Science, technology, engineering, and mathematics represent critical disciplines shaping tomorrow’s innovators, problem-solvers, and leaders. Yet in many schools, STEM achievements receive far less recognition than athletic accomplishments despite being equally worthy of celebration. Students who excel in science fairs, mathematics competitions, coding challenges, robotics tournaments, and engineering projects deserve visible acknowledgment that validates their efforts and inspires peers to pursue similar excellence.
A STEM Stars Recognition Wall transforms how schools celebrate academic achievement by creating dedicated spaces showcasing science and mathematics excellence with the same prominence traditionally reserved for athletic halls of fame. These displays honor individual student accomplishments, highlight program successes across disciplines, create role models for younger students exploring STEM interests, demonstrate institutional commitment to academic excellence, and build pride in intellectual achievement throughout school communities.
Why STEM Recognition Matters More Than Ever
The United States faces critical shortages of STEM-qualified professionals across industries from healthcare and technology to engineering and environmental science. Students pursuing STEM pathways need consistent encouragement, visible role models, and recognition that their academic efforts matter as much as achievements in other domains. Solutions like Rocket Alumni Solutions help schools create comprehensive STEM recognition programs through digital displays that celebrate science and mathematics excellence while inspiring future generations of innovators.
The Recognition Gap in STEM Education
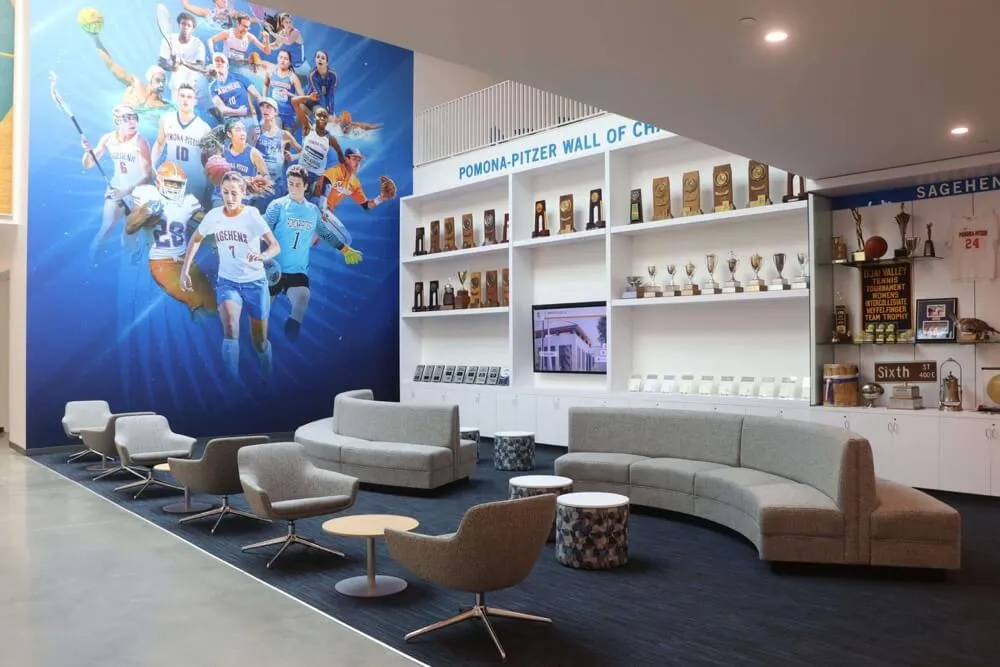
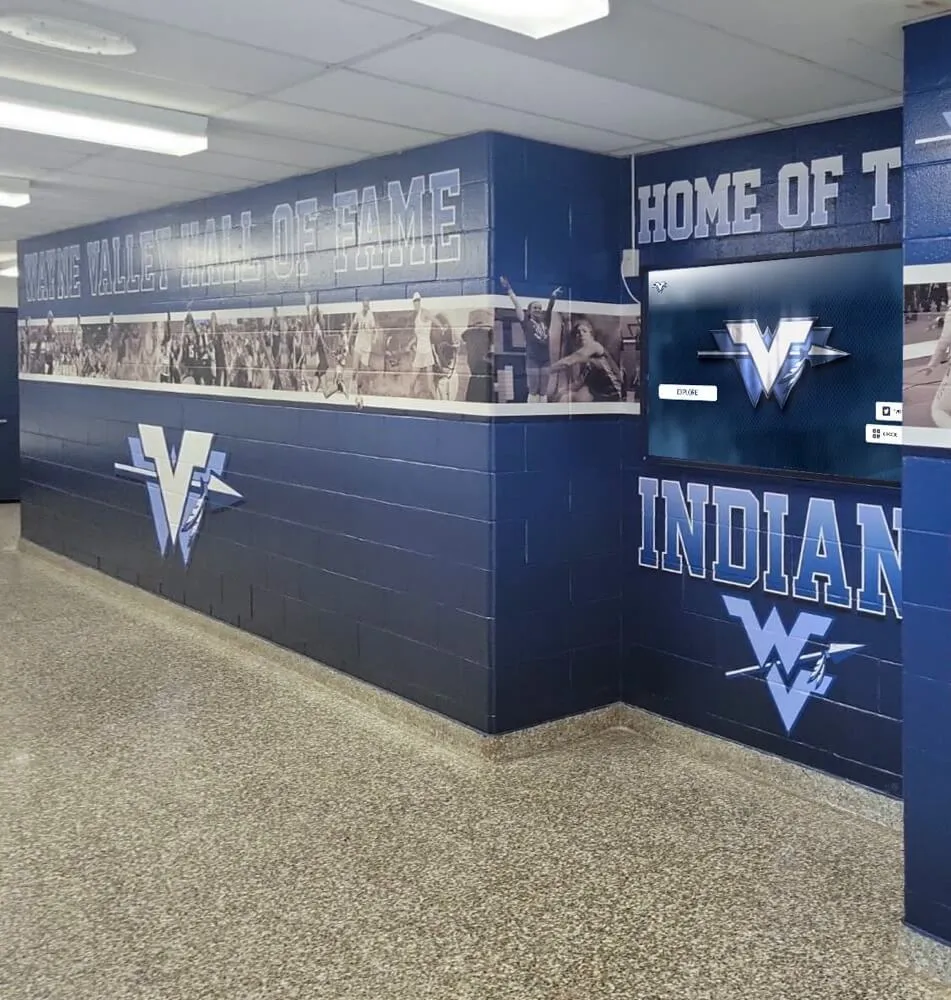
Walk through most high school athletic facilities and you’ll encounter trophy cases spanning entire hallways, record boards covering gymnasium walls, championship banners hanging from ceilings, and halls of fame featuring legendary athletes. These visible celebrations of competitive excellence serve important purposes—honoring achievement, motivating current participants, and building community pride. Yet walk through those same schools’ science departments, mathematics wings, or technology labs, and recognition often consists of modest bulletin boards with outdated certificate printouts, rarely updated announcement boards, forgotten trophy cases tucked in corners, and temporary displays taken down after brief appearances.
This recognition disparity communicates that athletic achievement matters more than academic excellence—a message contradicting schools’ stated priorities and national workforce needs. When students observe that athletic success generates immediate, prominent, lasting recognition while STEM achievements receive perfunctory acknowledgment before being forgotten, they internalize hierarchies of value that don’t reflect genuine importance of different forms of excellence.

The Consequences of Inadequate STEM Recognition
Research in educational psychology demonstrates that recognition powerfully influences student motivation, identity development, and persistence in challenging disciplines. When STEM accomplishments go largely unrecognized, several negative outcomes emerge:
Reduced STEM Engagement: Students naturally gravitate toward activities where they see peers receiving acknowledgment and celebration. Visible athletic recognition attracts participants, while absent STEM recognition suggests these activities merit less attention and involvement.
