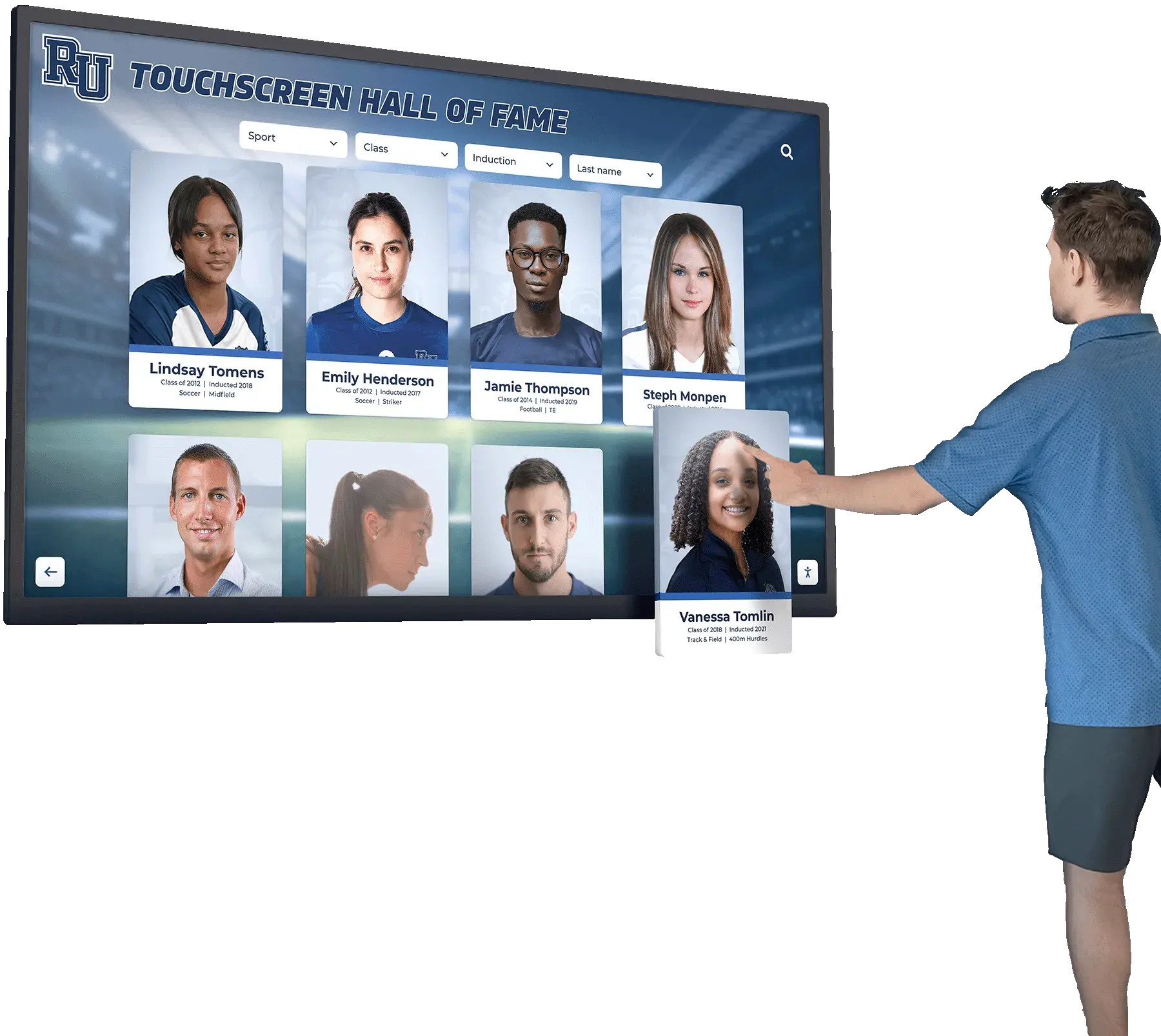
High schools and universities face a critical challenge: demonstrating the real-world outcomes of their educational programs. Parents want to know where graduates work, students need to envision post-graduation possibilities, and administrators must show measurable success to justify program investments. Meanwhile, alumni often remain invisible after graduation despite representing powerful proof of institutional impact and valuable mentors for current students.
