing emotional support alongside gameplay, and documenting patient responses and outcomes informing program evaluation.
Specialists develop expertise recognizing which games suit specific therapeutic applications. Calming puzzle games for anxiety reduction before procedures differ from active motion games supporting physical rehabilitation, which differ from collaborative multiplayer experiences addressing social isolation. This game selection expertise distinguishes therapeutic gaming from recreational play—choosing titles strategically based on clinical goals rather than simply entertainment preferences.
Building rapport with patients proves as important as gaming knowledge. Specialists help anxious children feel comfortable, explain games in developmentally appropriate ways, celebrate in-game achievements enthusiastically, and provide consistent supportive presence during challenging hospitalizations. Many specialists become favorite hospital staff members whom patients specifically request, creating positive associations countering negative medical experiences.
Collaboration with Clinical Teams
Effective therapeutic gaming integrates with broader care plans rather than operating independently. Specialists regularly collaborate with:
Physical and Occupational Therapists: Identifying games supporting rehabilitation goals, customizing gameplay parameters matching therapeutic protocols, documenting patient progress through gaming activities, and transitioning successful gaming exercises into home therapy programs continuing post-discharge.
Child Life Specialists: Coordinating comprehensive developmental support approaches, identifying patients who would particularly benefit from gaming interventions, collaborating on pre-procedure anxiety reduction strategies, and addressing psychosocial needs through complementary interventions.
Medical Staff: Understanding treatment schedules and medication effects impacting gaming appropriateness, receiving guidance on patient limitations and safety considerations, providing feedback on gaming’s observable effects on patient mood and cooperation, and integrating gaming into broader patient experience enhancement initiatives.
Social Workers and Mental Health Professionals: Addressing patients showing signs of depression, anxiety, or behavioral challenges, incorporating gaming into therapeutic approaches supporting mental health, and identifying patients needing more intensive support beyond gaming’s scope.
This collaborative approach ensures gaming serves therapeutic purposes integrated with comprehensive care rather than functioning as isolated entertainment distracting from clinical priorities.

Recognizing Patient Achievements and Milestones
While video games provide crucial therapeutic benefits during hospitalization, recognizing patients’ broader achievements—courage during treatment, reaching recovery milestones, completing difficult therapies—honors their extraordinary journeys through challenging circumstances. Digital recognition systems extend beyond entertainment to celebrate resilience, creating positive hospital memories alongside difficult medical experiences.
Celebrating Recovery Milestones Through Digital Recognition
Pediatric facilities increasingly implement recognition programs celebrating patient achievements during treatment. Digital recognition displays can honor:
Treatment Completion Milestones: Finishing chemotherapy cycles, completing surgical recovery protocols, reaching physical therapy goals, and achieving medication independence deserve celebration comparable to athletic or academic achievements. Recognition systems traditionally used for sports records adapt effectively to healthcare contexts celebrating different forms of courage and accomplishment.
Courage and Resilience Recognition: Some patients face particularly challenging circumstances—rare diagnoses requiring experimental treatments, extended hospitalizations spanning months, multiple surgeries and setbacks, or chronic conditions requiring ongoing medical management. Digital recognition platforms can create “walls of courage” honoring extraordinary bravery during difficult journeys.
Alumni Recognition for Former Patients: Healthcare facilities maintaining connections with former patients sometimes celebrate long-term survivors, patients who return to volunteer or support others, young people who overcome serious illnesses to achieve personal goals, and community members who give back after receiving life-saving care. These recognition programs mirror alumni recognition in educational institutions, adapting similar technology to healthcare contexts.
Solutions like Rocket Alumni Solutions provide healthcare facilities with digital recognition platforms originally designed for educational settings but adaptable to hospital contexts. The same technology celebrating athletic achievements can honor pediatric patients’ victories—replacing sports statistics with treatment milestones while maintaining engaging interactive presentations that families can explore during hospital visits.