Lost Role Models: Younger students exploring potential interests need visible examples of peers succeeding in various fields. Athletic walls of fame provide these role models in abundance. Without equivalent STEM recognition, students may not realize that peers who look like them excel in science and mathematics.
Undervalued Academic Effort: STEM disciplines require sustained intellectual effort comparable to athletic training—countless hours studying concepts, practicing problem-solving, preparing for competitions, and developing expertise. When this effort goes unrecognized while athletic training receives prominent celebration, students and families may question whether academic investment receives appropriate value.
Weakened STEM Culture: Schools aiming to strengthen STEM programs discover that culture matters tremendously. Recognition systems signal what institutions genuinely value beyond mission statements. Prominent STEM recognition creates environments where academic excellence feels central to school identity rather than secondary to athletic achievement.
Reduced Diversity in STEM: Visible recognition helps diverse students envision themselves in particular fields. When students from underrepresented groups see limited recognition for peers who share their backgrounds succeeding in STEM, they may conclude these fields aren’t for people like them—a perception that prominent, diverse STEM recognition directly combats.
Defining STEM Stars: What Achievements Deserve Recognition
Effective STEM recognition programs celebrate diverse forms of excellence across science, technology, engineering, and mathematics disciplines rather than focusing exclusively on competition results or test scores.
Individual Student Achievements
Competition Excellence: Students earning recognition in established competitions including Science Olympiad regional, state, and national placements, MATHCOUNTS chapter through national competitions, robotics tournaments (FIRST, VEX, etc.), programming competitions and hackathons, engineering challenges and innovation contests, state and national science fair awards, American Mathematics Competitions qualifiers, and physics and chemistry olympiad participants.
Competition success demonstrates mastery, competitive excellence, and ability to perform under pressure—all worthy of celebration comparable to athletic tournament achievements.
Academic Excellence and Course Completion: Recognition for sustained academic achievement including perfect scores on AP STEM examinations, completion of advanced mathematics sequences through calculus or beyond, dual enrollment in university STEM courses, exceptional performance in honors and advanced coursework, and consistent excellence across multiple STEM disciplines.
These achievements represent long-term commitment and intellectual development rather than single-event success, deserving recognition for sustained effort.
Research and Innovation: Original contributions to knowledge including independent research projects and publications, science fair projects demonstrating innovation and rigor, patent applications for student inventions, contributions to university research programs, and documented discoveries or innovations with real-world application.
Student research represents the highest form of academic engagement—creating new knowledge rather than simply consuming existing information.

Leadership and Mentorship: Contributions to STEM community including founding or leading STEM clubs and organizations, tutoring and mentoring younger students in STEM subjects, organizing science events, fairs, or outreach programs, advocacy for STEM education and opportunity, and demonstrated commitment to building STEM culture.
Leadership recognition celebrates students who lift entire programs rather than only individual achievement.