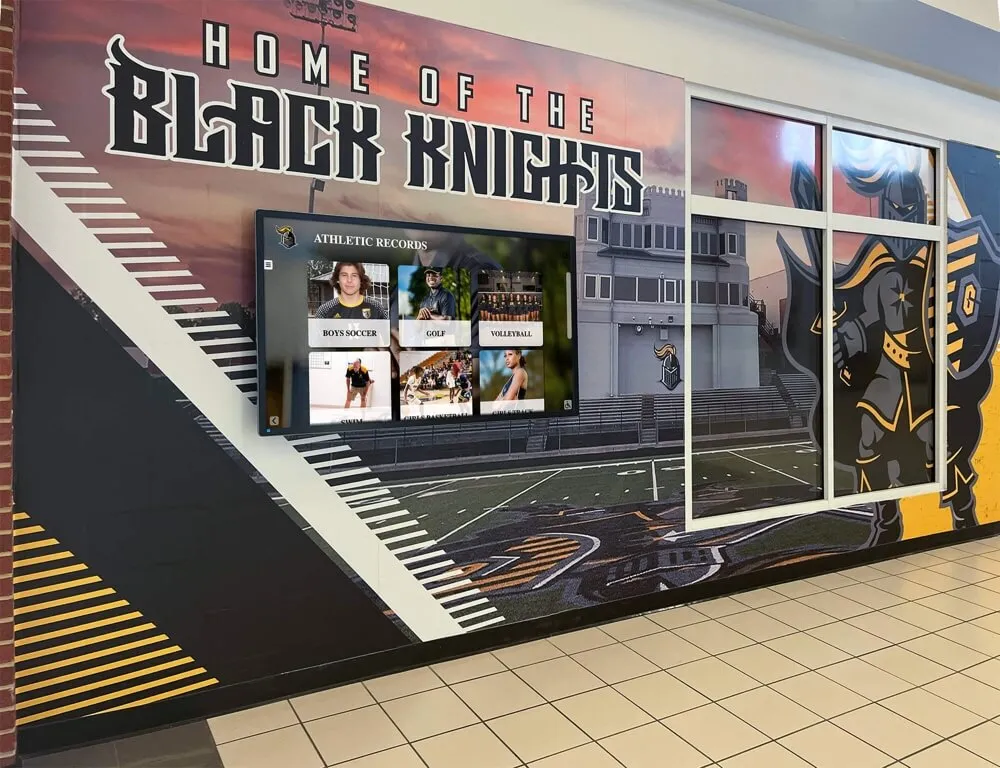
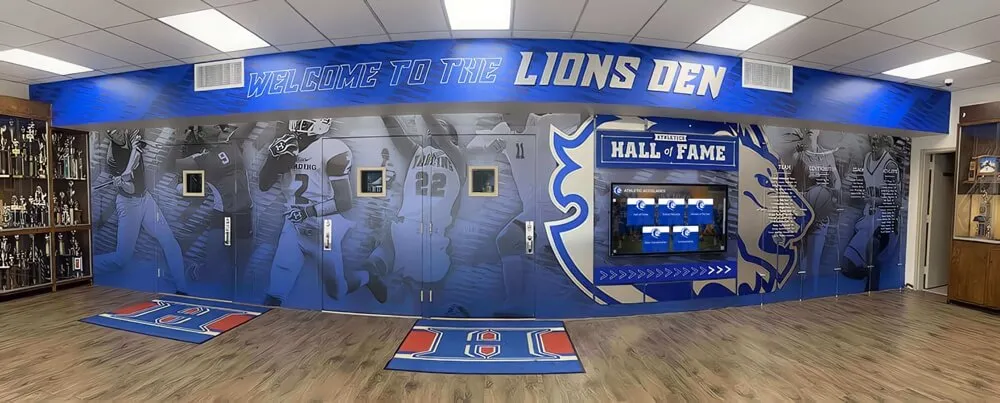
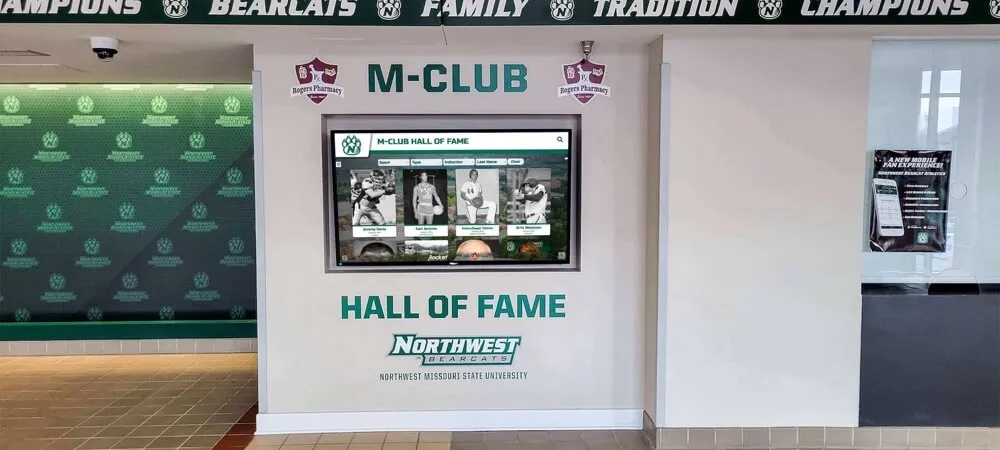
Interactive career pathways boards solve this visibility problem by showcasing the complete journey from enrollment through education to professional success. These digital recognition systems display college commitments, career trajectories, alumni achievements, and professional milestones in engaging formats that inspire current students while demonstrating program effectiveness to all stakeholders. Schools implementing comprehensive career pathway displays report increased student motivation, improved alumni engagement, enhanced recruitment, and stronger community partnerships.