Patient Milestone Walls and Interactive Displays
Some children’s hospitals implement physical recognition displays celebrating patient achievements alongside traditional gaming programs. These installations might feature:
Bell-Ringing Recognition: Many hospitals maintain traditions where patients ring ceremonial bells marking treatment completion—particularly for oncology patients finishing chemotherapy. Digital displays can preserve these moments permanently through photographs, patient statements, and treatment journey documentation, creating lasting recognition beyond momentary ceremonies.
Patient Artwork and Creative Expression Galleries: Art therapy provides therapeutic benefits during hospitalization while producing tangible creations expressing patients’ experiences. Digital art galleries can showcase this artwork prominently through rotating displays, enabling patients to see their creative work honored publicly while providing other patients with hope and inspiration.
Recovery Journey Documentation: Interactive displays can document individual patients’ complete treatment journeys—from diagnosis through treatment to recovery—creating narrative archives honoring their experiences comprehensively. These stories inspire current patients while preserving hospital community memory across years.
Digital recognition technology serves multiple purposes in pediatric contexts: providing patients with positive experiences and achievements during difficult circumstances, creating legacy documentation families treasure long after treatment ends, demonstrating to the community the courage and resilience children show during illness, and building institutional culture honoring patients as whole people rather than medical cases.

Gaming Achievements as Recognition Opportunities
Some therapeutic gaming programs incorporate achievement recognition within gaming contexts, celebrating in-game accomplishments and gaming milestones alongside therapeutic progress. This approach provides immediate positive reinforcement for patients who may experience predominantly negative feedback during medical treatment.
Gaming specialists might maintain leaderboards showing high scores in appropriate games, celebrate patients who complete particularly challenging games or levels, recognize gaming milestones like consecutive days playing or hours spent gaming, or organize tournaments with recognition for participants and winners. These gaming-specific achievements provide opportunities for success and recognition during periods when medical progress may feel slow or setbacks occur frequently.
Digital displays showing current patients’ gaming achievements create positive visual focal points in hospital spaces typically dominated by clinical equipment and medical information. Parents and visitors see children celebrated for accomplishments and engagement rather than solely defined by diagnoses and treatments.
Implementation Strategies for Healthcare Facilities
Hospitals considering therapeutic gaming programs face implementation decisions around program scope, equipment investments, staffing models, and outcome measurement. Understanding successful implementation approaches helps new programs avoid common pitfalls while accelerating time-to-value.
Assessing Organizational Readiness and Needs
Healthcare administrators should evaluate several factors before committing to formal therapeutic gaming programs:
Current Patient Experience Initiatives: How do gaming programs integrate with existing patient satisfaction efforts, Child Life department activities, and experience-of-care metrics? Gaming should complement rather than compete with established programs, filling gaps in current offerings rather than duplicating successful interventions.
Patient Population Characteristics: What age ranges predominate? Do patients experience primarily acute short stays or extended chronic care admissions? Are patients predominantly mobile or does the facility serve many bedbound or ICU patients? These factors influence equipment selections and program design—mobile carts versus fixed installations, casual games versus complex titles, individual versus multiplayer focus.
Available Space and Infrastructure: Can the facility dedicate space for gaming lounges or common areas, or must programs rely entirely on mobile equipment visiting patient rooms? Is network infrastructure adequate for online gaming and multiplayer functionality? Do infection control protocols permit shared equipment or require disposable/easily sanitized alternatives?
Budget and Funding Sources: What internal budget exists for patient experience programs? Are external funding sources available through foundations, charitable partnerships, or community fundraising? Can equipment costs distribute across multi-year procurement plans or do programs require complete implementation before launching?
Staff Capacity and Expertise: Does the Child Life department have capacity absorbing additional responsibilities, or do effective programs require dedicated gaming specialist positions? What gaming expertise exists among current staff? Can the organization support specialist hiring and ongoing training?
Honest assessment prevents implementing unsustainable programs that launch enthusiastically before fading through inadequate resources or poor institutional fit.