Creative Application: Novel uses of STEM knowledge including innovative solutions to community problems, development of apps or technologies serving school or community, application of STEM to arts integration projects, entrepreneurial ventures applying STEM knowledge, and interdisciplinary projects bridging STEM with humanities.
This recognition honors students who translate STEM knowledge into tangible real-world impact.
Team and Program Achievements
Beyond individual recognition, STEM Stars walls celebrate collective accomplishments:
Team Competition Results: Robotics team tournament successes and advancement, science bowl and quiz bowl championships, coding team competition results, engineering challenge team accomplishments, and collaborative research team achievements.
Program Milestones: Overall science fair participation and achievement rates, AP examination pass rates and perfect score counts, advanced mathematics course completion statistics, career and technical education program successes, and STEM pathway completion and certification achievements.
Institutional Recognition: Program awards and accreditations for STEM excellence, grants received for STEM programs and equipment, partnerships with universities and industry, notable alumni working in STEM fields, and faculty recognition for teaching excellence.
These program-level recognitions demonstrate sustained institutional commitment to STEM education while celebrating collective success.
Essential Components of Effective STEM Recognition Walls
Successful STEM Stars displays incorporate several critical elements that transform simple achievement lists into engaging, inspirational recognition experiences.
Comprehensive Achievement Documentation
Individual Profiles: Detailed recognition of each STEM star including student name and graduation year, specific achievement description and context, competition level and placement, photographs showing students with projects or awards, achievement dates and circumstances, and current pursuits for alumni (college, career, research).
Comprehensive profiles transform names-and-dates lists into stories that humanize achievement and create personal connections with viewers.
Visual Documentation: High-quality imagery brings achievements to life including photos of students with science fair displays, images of robotics teams and their creations, students presenting research or demonstrations, award ceremonies and recognition moments, before-and-after project documentation, and action shots of students engaged in STEM activities.
Visual content creates emotional engagement that text-only recognition cannot match while making STEM work tangible for viewers unfamiliar with specific disciplines or competitions.
Achievement Context: Explanatory information helping viewers understand significance including competition size and selectivity, percentage of students achieving specific results, historical context comparing to past achievements, advancement pathways showing progression, and real-world applications of projects or research.
Context prevents recognition from becoming meaningless trophy lists while educating viewers about what various achievements actually represent.

Organization and Accessibility
Logical Categorization: Organize content enabling intuitive navigation including discipline-specific sections (biology, chemistry, physics, mathematics, computer science, engineering), achievement type categories (competitions, research, coursework, leadership), grade level or year groupings, and special recognition sections (national qualifiers, perfect scores, major awards).
Thoughtful organization prevents overwhelming visitors while helping specific audiences quickly find relevant content.
Searchable Databases: For digital implementations, robust search functionality including name search for specific students, year ranges for class cohorts or time periods, achievement type filtering, discipline or subject filtering, and keyword search for projects or topics.
Search capabilities particularly benefit alumni exploring their own histories and families celebrating specific students’ accomplishments.
Multiple Access Points: Ensure broad accessibility through physical displays in STEM department areas, digital touchscreen systems in central locations, web-based access for remote viewing, mobile-optimized interfaces, and integration with school websites and directories.
Multiple touchpoints maximize recognition impact while serving diverse audiences from current students and families to alumni and prospective families evaluating programs.
Educational Value and Inspiration
Learning Opportunities: Recognition displays should educate beyond simple celebration including explanations of STEM concepts in student projects, descriptions of competition formats and challenge details, information about STEM career pathways, resources for students interested in similar pursuits, and connections to current real-world applications.
Educational elements transform recognition walls from backward-looking celebration into forward-looking inspiration that actively encourages STEM engagement.
Role Model Accessibility: Help students envision themselves in STEM fields including diverse representation across demographics showing STEM is for everyone, pathway documentation showing how students developed from novices to experts, student reflections about what drove their STEM interests, overcoming challenge stories demonstrating persistence, and accessible next steps for students wanting to explore similar paths.
Effective role modeling requires intentional design ensuring diverse students see achievers who reflect their own identities and backgrounds rather than reinforcing stereotypes about who belongs in STEM.
Digital vs. Traditional STEM Recognition Displays
Schools implementing STEM recognition face important decisions about display technology—traditional physical installations versus modern digital systems. Each approach offers distinct advantages and limitations.