Why Interactive Career Pathways Boards Transform Schools
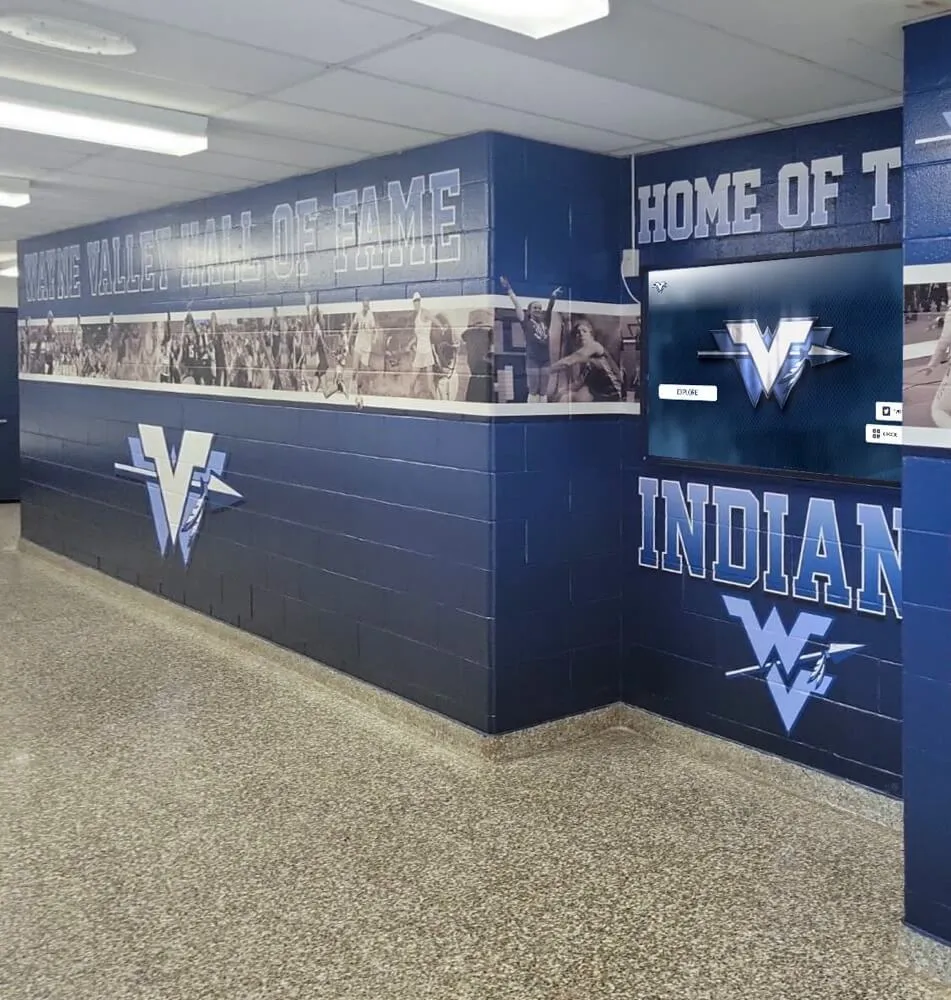
Traditional career displays—static bulletin boards with outdated photos and limited information—fail to demonstrate the breadth and diversity of student success. Interactive career pathways boards from solutions like Rocket Alumni Solutions provide dynamic, comprehensive platforms that celebrate diverse career paths, showcase ongoing professional development, and create mentorship connections between alumni and current students. These systems transform career guidance from abstract advice into concrete examples that students can explore, understand, and aspire to follow.
Understanding Career Pathways Boards
Career pathways boards represent more than simple employment listings or college acceptance announcements. They create comprehensive narratives showing the connections between education, skill development, and professional success.
What Makes Career Pathways Different from Traditional Recognition
Traditional recognition focuses primarily on academic achievements—honor rolls, valedictorians, scholarship recipients—or athletic success through trophy cases and championship banners. Career pathways boards extend recognition timelines forward, acknowledging what happens after graduation and demonstrating long-term program effectiveness.

While academic recognition celebrates inputs and immediate outcomes (grades earned, tests passed, competitions won), career recognition highlights ultimate outcomes: meaningful employment, graduate school success, entrepreneurial ventures, community contributions, and professional advancement. This outcome focus resonates powerfully with students making educational decisions and families investing in those decisions.
Career pathways boards also celebrate diversity of success rather than hierarchical achievement. Not every student becomes a doctor, lawyer, or engineer—nor should they. Comprehensive career displays honor trades, arts, service professions, entrepreneurship, and diverse paths to fulfilling careers. This inclusive approach helps all students envision futures aligned with their interests and strengths rather than feeling pressured into narrow “prestigious” paths that may not fit.
The Critical Role in College and Career Readiness
College and career readiness programs emphasize exposure, exploration, and preparation. Students need to understand career possibilities, requirements for various paths, and skills necessary for success. Career pathways boards support each element.
Exposure Through Example: Students discover career possibilities by seeing what graduates actually do. A student interested in healthcare might discover that alumni work not just as doctors and nurses but also as medical researchers, healthcare administrators, pharmaceutical representatives, physical therapists, genetic counselors, and medical device engineers. This exposure expands understanding of career possibilities within broad interest areas.
Clarifying Educational Requirements: Effective career displays connect educational experiences to career outcomes. When students see that the marine biologist studied biology and participated in environmental club, or that the software engineer took AP Computer Science and joined coding competitions, they understand concrete pathways from current opportunities to future careers.
Building Professional Skills Awareness: Modern career pathways boards can highlight skills that contribute to professional success—communication, problem-solving, collaboration, technical expertise, leadership. By showcasing how diverse educational experiences develop these transferable skills, displays help students understand that career preparation extends beyond specific courses.
Key Components of Effective Career Pathways Displays
Comprehensive career pathways boards integrate several information categories to tell complete career stories:
College Commitments and Destinations: Where students continue education immediately after graduation—four-year universities, community colleges, technical schools, military academies. This information provides immediate post-graduation context while establishing educational foundations for eventual careers. Resources on showcasing college commitments demonstrate effective approaches for highlighting higher education paths.
Career Fields and Industries: Broad categorizations showing where alumni work—healthcare, technology, education, business, trades, arts, public service, entrepreneurship. Field-level organization helps students explore areas of interest without requiring exact job title knowledge.