Partnering with Charitable Organizations
Most pediatric gaming programs benefit from charitable partnerships reducing equipment costs while connecting institutions to established expertise. Major organizations supporting hospital gaming include:
Child’s Play Charity: Child’s Play pioneered hospital gaming donations and now supports nearly 200 hospital partners worldwide. They provide equipment funding, capacity building grants supporting specialist positions, comprehensive therapeutic gaming guides and resources, and a network connecting hospitals implementing programs. Hospitals can register as partners to access these resources.
Gamers Outreach: Gamers Outreach focuses specifically on providing GO Karts and gaming equipment to pediatric facilities. Their standardized cart design simplifies equipment selection while their fundraising infrastructure enables hospitals to connect with donors supporting specific equipment acquisitions. The organization raised over $2 million through 2026 fundraising events, demonstrating strong donor enthusiasm for hospital gaming.
Starlight Children’s Foundation: Starlight provides Gaming Stations specifically designed for medical environments, pre-loaded with age-appropriate content and meeting clinical requirements. Their equipment specifically addresses infection control and safety considerations that generic gaming equipment may not satisfy.
These partnerships typically require hospitals to submit applications describing patient populations, planned program approaches, and equipment needs. Approval connects facilities to equipment donations, technical support, and program development guidance accelerating implementation while reducing costs.

Pilot Programs and Phased Implementation
Successful programs often begin with limited pilots demonstrating value before committing to comprehensive implementation. Pilot approaches might include:
Single Unit Implementation: Deploy initial gaming equipment on one patient care unit—perhaps oncology, orthopedics, or another department with longer patient stays enabling repeated gaming specialist interaction. Document outcomes systematically, gather patient and family feedback, identify operational challenges and solutions, and demonstrate measurable value justifying expanded investment.
Limited Specialist Hours: Rather than immediately hiring full-time gaming specialists, some hospitals begin with part-time positions or train existing Child Life specialists in gaming applications. This approach tests specialist role effectiveness while limiting financial commitment before full program justification.
Equipment Variety Testing: Pilot programs can deploy diverse equipment types across small patient populations, evaluating which gaming platforms prove most valuable, what games generate strongest patient engagement, how different patient populations respond to various gaming options, and which equipment survives clinical environments reliably. These findings inform larger procurement decisions optimizing resource allocation.
Phased implementation provides learning opportunities and demonstrates value to institutional leadership before requesting major budget commitments. Successful pilots generate internal champions and documented outcomes supporting program expansion.
Measuring Outcomes and Demonstrating Value
Healthcare administrators require evidence that gaming programs deliver value justifying ongoing investment. Outcome measurement should include:
Patient Experience Metrics: Do patient satisfaction scores improve in units or during time periods with gaming specialist access? How do patients and families specifically comment on gaming availability in experience surveys? What proportion of eligible patients choose to participate in gaming programs?
Clinical Indicators: Are there measurable differences in pre-procedure anxiety scores for patients who game beforehand? Do pain scores decrease during procedures when patients use gaming distraction? Does physical therapy compliance improve when gamified? How do length-of-stay metrics compare for patients engaged in gaming versus those who are not?
Staff Observations: Do nurses and physicians observe improved patient cooperation, decreased behavioral challenges, or better mood in patients regularly engaging with gaming specialists? How does gaming affect family stress levels observable to clinical teams?
Program Utilization: How many patients do specialists reach daily? What average session duration occurs? Which games generate strongest engagement? What equipment proves most reliable and valuable? These operational metrics guide program refinement and resource allocation.
Systematic outcome measurement demonstrates value to institutional leadership, informs program improvements, validates approaches to external funders and charitable partners, and provides evidence supporting similar programs at other institutions.
Future Directions: Gaming and Healthcare Technology Evolution
Therapeutic gaming in pediatric facilities continues evolving as gaming technology advances and healthcare applications expand. Understanding emerging directions helps administrators plan for long-term program development rather than optimizing exclusively for current capabilities.