Traditional Physical Displays
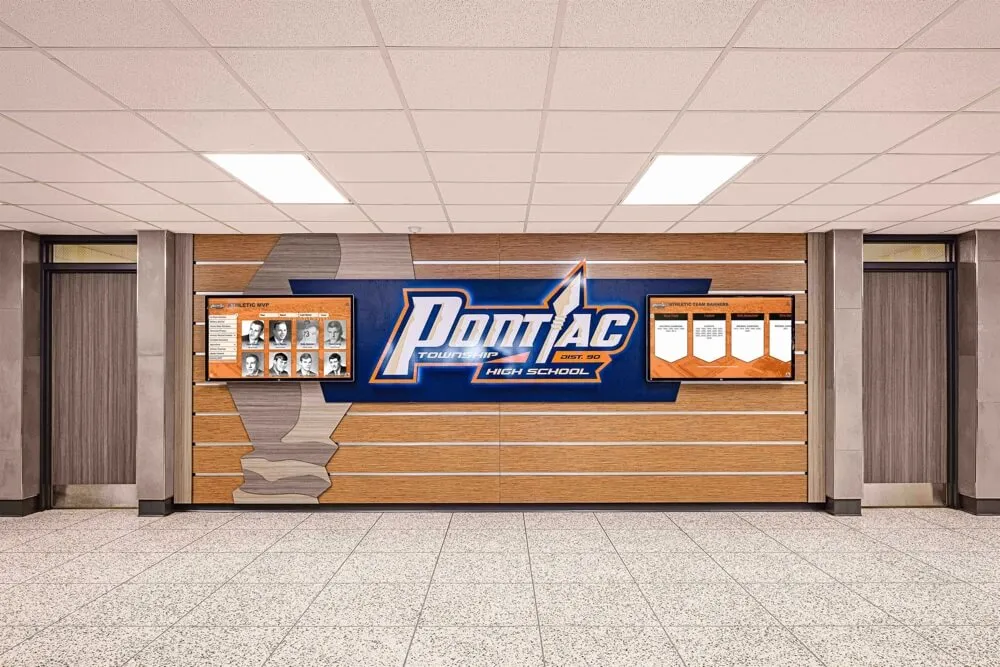
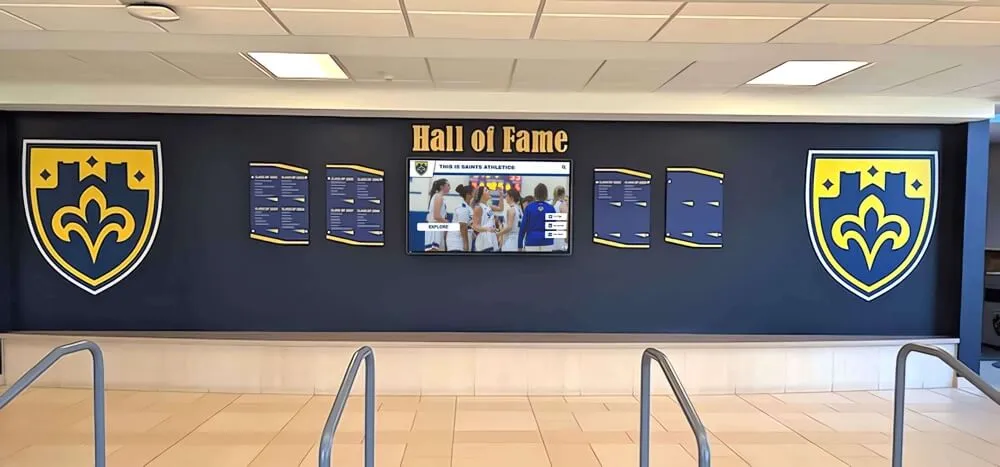
Physical recognition displays include bulletin boards with certificates and photos, trophy cases with awards and projects, wall-mounted plaques with engraved names, photo walls with framed images, and banner displays celebrating achievements.
Advantages of Physical Displays:
- Lower initial cost compared to digital systems
- No ongoing technical maintenance requirements
- Tangible, permanent presence
- Familiar implementation process
- No power or network infrastructure needed
- Can incorporate three-dimensional objects like trophies or project models
Limitations of Physical Displays:
- Limited space constraining amount of recognition
- Static content requiring physical updates
- Difficult to modify or correct errors
- Limited contextual information beyond brief text
- No interactive exploration or search capability
- Expensive ongoing costs for new plaques and materials
- Risk of fading, damage, or deterioration over time
- Cannot accommodate multimedia content
- Difficult to reorganize as programs evolve
Traditional displays work adequately for schools with limited recognition volume, stable achievement patterns, and modest budgets. However, these limitations become increasingly problematic as STEM programs grow and recognition needs expand.
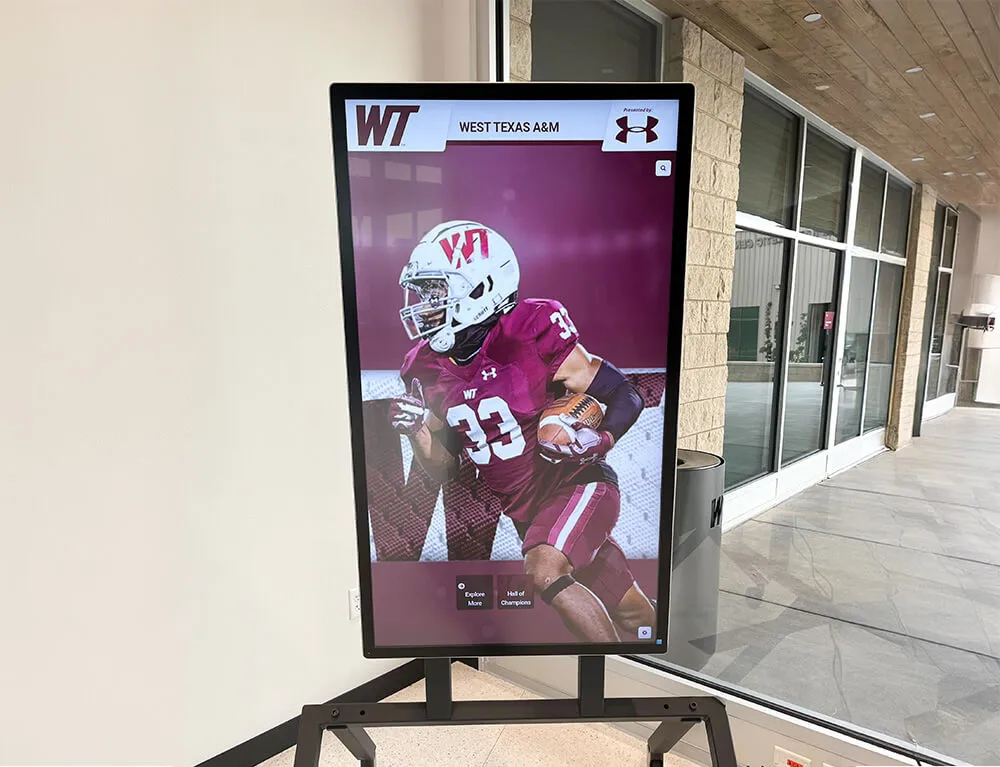
Modern Digital Recognition Displays
Digital STEM recognition systems use touchscreen displays, video screens, or interactive kiosks with regularly updated content managed through cloud-based platforms.