Specific Roles and Companies: Detailed information about alumni positions and employers—job titles, company names, responsibilities, and career progressions. This specificity helps students understand concrete opportunities and employers actively hiring people like them.
Professional Milestones and Achievements: Recognition of significant career accomplishments—promotions, patents, publications, awards, leadership roles, community contributions. These milestones demonstrate ongoing professional development and achievement that extends years beyond graduation.
Career Journey Narratives: Stories explaining how individuals moved from education through entry positions to current roles. These narratives reveal decision points, skill development, setbacks overcome, and strategies employed—providing roadmap-style guidance that statistics alone cannot offer.
Strategic Benefits for Educational Institutions
Schools implementing interactive career pathways boards discover multiple advantages extending across institutional priorities.
Enhancing Student Motivation and Goal-Setting
Students engage more deeply with education when they understand its connection to meaningful futures. Career pathways boards make these connections tangible and personal.
When students encounter alumni who started in similar circumstances—same hometowns, similar academic profiles, comparable interests—succeeding in careers they find appealing, abstract futures become concrete possibilities. This identification creates motivation through accessible role models rather than distant celebrities or exceptional outliers that students struggle to relate to.

Interactive displays invite exploration that static boards cannot match. Students search for alumni in fields they’re considering, filter by colleges they’re researching, and discover unexpected career paths connecting to their interests. This active engagement creates personal investment that passive reading or lecture-based career guidance rarely achieves.
The goal-setting impact proves particularly valuable. Students discovering specific careers they want to pursue can research the educational paths alumni followed, courses they recommend, skills they developed, and experiences that proved valuable. This intelligence transforms vague aspirations (“I want to help people”) into concrete plans (“I’ll major in social work, intern at community organizations, and consider graduate school for clinical licensure”).
Demonstrating Program Value and Outcomes
Administrators need evidence justifying program investments, responding to community questions, and communicating institutional effectiveness. Career pathways data provides compelling outcome documentation.
When vocational programs can demonstrate that 85% of graduates secure employment in their trained fields within six months, with starting salaries averaging specific amounts, stakeholders see tangible return on investment. Similarly, when college preparatory tracks show consistent acceptance to quality universities with sustained collegiate performance, families recognize program quality.
Career pathways displays transform anecdotal success stories into systematic evidence. Rather than mentioning a few notable alumni during presentations, comprehensive displays demonstrate patterns of success across decades, diverse career fields, and varied student profiles. This breadth proves institutional effectiveness rather than highlighting exceptional outliers.
Accreditation processes increasingly emphasize outcomes assessment. Career pathways tracking provides documentation for self-studies and external reviews, demonstrating that institutions monitor alumni success, maintain engagement beyond graduation, and use outcome data to inform program improvements.
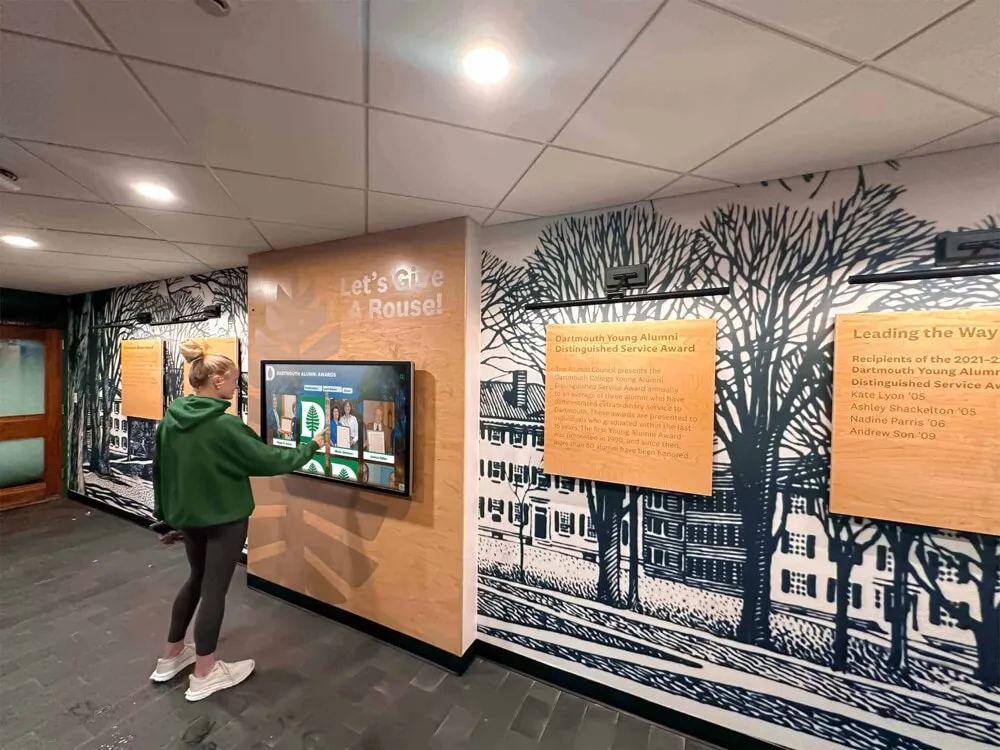
Strengthening Alumni Relations and Engagement
Alumni who see their achievements recognized feel valued by their alma maters. This acknowledgment strengthens emotional connections and often translates into increased engagement and support.
Career recognition creates natural conversation starters during alumni events, reunions, and fundraising appeals. Alumni visiting campus encounter their profiles displayed prominently, generating pride and positive associations with the institution. These emotional responses often increase willingness to volunteer time, mentor students, provide internship opportunities, or contribute financially.