Expanded Virtual Reality Therapeutic Applications
Virtual reality adoption in healthcare continues growing beyond current gaming applications. VR technology shows particular promise for:
Procedural Pain Management: Immersive VR experiences during painful procedures provide distraction exceeding traditional gaming’s effectiveness. Patients “transported” to engaging virtual environments report significantly reduced pain perception compared to passive distraction or no intervention. As VR equipment becomes more affordable and infection control protocols for shared headsets improve, VR pain management may become standard practice.
Phobia Treatment and Anxiety Management: VR enables graduated exposure therapy for medical phobias—fear of needles, MRI scanners, or surgical environments. Patients can experience anxiety-provoking situations virtually in controlled, safe contexts, building tolerance before actual medical encounters.
Physical Rehabilitation: VR rehabilitation applications continue developing sophistication, providing engaging virtual environments where therapeutic movements become gameplay mechanics. Patients recovering from neurological conditions, orthopedic surgeries, or developmental delays benefit from VR rehabilitation that feels recreational rather than clinical.
Therapeutic Escapism: Some seriously ill children face circumstances they cannot change or control. VR offers temporary escape to fantastical environments, enabling experiences—visiting beaches, exploring space, creating art—physically impossible given medical limitations. This psychological refuge provides meaningful quality of life enhancement for palliative patients.

Artificial Intelligence Personalizing Gaming Experiences
Artificial intelligence technologies increasingly enable personalized gaming experiences adapting to individual patient needs, capabilities, and therapeutic goals. AI applications in therapeutic gaming might include:
Adaptive Difficulty Systems: AI-powered games automatically adjust challenge levels maintaining optimal engagement—difficult enough to feel accomplishing but not so hard as to frustrate patients already experiencing stress. These systems recognize player performance patterns and modify gameplay ensuring consistent engagement regardless of patient capabilities or experience levels.
Therapeutic Goal Optimization: AI systems could analyze patient conditions, treatment plans, and therapeutic objectives, recommending specific games and activities optimally supporting individual goals. Rather than gaming specialists manually selecting titles, intelligent systems might provide evidence-based suggestions improving therapeutic outcomes.
Natural Conversation Interfaces: Voice-controlled gaming through AI assistants enables patients with severe physical limitations to game independently. Natural language processing allows patients to control games conversationally rather than requiring precise commands, reducing barriers to access.
Emotional State Recognition: Some AI systems analyze voice patterns, facial expressions, and gameplay behaviors inferring emotional states. In therapeutic contexts, such systems might recognize when patients become frustrated, anxious, or disengaged, prompting gaming specialists to intervene or automatically adjusting gameplay to better support patient needs.
Integration with Electronic Health Records and Treatment Planning
As therapeutic gaming becomes standard practice, integration with electronic health record (EHR) systems enables seamless documentation and treatment planning. Future gaming programs might feature:
Automated Activity Logging: Gaming sessions automatically document in patient records without requiring specialists to manually enter information, reducing administrative burden while ensuring complete documentation supporting billing and outcome tracking.
Provider Order Entry: Physicians and therapists might formally order therapeutic gaming interventions specifying goals, frequency, and duration—similar to ordering physical therapy or occupational therapy. These formal orders integrate gaming into care plans rather than positioning it as optional recreational activity.
Progress Tracking and Goal Monitoring: EHR integration enables tracking therapeutic goals through gaming activities. Physical therapists monitor range of motion improvements through motion-controlled gameplay. Mental health providers track anxiety metrics before and after gaming sessions. This integrated tracking demonstrates gaming’s clinical value through quantified outcomes.
Care Team Visibility: All providers accessing patient records see gaming specialist documentation, enabling coordinated care where gaming reinforces therapeutic approaches across disciplines. Specialists understand how gaming fits within comprehensive treatment plans rather than working in isolation.