Advantages of Digital Systems:
- Unlimited capacity for recognizing achievements
- Easy content updates requiring no physical changes
- Rich multimedia including photos, videos, and detailed descriptions
- Interactive exploration through search and filtering
- Professional, polished appearance that’s always current
- Ability to reorganize and recategorize content instantly
- No ongoing material costs for updates
- Analytics tracking engagement and popular content
- Integration with school websites and systems
- Accessibility features for diverse users
- Remote content management from anywhere
Limitations of Digital Systems:
- Higher initial investment compared to basic physical displays
- Requires power and network connectivity
- Potential technical issues requiring troubleshooting
- Need for ongoing content management and updates
- May require staff training for system operation
For schools serious about comprehensive, long-term STEM recognition that grows with programs, modern digital recognition displays provide capabilities that traditional approaches simply cannot match. The investment in digital systems returns value through unlimited capacity, easy maintenance, and engaging experiences that actively inspire students rather than passively displaying information.

Implementation Planning: Creating Your STEM Stars Recognition Wall
Successful STEM recognition programs require thoughtful planning ensuring displays effectively celebrate achievement, inspire participation, and remain sustainable over time.
Phase 1: Assessment and Goal Setting (Months 1-2)
Inventory Current STEM Achievements: Document what already exists across your institution including competition participation and results over past 5-10 years, advanced course completion and AP examination results, research projects and publications, student awards and recognition, STEM club activities and leadership, and notable alumni pursuing STEM careers.
Complete inventories reveal the depth of achievement often hidden when no centralized recognition exists.
Define Recognition Scope: Establish boundaries for what qualifies for inclusion including minimum achievement levels for different categories, time period to include (current year only, past decade, comprehensive history), whether to include team or only individual achievements, criteria for research project inclusion, and approach to ongoing versus one-time achievements.
Clear scope prevents later confusion and inconsistency while ensuring recognition feels appropriately selective without being impossible to achieve.
Identify Stakeholders: Engage relevant parties in planning including STEM department heads and teachers, school administrators and counselors, students currently achieving in STEM fields, families of recognized students, alumni working in STEM careers, and community STEM partners and employers.
Diverse perspectives ensure recognition programs serve multiple purposes while building broad ownership supporting long-term sustainability.
Establish Budget Parameters: Determine available resources including one-time capital funds for display systems, ongoing operational budget for updates and maintenance, in-kind contributions from boosters or partners, grant opportunities for STEM recognition, and phased implementation options if immediate comprehensive approach exceeds budget.
Phase 2: Content Development (Months 2-4)
Compile Achievement Data: Systematically gather information about recognized individuals including student names and graduation years, achievement descriptions with dates, competition levels and results, project titles and descriptions, award types and issuing organizations, supporting documentation and verification, and current information for alumni when available.
Thorough data collection ensures accurate, complete recognition while creating valuable institutional records.
Gather Visual Assets: Collect high-quality imagery including photos of students with projects or awards, competition or event photographs, certificate and award documentation, research poster or presentation images, team photographs, and action shots of students engaged in STEM work.
Professional-quality images dramatically enhance recognition impact. Student awards recognition programs that invest in strong visual documentation create far more engaging displays than text-heavy alternatives.
Develop Contextual Content: Create explanatory materials helping viewers understand achievements including competition descriptions and selectivity information, achievement significance and historical context, STEM concept explanations for projects, pathway information about how students developed expertise, and resources for students interested in similar pursuits.
Rich context transforms recognition from simple name lists into educational experiences that actively promote STEM engagement.
Organize Classification System: Establish logical organizational structure including primary categorization approach (by discipline, achievement type, year), secondary filtering options for digital displays, naming and tagging conventions ensuring consistency, hierarchy determining feature placement, and integration with existing school recognition systems.
Phase 3: Technology Selection and Implementation (Months 3-5)
Evaluate Display Options: Consider various approaches including location options throughout campus, physical display types and limitations, digital system capabilities and features, budget constraints and total cost of ownership, and integration with existing school systems.
For schools choosing digital solutions, platforms like Rocket Alumni Solutions provide purpose-built features specifically designed for educational recognition, making implementation straightforward compared to repurposing generic digital signage systems.
Plan Installation: Coordinate technical and logistical requirements including optimal placement in high-traffic areas, electrical and network infrastructure, mounting and physical installation, accessibility considerations, and launch timeline coordination.
Configure Content Management: Set up systems for ongoing management including user roles and permissions, content update workflows, approval processes for additions, quality standards for photos and text, and training for staff maintaining displays.