Interactive displays facilitate ongoing relationship maintenance. Schools can update career information as alumni advance professionally, recognizing promotions, significant projects, or career transitions. These touchpoints maintain connection during years when alumni might otherwise drift away from institutional engagement. Approaches for building sustained alumni engagement demonstrate systematic strategies for maintaining long-term relationships.
Alumni benefit personally from career recognition. Professional profiles displayed on school platforms provide credibility enhancement, networking opportunities through alumni connections, visibility to current students seeking mentors or career guidance, and personal satisfaction from being acknowledged by institutions that shaped their development.
Supporting Recruitment and Enrollment
Prospective families evaluate schools partially through graduate outcomes. Career pathways displays provide compelling evidence during recruitment cycles.
When families tour campuses and encounter comprehensive displays showing hundreds of successful graduates across diverse careers, they see proof of institutional effectiveness rather than relying on promises or reputation. This evidence particularly resonates with families skeptical about educational investments and wanting assurance that programs deliver results.

Displays showcasing diverse success paths appeal to varied student interests. Families with children passionate about arts, trades, sciences, or business all find examples of successful graduates in relevant fields. This inclusive representation communicates that schools support multiple definitions of success rather than pushing all students toward narrow paths.
Career outcome data influences school choice decisions. When families compare institutions and one provides detailed, accessible career information while competitors offer vague assurances, the transparency creates competitive advantage. Online accessibility extends this advantage to families researching schools remotely before investing time in campus visits.
Essential Features of Interactive Career Pathways Boards
Effective career pathways systems require specific capabilities beyond basic display technology.
Comprehensive Alumni Database Management
The foundation of career recognition requires robust systems for collecting, organizing, and maintaining alumni information over time.
Platforms must accommodate diverse information types—biographical details, educational histories, career trajectories, current positions, contact preferences, and permission management. Flexible field structures allow schools to capture information relevant to their specific programs and career emphasis areas.
Intuitive content management enables staff without technical expertise to add alumni, update career information, upload photos and media, manage privacy settings, and publish changes quickly. Systems requiring IT involvement for routine updates create bottlenecks that lead to outdated information.
Automated update workflows reduce administrative burden. Some platforms enable alumni to submit their own updates through secure portals, which staff then approve and publish. This crowdsourcing approach maintains currency while distributing data collection workload.