Augmented Reality Wayfinding and Hospital Navigation
Augmented reality applications extend beyond therapeutic gaming to practical hospital navigation addressing anxiety many pediatric patients experience in unfamiliar medical environments. AR wayfinding apps can:
- Overlay directional arrows guiding patients and families through complex hospital layouts
- Provide gamified scavenger hunts familiarizing patients with hospital spaces before procedures
- Create engaging distractions during transport to surgery or frightening locations
- Offer virtual tours helping patients understand what to expect in various hospital areas
These applications reduce anxiety through familiarity and control while making hospital navigation feel like adventure rather than medical necessity.
Making the Case: Justifying Therapeutic Gaming Investment
Healthcare administrators evaluating therapeutic gaming programs must justify investments competing with clinical priorities and budget constraints. Building compelling business cases requires addressing common objections while demonstrating measurable value.
Addressing Common Administrative Concerns
“Gaming Is Recreation, Not Treatment”: This objection reflects outdated understanding of gaming’s therapeutic applications. Documented research demonstrates measurable clinical benefits—anxiety reduction, improved pain management, enhanced rehabilitation outcomes. Gaming becomes treatment when deployed strategically by trained specialists targeting specific therapeutic goals rather than simply providing entertainment. Frame gaming as an evidence-based intervention comparable to music therapy, art therapy, or other established complementary approaches.
“Equipment Costs Are Prohibitive”: While comprehensive programs require substantial investment, charitable partnerships dramatically reduce costs. Organizations like Child’s Play, Gamers Outreach, and Starlight provide equipment funding making programs financially accessible. Additionally, comparing gaming equipment costs to traditional medical equipment reveals relatively modest investment—a complete GO Kart costs less than many single-use medical devices while serving thousands of patients across years. Emphasize total cost of ownership across expected equipment lifespan rather than initial sticker prices.
“We Lack Staff Capacity”: Dedicated gaming specialist positions require budget allocation, but several alternatives exist for resource-constrained facilities. Train existing Child Life specialists in therapeutic gaming approaches. Partner with volunteer organizations providing gaming support. Implement part-time positions or share specialists across facilities. Start small with limited hours demonstrating value before requesting full positions. Many successful programs began with minimal staff investment, expanding as demonstrated value justified increased allocation.
“Infection Control Prohibits Shared Equipment”: While infection control requires careful attention, purpose-built medical gaming equipment addresses these concerns through materials withstanding frequent disinfection, designs eliminating pathogen-harboring crevices, and antimicrobial surfaces resisting bacterial growth. Additionally, disposable controller covers, UV sanitization systems, and patient-specific equipment assignment provide layers of protection enabling safe shared equipment use. Infection control requires planning and protocols, not program prohibition.

Building the Business Case: ROI and Value Demonstration
Effective business cases quantify benefits wherever possible while acknowledging qualitative value:
Patient Experience Score Improvements: Higher patient satisfaction scores affect hospital reputation, support fundraising, and increasingly influence reimbursement through value-based payment models. If gaming programs improve experience scores measurably, calculate the financial value of these improvements through enhanced reputation and potential reimbursement impacts.
Length of Stay Reductions: If gaming improves patient cooperation with treatment, reduces anxiety requiring intervention, or enhances rehabilitation participation, these effects may reduce length of stay. Even modest average reductions—hours rather than days—generate substantial cost savings across patient populations when aggregated annually.
Reduced Medication Needs: Effective non-pharmacological pain management and anxiety reduction through gaming may decrease medication requirements. Beyond direct medication costs, reduced pharmaceutical use avoids side effects potentially complicating care and extending stays. Quantify potential savings through reduced medication utilization.
Staff Efficiency: Gaming specialists absorbing some patient emotional support and engagement work may free nurses and other clinical staff to focus on medical tasks rather than entertainment and distraction. This efficiency gain can improve staff satisfaction, reduce burnout, and optimize expensive clinical labor allocation.
Charitable Fundraising Opportunities: Gaming programs attract donors—particularly younger donors enthusiastic about gaming—who might not otherwise support pediatric facilities. Gaming equipment fundraising campaigns can generate donations exceeding equipment costs, creating net revenue supporting broader programs. Highlight fundraising potential as revenue generator rather than pure expense.