Phase 4: Launch and Promotion (Month 5-6)
Unveiling Event: Create memorable launch generating awareness including formal ceremony recognizing inaugural inductees, student and family invitations, media coverage and publicity, demonstration of display features and capabilities, and celebration of STEM program excellence.
Launch events communicate that STEM recognition matters institutionally while creating positive associations with academic achievement.
Ongoing Promotion: Maintain visibility after initial launch including regular social media features highlighting recognized students, integration into school tours and open houses, connection to STEM recruitment and advising, periodic updates celebrating new achievements, and annual recognition events or ceremonies.
Advanced Features for Digital STEM Recognition Systems
Schools implementing modern digital recognition platforms access capabilities impossible with traditional displays, creating richer, more engaging experiences that actively promote STEM participation.
Interactive Exploration Tools
Advanced Search and Filtering: Users explore content through multiple pathways including name search for specific students, year ranges showing class cohorts, discipline or subject filtering, achievement type selection, keyword search for projects or topics, and combined filters for precise results.
Interactive exploration transforms passive viewing into active engagement where students discover role models with interests matching their own.
Timeline Visualizations: Present STEM achievement history through engaging formats including chronological achievement timelines, year-by-year program growth, decade retrospectives, and filtering showing how programs evolved over time.
Historical context helps current students understand they’re part of ongoing excellence traditions while demonstrating sustained institutional commitment to STEM.
Achievement Comparisons: Statistical presentations providing context including achievement frequency over time, discipline distribution showing strengths, competition success rates, and comparison to state or national data where available.
Data visualizations help students, families, and community members understand program quality and achievement significance.

Multimedia Enhancement
Video Integration: Rich media brings achievements to life including student project presentations, competition highlights, student reflections about their STEM journey, alumni career updates, and documentary-style features about major achievements.
Video content creates emotional engagement text and photos alone cannot provide while making STEM work concrete for viewers unfamiliar with specific disciplines.
Audio Narratives: Recorded content adds personal dimension including student explanations of their projects, teacher commentary about exceptional work, alumni reflecting on how STEM interests developed, and interviews about research or innovation processes.
Social Integration
Sharing Capabilities: Enable recognition to extend beyond physical displays including social media sharing of individual profiles, email notifications about student recognition, alumni network integration, and download options for students and families.
Digital sharing amplifies recognition impact exponentially beyond viewers physically visiting displays.
Community Contributions: Facilitate ongoing engagement including nomination submission for new recognitions, alumni update forms maintaining current information, parent or community member commendations, and photo contribution options for events and activities.
Ensuring Equity and Inclusion in STEM Recognition
STEM recognition programs must intentionally address equity ensuring all students see pathways to recognition rather than systems inadvertently favoring those with existing advantages.
Recognizing Diverse Forms of Excellence
Multiple Achievement Pathways: Create recognition opportunities across spectrum including high-level competition success, significant growth and improvement, sustained academic excellence, leadership and mentorship contributions, creative STEM application and innovation, and community service applying STEM knowledge.
Diverse categories ensure students who may not win major competitions still receive acknowledgment for meaningful STEM engagement and achievement.
Addressing Access Barriers
Resource Equity: Consider whether recognition criteria assume access including competition fees and travel costs, specialized equipment or materials, summer programs requiring tuition, enrichment opportunities dependent on family resources, and time availability for activities outside school.
When recognition depends heavily on opportunities not accessible to all students, programs inadvertently privilege advantaged students while excluding those with equal ability but fewer resources. Schools serious about equity ensure recognition pathways exist requiring only effort, talent, and commitment rather than family wealth.
Proactive Opportunity Expansion: Address access barriers directly including fee assistance for competition participation, school-provided transportation to events, lending libraries for equipment and materials, free after-school STEM clubs and activities, and mentorship connecting interested students with opportunities.
Cultural Responsiveness
Representation Matters: Ensure diverse students see themselves in recognition including intentional attention to demographic balance, recognition highlighting underrepresented groups’ achievements, culturally relevant project and application examples, and multilingual accessibility where appropriate.
When students from particular backgrounds rarely see recognition for peers who look like them, implicit messages suggest STEM fields may not welcome certain groups. Intentionally highlighting diverse achievers directly combats these perceptions.
Community-Connected STEM: Value applications with cultural relevance including projects addressing community challenges, innovation solving problems in students’ cultural contexts, research exploring culturally significant topics, and mentorship within students’ communities.
Recognition validating culturally-rooted STEM work demonstrates these disciplines serve all communities rather than being disconnected from students’ daily realities.
Maintaining and Growing STEM Recognition Programs
Sustainable recognition requires ongoing attention ensuring displays remain current, accurate, and continue serving their motivational purposes.
Content Update Workflows
Regular Addition Processes: Establish systematic approaches for new recognition including quarterly reviews identifying recent achievements, annual comprehensive audits, defined submission and verification procedures, approval workflows preventing errors, and prompt addition after verification.
Recognition timing matters significantly—immediate acknowledgment carries far greater motivational impact than delayed recognition months later. Digital systems enable near-real-time updates impossible with traditional physical displays requiring plaque production and installation.
Quality Maintenance: Preserve display value through ongoing attention including correction of discovered errors, enhancement of minimal profiles with additional context, image quality improvement for older content, reorganization as categorization needs evolve, and archival of outdated or no-longer-relevant content.