Data privacy and permission management prove critical. Systems must respect alumni preferences about what information appears publicly versus to authenticated users only, how much detail about employers or positions gets shared, whether contact information becomes available, and when profiles should be removed or archived. Robust permission controls build trust that encourages participation.
Advanced Search and Filtering Capabilities
Interactive displays become valuable when users can quickly find relevant information rather than browsing chronologically through hundreds of profiles.
Multi-criteria search enables users to filter by career field or industry, college or university attended, graduation year or decade, geographic location of current work, specific employers or companies, skills or areas of expertise, and combinations of multiple criteria simultaneously.
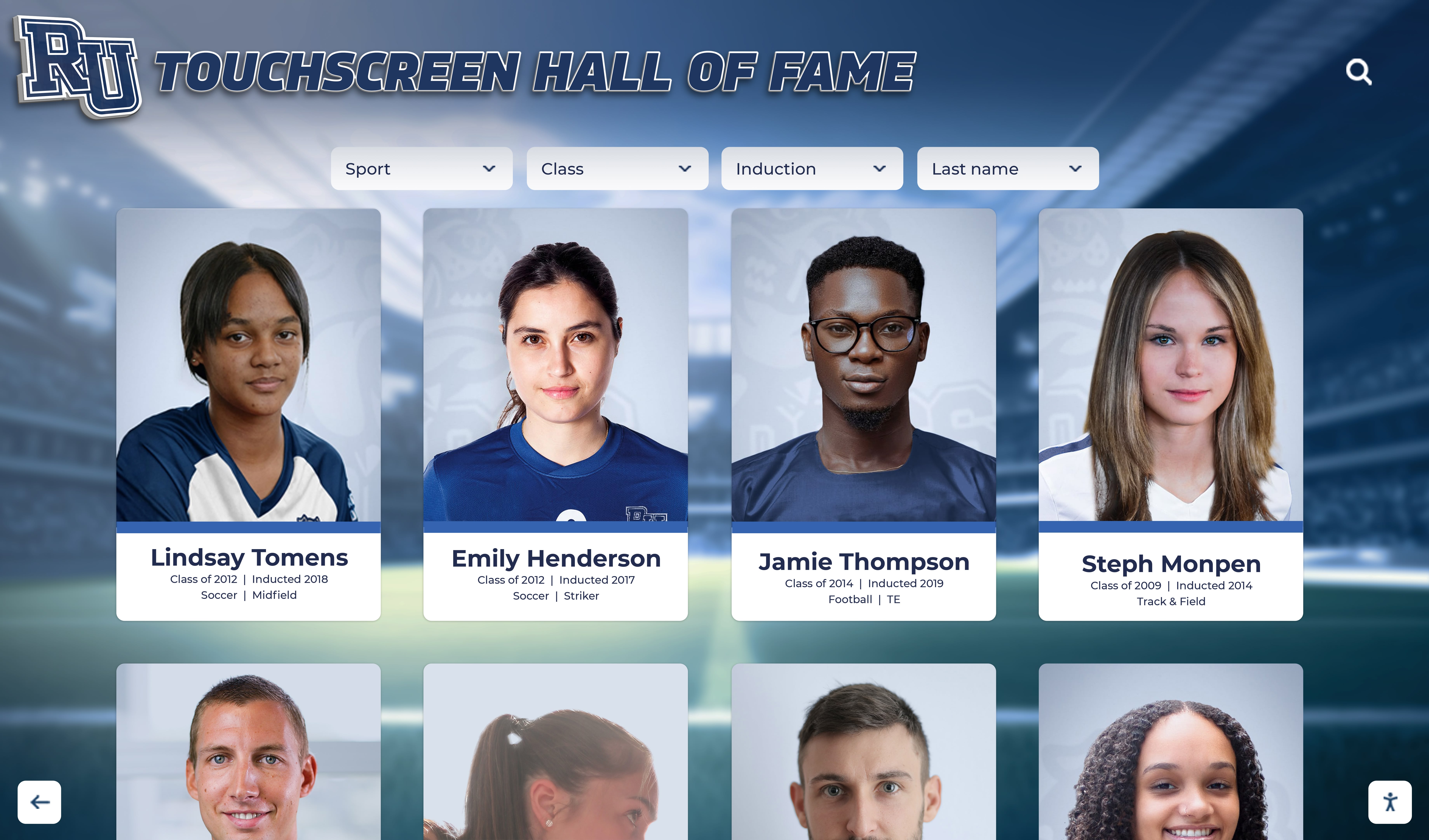
Intuitive interfaces make complex searches accessible. Students with limited search experience should easily discover alumni working in healthcare, alumni who attended specific universities, or alumni working in specific cities. Well-designed filtering presents options clearly and provides helpful categorization that guides exploration.
Saved searches and favorites allow users to bookmark relevant profiles, save search criteria for future use, create customized collections for classroom use, and return to interesting profiles without remembering search paths. These features support deeper engagement than single-session browsing allows.
Analytics tracking search patterns provides valuable insight into student interests, popular career fields, most-viewed profiles, and seasonal usage patterns. This data helps schools understand career guidance needs and identify where additional resources or programming might prove valuable.
Rich Multimedia Content Support
Text-only career information limits engagement and understanding. Multimedia capabilities create richer, more compelling career stories.
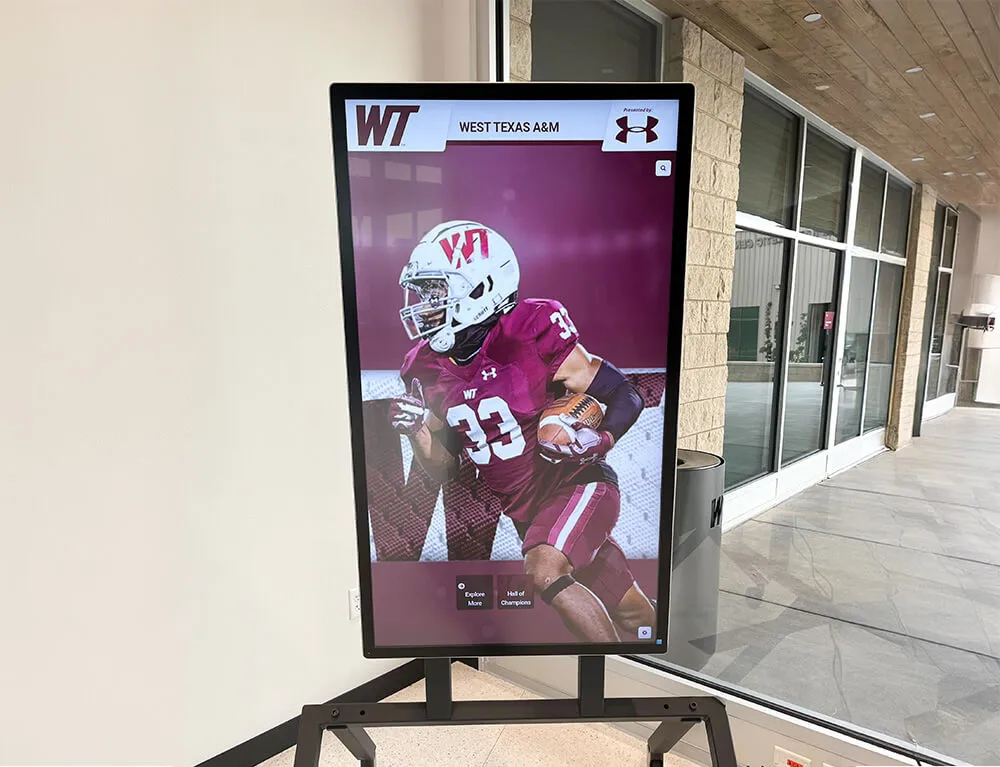
Professional photography presents alumni as successful professionals, creating aspirational images students can envision themselves resembling eventually. High-quality portraits, workplace photos, and activity images bring career descriptions to life visually.
Video integration proves particularly powerful. Short interview clips where alumni discuss their work, reflect on their educational preparation, offer advice to current students, and share career journey stories create authentic voices that resonate more deeply than written profiles. Video content significantly increases engagement duration and emotional impact.
Career journey timelines visualize progression from graduation through career milestones, showing how professionals move between positions, advance within organizations, or transition between fields. These visual narratives help students understand that careers develop over time through strategic choices rather than appearing fully formed immediately after graduation.
Document and media galleries can showcase work samples, publications, patents, project photos, awards, or other tangible evidence of professional accomplishment. This documentation provides credibility while giving students concrete examples of professional output in various fields.