Competitive Differentiation: In markets where families choose among pediatric facilities, comprehensive patient experience programs including therapeutic gaming differentiate progressive institutions from competitors. This differentiation supports patient volume, physician recruitment, and community reputation—all generating long-term value difficult to quantify but strategically important.
Starting Small: Minimal Viable Programs
Healthcare administrators uncertain about comprehensive program commitment can begin with minimal viable programs demonstrating value before major investment:
Single Department Pilot: Implement gaming in one unit—oncology, orthopedics, or rehabilitation—where patient stays enable meaningful specialist relationships and repeated interventions. Document outcomes systematically over 6-12 months. If the pilot demonstrates value, expand to additional units with evidence supporting investment.
Charitable Partnership Focus: Apply to Child’s Play, Gamers Outreach, or Starlight requesting donated equipment. These partnerships provide gaming resources with minimal institutional investment, enabling program experimentation before committing internal budgets. Successful charitable-funded pilots can demonstrate value justifying institutional support for program expansion.
Volunteer-Supported Model: Some hospitals recruit gaming volunteers—community members, retired individuals, or college students—providing gaming support under Child Life supervision. While volunteers cannot replace trained specialists for therapeutic applications, they can provide basic gaming access and companionship demonstrating patient interest and engagement before hiring dedicated staff.
Equipment Donation Campaigns: Launch community equipment donation drives inviting individuals to contribute new gaming equipment, controllers, and games. This grassroots approach builds community connection while acquiring equipment at minimal institutional cost. Local gaming communities often enthusiastically support such campaigns.
These minimal approaches demonstrate gaming’s value while limiting risk and investment. Successful small programs generate momentum, internal champions, and documented outcomes supporting comprehensive program development.
Connecting Gaming to Broader Patient Experience Strategies
Therapeutic gaming programs deliver maximum value when integrated within comprehensive patient experience strategies rather than operating as isolated initiatives. Healthcare administrators should consider how gaming connects to related efforts:
Holistic Child Life Programming
Gaming complements traditional Child Life activities rather than replacing them. Child Life departments deliver comprehensive developmental support through:
- Preparation for medical procedures reducing anxiety through education
- Therapeutic play processing medical experiences and emotions
- Creative arts expression enabling emotional communication
- Family support helping parents and siblings cope with hospitalization
- School/education coordination maintaining academic continuity
- Grief and bereavement support for patients facing loss
Gaming integrates into this comprehensive approach, providing one tool within diverse intervention strategies. Some patients respond particularly well to gaming while others prefer art therapy, music, or other modalities. Child Life specialists assess individual needs and preferences, selecting appropriate interventions rather than universally prescribing gaming.
This integrated approach positions gaming as valuable component within broader child development support rather than siloed technology initiative.
Physical Space Design and Patient Areas
Hospital design increasingly emphasizes patient experience through dedicated spaces supporting non-clinical activities. Gaming programs function optimally within thoughtfully designed environments:
Gaming Lounges: Dedicated spaces where mobile patients gather for multiplayer gaming, tournaments, and social connection. These lounges require appropriate furniture, sound management, and visibility enabling supervision while providing patient autonomy.
Bedside Flexibility: Many patients cannot leave rooms due to medical conditions or isolation requirements. Programs serving these populations require mobile equipment, infection control protocols, and specialist workflows reaching bedside patients systematically.
Family Areas: Some facilities provide gaming access in family waiting areas and parent lounges, recognizing that siblings and parents also experience hospitalization stress. Gaming provides coping mechanisms for entire families rather than exclusively patients.
Outdoor/Healing Spaces: When weather and patient conditions permit, portable gaming equipment in outdoor healing gardens or rooftop spaces combines gaming’s benefits with fresh air and natural environments. This integration enhances wellbeing through multiple complementary approaches.
Coordinating gaming programs with facility design during renovation or construction ensures spaces optimally support program goals rather than forcing programs into inadequate environments.