Program Assessment
Engagement Metrics: Evaluate recognition program effectiveness through measurement including visitor interaction frequency and duration for digital displays, search patterns revealing popular content, social media sharing and engagement, student awareness of recognition opportunities, and participation rate changes in STEM activities.
Data-informed assessment enables continuous improvement while demonstrating program value to stakeholders.
Outcome Tracking: Monitor broader impacts including STEM course enrollment trends, competition participation rates, advanced STEM pathway completion, diversity representation in STEM programs, and alumni STEM career pursuit rates.
While attribution proves difficult, monitoring outcomes alongside recognition implementation helps assess whether programs contribute to desired STEM culture strengthening.
Stakeholder Feedback: Gather qualitative perspectives including student surveys about recognition awareness and motivation, teacher observations about cultural impacts, family satisfaction with recognition approaches, alumni reflections about recognition’s role in their journeys, and community perception of institutional STEM commitment.
Integrating STEM Recognition with Broader School Programs
STEM Stars Recognition Walls create maximum impact when integrated strategically with broader educational initiatives rather than functioning as isolated displays.
Curriculum Connections
Classroom Integration: Connect recognition to learning experiences including student research about recognized alumni’s careers, analysis of award-winning projects as exemplars, historical exploration of program development, mathematical analysis of achievement trends, and goal-setting using recognition as aspiration targets.
Curricular integration ensures recognition actively supports learning rather than simply celebrating past achievement.
Advising and Pathway Development
Student Support: Use recognition to guide interests including highlighting achievement pathways in student advising, showcasing role models during course selection, connecting interested students with mentors, demonstrating STEM career possibilities, and illustrating how coursework leads to achievement.
Recognition becomes active recruitment and retention tool when integrated into advising rather than treated as separate from academic planning.
Community Engagement and Outreach
Public Relations: Leverage recognition in external communication including prospective family tours highlighting STEM excellence, community event displays showcasing programs, partnership development with STEM employers, alumni engagement through recognition connections, and media coverage celebrating achievements.
Visible STEM recognition strengthens school reputation while attracting families valuing academic excellence and demonstrating institutional priorities to broader communities.
Schools seeking to maximize their investment in recognition should explore inclusive digital recognition programs that serve multiple purposes simultaneously rather than single-function displays with limited integration potential.

Budget Considerations and Funding Strategies
STEM recognition implementation requires financial investment, though costs vary dramatically based on scope, technology choice, and content development approach.
Investment Requirements
Physical Display Systems: Basic recognition walls using traditional approaches including bulletin board installations at $200-$800, trophy case additions at $1,500-$5,000, wall-mounted plaque systems at $3,000-$8,000, and professional signage and graphics at $2,000-$6,000.
Digital Recognition Systems: Modern touchscreen solutions including entry-level touchscreen displays at $8,000-$15,000, mid-range installations with professional mounting at $15,000-$30,000, comprehensive multi-display systems at $30,000-$60,000+, and annual software subscriptions at $2,000-$8,000.
Digital systems carry higher initial costs but often prove more cost-effective long-term due to unlimited capacity, no ongoing material costs for updates, and significantly richer recognition experiences. Schools should evaluate digital trophy case solutions understanding total cost of ownership over 5-10 years rather than focusing exclusively on initial purchase price.
Content Development: Professional services and time investment including photography and media collection at $1,000-$5,000, data compilation and verification consuming 100-200 staff hours, content writing and profile creation, historical research and alumni outreach, and ongoing maintenance and updates.
Funding Sources
District Operating Budgets: Core institutional funding including technology budget allocations, curriculum and instruction funds, facilities improvement line items, and administrative discretionary funds.
STEM Grants: Targeted external funding including federal STEM education grants, state mathematics and science education funding, corporate STEM initiative grants, foundation support for STEM programs, and university partnership funding.
Many grant programs specifically support recognition components as part of comprehensive STEM program development, particularly when recognition addresses equity and access.
Booster Organizations: Community fundraising including general booster club support, STEM-specific booster organizations, parent-teacher organization contributions, and targeted fundraising campaigns for specific projects.
Business Partnerships: Local employer support including direct sponsorship with recognition, equipment or material donations, employee volunteer support for content development, and in-kind professional services.
Alumni Giving: Former student contributions including major gifts from STEM-career alumni, class gift campaigns directed to recognition, reunion-connected giving opportunities, and memorial or honorific naming opportunities.
Compelling cases for recognition funding emphasize both backward-looking celebration of excellence and forward-looking investment in strengthening STEM culture, increasing participation, and building pathways addressing workforce needs.
The Future of STEM Recognition in Education
As STEM education evolves and technology advances, recognition programs will incorporate emerging capabilities creating even richer, more engaging experiences.
Emerging Technologies
Artificial Intelligence Integration: AI-enhanced features including automated tagging and categorization of content, personalized content recommendations for visitors, natural language search enabling conversational queries, predictive analytics identifying achievement trends, and translation capabilities supporting multilingual audiences.
Augmented Reality Features: Immersive experiences bringing recognition to life including AR overlays providing additional context when viewing displays, virtual project demonstrations and recreations, interactive 3D models of student creations, spatial computing for museum-style exhibitions, and immersive storytelling about STEM journeys.
Advanced Analytics: Sophisticated measurement and optimization including detailed engagement tracking and pattern analysis, A/B testing of content presentation approaches, predictive modeling of recognition’s motivational impact, correlation analysis between recognition and participation, and continuous optimization based on data insights.