Social Connectivity and Mentorship Features
Modern career pathways boards facilitate connections between alumni and current students rather than functioning purely as information displays.
Integrated messaging or contact request features allow students to reach out to alumni for informational interviews, job shadowing opportunities, advice about career paths, or mentorship relationships. Structured request forms help students craft appropriate messages while protecting alumni privacy by not exposing personal contact information publicly.
Mentorship program integration connects career displays with formal mentoring initiatives. Students exploring specific career fields can see which alumni volunteer as mentors, review mentor profiles including availability and preferred topics, and submit mentorship requests through integrated systems that track relationships and facilitate ongoing communication.
Social media connections enable students to follow alumni on professional platforms, view additional career content alumni share publicly, participate in broader alumni networks, and build professional relationships that extend beyond school-mediated interaction.
Alumni-student event coordination uses career data to facilitate targeted outreach. Schools can identify alumni in specific fields for career panels, alumni willing to host job shadows or internships, professionals located near campus who can engage more easily, and graduates with particular expertise relevant to classroom topics or student projects. Strategies for engaging with your local community demonstrate effective approaches for building these connections.
Implementation Strategies for Maximum Impact
Successful career pathways programs require thoughtful planning addressing technical, content, and cultural dimensions.
Assessment and Planning Phase
Begin by understanding current state and defining specific objectives.
Stakeholder Input Collection: Survey students about career interests and information needs. Interview teachers about how career information might support instruction. Consult counselors about college and career guidance challenges. Engage alumni about willingness to participate and preferred recognition approaches.
Existing Resource Audit: Inventory current career information—what data exists, where it’s stored, how current it is, what gaps require filling. Review existing alumni engagement programs and identify opportunities to integrate career recognition. Assess current recognition systems and evaluate whether career pathways can leverage existing infrastructure.
Goal Definition: Establish clear objectives that career pathways should accomplish. Goals might include increasing student college-going rates, improving career planning engagement, strengthening alumni connections, demonstrating program outcomes for accreditation, or supporting specific recruitment priorities. Clear objectives guide implementation decisions and enable later effectiveness assessment.
Resource Allocation: Identify budgets for technology platforms, content development time, ongoing maintenance staffing, professional development, and promotion activities. Realistic resource planning prevents implementation failures when enthusiasm exceeds capacity.
Technology Platform Selection
Choose systems offering capabilities aligned with your specific needs and technical environment.
Evaluate Purpose-Built Solutions: Platforms designed specifically for educational career recognition typically provide better feature alignment, easier implementation, superior support, and more cost-effective ownership than custom development or general-purpose tools. Solutions like Rocket Alumni Solutions offer comprehensive capabilities specifically designed for schools.
Consider Integration Requirements: Assess how career systems will connect with student information systems, alumni databases, website platforms, authentication systems, and analytics tools. Strong integration capabilities reduce duplicate data entry and enable more sophisticated functionality.
Evaluate Scalability: Ensure platforms accommodate growth as career information expands, support multiple displays across campus if desired, enable both physical and web-based access, and provide performance that remains responsive as content volume increases.
Assess Support and Training: Understand vendor support models, available training resources, implementation assistance, ongoing update mechanisms, and long-term viability. Educational institutions require partners committed to sustained relationships rather than one-time sales.
Content Development and Alumni Outreach
Building comprehensive career pathways databases requires systematic approaches to alumni outreach and information collection.
Phased Outreach Strategy: Begin with recent graduates whose contact information is current and who likely remember the institution fondly. Expand systematically to older alumni classes using reunion events, targeted mailings, social media campaigns, and phone outreach. Prioritize depth over breadth initially—starting with 50-100 detailed, compelling profiles proves more effective than 500 minimal listings.

Compelling Participation Messaging: Communicate clearly why alumni participation matters—inspiring current students, demonstrating program effectiveness, preserving institutional history, and connecting alumni with each other. Emphasize that participation requires reasonable time commitment with flexible information sharing based on comfort levels.
Multiple Submission Channels: Provide varied ways to submit information—online forms, email templates, phone interviews, in-person data collection at events. Different alumni prefer different communication methods, so multiple channels increase participation rates.
Ongoing Update Processes: Establish systematic approaches for maintaining currency—annual update requests, social media monitoring for career changes, leveraging LinkedIn data where permitted, and encouraging alumni to update their own profiles through secure portals.
Privacy and Permission Management: Develop clear policies about what information gets shared publicly, how alumni can modify permissions, procedures for removing information upon request, and compliance with data protection regulations. Transparent privacy practices build trust and encourage participation.
Strategic Display Placement and Integration
Physical and virtual locations significantly impact engagement and effectiveness.
High-Traffic Physical Locations: Position displays where students naturally gather—main hallways, cafeterias, career counseling areas, college prep classrooms, or library spaces. Multiple locations create repeated exposure reinforcing career awareness.
Classroom Integration: Enable teachers to access career pathways during relevant lessons—science teachers highlighting STEM careers, English teachers featuring writing and communication professionals, social studies teachers showcasing government and nonprofit careers. This curricular integration makes career exploration educational rather than extracurricular.
Website and Online Access: Ensure career pathways appear prominently on school websites accessible to students, families, and alumni globally. Mobile-optimized displays reach students researching on smartphones and alumni browsing from diverse locations.
Event-Based Activation: Feature career displays prominently during recruitment events, alumni weekends, college fairs, career days, and parent information sessions. Strategic timing increases visibility when audiences are most receptive to career information.