Technology Infrastructure Planning
Gaming programs depend on robust technology infrastructure beyond equipment itself:
Network Capacity: Online gaming, multiplayer functionality, and streaming services require substantial bandwidth. Healthcare IT departments must ensure network capacity supports gaming without compromising clinical systems. Separate guest networks for gaming prevent security concerns while enabling necessary connectivity.
Content Management: Gaming libraries require regular updating—new games maintain patient interest while outdated titles become less engaging. Programs need procurement processes for ongoing game acquisition, content rating and appropriateness review, and licensing management ensuring compliance with terms of service.
Technical Support: Gaming equipment breaks, software updates cause issues, and network problems interrupt connectivity. Effective programs require technical support addressing these challenges promptly—whether through gaming specialists with technical training, IT department support, or vendor service agreements. Equipment downtime directly impacts patient experience.
Security and Privacy: Gaming systems must meet healthcare security requirements, particularly when connected to institutional networks. Programs need policies around patient data protection, age-appropriate content controls, and internet access restrictions preventing inappropriate content exposure.
Integrating gaming into technology planning ensures infrastructure supports program success rather than creating barriers and limitations.
Transforming Pediatric Care Through Strategic Gaming Integration
Video games at children’s hospitals have evolved from charitable donations providing simple distraction to sophisticated therapeutic programs delivering measurable clinical benefits. Research increasingly validates gaming’s role in anxiety reduction, pain management, physical rehabilitation, social connection, and cognitive engagement during hospitalization. Dedicated gaming specialists integrate games strategically into treatment plans, collaborating with clinical teams to optimize therapeutic outcomes.
Healthcare administrators implementing gaming programs face multiple decisions around equipment selection, staffing models, charitable partnerships, outcome measurement, and integration with broader patient experience strategies. Successful programs typically begin small—pilot implementations demonstrating value before comprehensive investment—while leveraging charitable partnerships reducing equipment costs and connecting institutions to established expertise.
Beyond gaming’s immediate therapeutic benefits, pediatric facilities increasingly recognize opportunities to celebrate patient achievements, recovery milestones, and extraordinary courage through digital recognition systems. Solutions like Rocket Alumni Solutions adapt recognition technology originally designed for educational athletic and academic achievement to healthcare contexts—honoring patients’ victories through engaging interactive displays families can explore during hospital visits and revisit long after treatment concludes.
As gaming technology continues advancing—through virtual reality, artificial intelligence personalization, augmented reality applications, and electronic health record integration—therapeutic applications will expand further. Forward-thinking healthcare administrators position institutions at this evolution’s forefront by implementing foundational programs today that can grow and adapt as technology and clinical understanding progress.
Pediatric patients face extraordinary challenges beyond physical illness. Comprehensive care addresses not just medical conditions but psychological, emotional, social, and developmental needs during vulnerable periods. Video games represent powerful tools advancing this comprehensive approach—transforming hospital stays from exclusively negative medical experiences into opportunities for engagement, achievement, and recognition celebrating young people’s remarkable resilience during difficult circumstances.
Ready to explore how digital recognition technology can celebrate patient milestones and achievements in your healthcare facility? Schedule a consultation to discover how interactive displays designed for schools and athletic programs adapt effectively to pediatric healthcare contexts—honoring courage, preserving recovery stories, and creating positive hospital memories alongside necessary medical treatment.
Sources:
- Specially Designed Video Games May Benefit Mental Health of Children and Teenagers | Johns Hopkins Medicine
- Seattle Children’s Therapeutic Gaming Program Uses Video Games
- Press play, not pause: Gaming program levels up hospital stays - Mary Bridge Children’s
- Therapeutic Gaming Program Boosts the Patient Experience | Children’s Hospital Association
- ‘Gaming Guy’ at CHRISTUS Children’s plays video games with patients to help them feel better
- Our Mission: Giving Kids Access to Play through Video Games | Gamers Outreach
- Child’s Play Charity
- Gaming | Starlight Children’s Foundation
- Transforming Patient Care Through VR | Children’s Hospital Colorado