Evolving Recognition Paradigms
Micro-Credentials and Digital Badges: Supplementing traditional awards with modern alternatives including stackable micro-credentials for specific skills, digital badges documenting competency development, blockchain-verified achievement records, and portable credentials following students beyond school.
Competency-Based Recognition: Shifting from event-based to development-focused acknowledgment including recognition for mastery demonstration rather than just competition placement, documentation of skill progression over time, celebration of revision and iteration processes, and acknowledgment of collaborative contributions alongside individual achievement.
Celebrating STEM Excellence: Building Culture Through Recognition
Creating STEM Stars Recognition Walls represents far more than adding displays to school facilities—it demonstrates institutional commitment to valuing science, technology, engineering, and mathematics achievement with prominence equal to other forms of excellence. When schools invest in professional, comprehensive STEM recognition, they send clear messages that academic achievement matters profoundly, STEM disciplines deserve celebration and support, intellectual accomplishment creates school pride and identity, diverse forms of excellence receive acknowledgment, and student effort in challenging academic domains brings meaningful recognition.
These messages powerfully influence school culture, student motivation, parent perceptions, and community understanding of institutional priorities. Recognition alone doesn’t create STEM excellence, but visible, prominent celebration of achievement contributes significantly to environments where STEM engagement feels valued, celebrated, and central to school identity rather than secondary to other priorities.
Effective STEM recognition programs share common characteristics: comprehensive inclusion celebrating diverse achievement types, professional presentation creating impressive visual impact, rich content providing context and educational value, accessibility through multiple touchpoints and technologies, equity ensuring recognition pathways exist for all students, sustainability through manageable update processes, and integration with broader STEM program goals and initiatives.
Schools beginning STEM recognition journeys should focus initial efforts on core achievements demonstrating existing excellence, establish sustainable update workflows supporting long-term maintenance, invest in technology enabling growth as programs expand, engage diverse stakeholders building broad ownership, connect recognition to recruitment and retention goals, and plan iterative development rather than assuming initial implementation represents final state.
For schools serious about comprehensive, professional STEM recognition that inspires students while preserving institutional history, digital recognition platforms like Rocket Alumni Solutions provide purpose-built capabilities specifically designed for educational environments. These systems offer intuitive content management, unlimited capacity for growth, engaging interactive experiences, and integration with broader recognition programs—transforming STEM celebration from basic bulletin boards into sophisticated systems rivaling any athletic hall of fame.
Your students’ STEM achievements deserve recognition matching the significance of their accomplishments. Whether they’re breaking school records, earning national competition honors, conducting original research, or leading peers toward STEM excellence, these young scientists, mathematicians, engineers, and technologists represent your institution’s future and our collective innovation capacity. Celebrate them prominently, professionally, and permanently through recognition systems demonstrating that intellectual achievement matters as much as any championship trophy.
Frequently Asked Questions
What achievements should be included in a STEM Stars Recognition Wall?
Include diverse STEM accomplishments: competition placements (Science Olympiad, MATHCOUNTS, robotics), advanced course completion (AP perfect scores, advanced math sequences), research achievements, individual awards, leadership roles, creative STEM applications, and sustained academic excellence. Create multiple recognition tiers ensuring accessibility while maintaining meaningful standards.
How do digital STEM recognition systems compare to traditional physical displays?
Digital systems offer unlimited capacity, easy content updates, rich multimedia integration, interactive exploration, and professional appearance without ongoing material costs. Physical displays have lower initial costs but limited space, difficult updates, no interactivity, and accumulating expenses for new plaques. For comprehensive long-term recognition, digital platforms provide capabilities traditional approaches cannot match.
How can we ensure our STEM recognition program promotes equity and inclusion?
Create diverse recognition pathways beyond just competition wins, address access barriers to opportunities, highlight underrepresented groups’ achievements intentionally, value community-connected applications, eliminate financial barriers to participation, and ensure selection committees include diverse perspectives. Monitor recognition distribution patterns identifying unintended biases.
What’s the typical cost of implementing a STEM recognition system?
Physical systems range from $2,000-$15,000 depending on scope. Digital touchscreen displays cost $8,000-$30,000 initially plus $2,000-$8,000 annual subscriptions, with higher-end systems reaching $60,000+. Consider total cost of ownership over 5-10 years rather than just initial investment, as digital systems often prove more cost-effective long-term through unlimited capacity and no ongoing material expenses.
How do we maintain and update STEM recognition displays over time?
Establish regular review cycles (quarterly or annual) identifying new achievements, create clear submission and verification workflows, assign specific staff responsibility for updates, maintain quality standards for photos and content, leverage digital platforms enabling easy additions, and integrate recognition into existing STEM program operations rather than treating as separate initiative requiring special attention.
How can STEM recognition integrate with existing school recognition programs?
Position STEM recognition alongside athletic halls of fame in prominent locations, use consistent branding and quality standards across all recognition, connect through unified digital platforms when possible, coordinate recognition ceremonies and events, share resources and infrastructure, and ensure institutional messaging emphasizes multiple forms of excellence rather than privileging particular achievement types.
What if we have limited historical information about past STEM achievements?
Start with current achievements demonstrating immediate value while systematically researching historical accomplishments, leverage yearbooks and archives, reach out to alumni through surveys, engage long-time faculty who remember past achievements, accept some historical gaps acknowledging preservation importance going forward, and add historical content incrementally as information emerges rather than waiting for complete historical documentation before launching.