Creating Engaging Career Pathway Content
The quality and presentation of career information determines whether displays inspire and inform or become ignored background.
Compelling Career Narratives
Transform basic employment data into engaging stories that students connect with emotionally and intellectually.
Journey-Focused Storytelling: Rather than listing credentials and positions, tell stories about career evolution—how interests emerged, key decisions made, challenges overcome, skills developed, and opportunities pursued. These narrative arcs provide roadmaps students can learn from rather than static endpoints they might aspire to but not understand how to reach.
Authentic Voice and Perspective: Feature alumni reflections in their own words rather than institutional descriptions. First-person narratives create authenticity and personality that help students relate to alumni as real people rather than distant success stories.
Diverse Path Recognition: Showcase non-linear careers including position changes, industry transitions, entrepreneurial ventures, career breaks for family or education, and various definitions of success. This diversity demonstrates that multiple paths lead to fulfillment and that early career decisions don’t irrevocably determine lifelong trajectories.
Connection to School Experience: Explicitly link current educational opportunities to career preparation. When alumni mention that debate prepared them for law, that calculus proved essential in engineering, or that art electives developed creativity valued in marketing, students understand concrete connections between present activities and future possibilities.
Visual Design and Professional Presentation
Aesthetic quality affects credibility and engagement significantly.
Professional Photography Standards: Use high-resolution images with good lighting, appropriate backgrounds, and consistent styling. Poor-quality photos undermine messages about professional success and create amateurish impressions that reduce engagement.
Consistent Design Language: Develop visual templates ensuring consistent presentation across profiles—standardized layouts, typography, color schemes, and organization. Consistency creates professional polish while making information easier to scan and compare.
Information Hierarchy: Structure content with clear priorities—most important information prominent, supporting details accessible but not overwhelming, white space preventing cluttered appearances. Well-organized information invites engagement while overwhelming density discourages exploration.
Accessibility Considerations: Ensure displays meet accessibility standards with appropriate contrast ratios, readable font sizes, alternative text for images, keyboard navigation support, and screen reader compatibility. Inclusive design serves all students while demonstrating institutional values.
Multimedia Integration
Rich media transforms career information from abstract descriptions into tangible understanding.
Video Interviews and Testimonials: Short clips where alumni discuss their work, share advice, reflect on preparation, or demonstrate aspects of their careers provide authentic voices and faces that text cannot match. Video significantly increases emotional engagement and memory retention.
Career Environment Imagery: Photos or videos showing alumni in work environments—hospitals, construction sites, laboratories, offices, studios, classrooms—help students visualize career contexts. These environmental images make careers feel real rather than abstract.
Work Sample Showcases: Where appropriate, display examples of alumni professional output—architectural designs, published research, software interfaces, performances, business plans. Tangible work products demonstrate what professionals actually produce and provide inspiration for student aspiration.
Measuring Success and Optimizing Programs
Effective career pathways programs establish metrics, collect data, and continuously improve based on evidence.
Key Performance Indicators
Define specific measures tracking whether career displays achieve intended objectives.
Engagement Metrics: Monitor display interaction frequency and duration, search patterns and popular filters, most-viewed profiles and career fields, time-of-day and seasonal usage patterns, and repeat visitor rates. Analytics reveal what content resonates and where students focus attention. Resources on measuring digital hall of fame success provide frameworks for comprehensive assessment.
Student Outcome Indicators: Track changes in college application patterns, career exploration activity participation, student-reported career planning confidence, and post-graduation success metrics. While multiple factors influence these outcomes, improvement coinciding with career pathway implementation suggests program impact.
Alumni Engagement Measures: Monitor alumni participation rates in profile submission, update frequency and information currency, mentorship program involvement, event attendance changes, and satisfaction with recognition approaches. Strong alumni engagement indicates that recognition efforts resonate with graduates and create valued relationships.
Institutional Impact Metrics: Assess recruitment effectiveness through prospective family feedback, program value documentation for external reviews, media coverage and community awareness, and satisfaction among internal stakeholders including teachers, counselors, and administrators.
Continuous Improvement Processes
Use data and feedback to refine career pathways programs over time.
Regular Content Audits: Schedule quarterly reviews checking information currency, identifying outdated profiles requiring updates, discovering gaps in career field coverage or demographic representation, and assessing whether content aligns with current student interests and institutional priorities.
User Feedback Collection: Survey students about career information needs and display effectiveness. Interview alumni about recognition experiences and participation barriers. Consult staff about how displays support their work with students. Systematic feedback reveals improvement opportunities that metrics alone might miss.
Feature Utilization Analysis: Examine which display capabilities students actually use versus features that seemed valuable during planning but see limited engagement. Focus development resources on high-impact features while simplifying or removing unused complexity.
Comparative Effectiveness Research: When possible, compare student outcomes between those who engage significantly with career displays and those who don’t. While correlation doesn’t prove causation, patterns suggesting relationship between career pathway usage and improved outcomes justify continued investment.
Advanced Applications and Future Trends
Forward-thinking institutions explore emerging approaches that extend career pathway concepts.
Artificial Intelligence and Personalization
AI technologies enable customized career guidance experiences tailored to individual student profiles, interests, and academic performance.
Intelligent recommendation systems might suggest alumni for students to explore based on interest inventories, academic profiles, or stated career considerations. These personalized suggestions help students discover relevant examples they might not find through random browsing.
Chatbot interfaces could answer student career questions by pulling information from alumni databases—“What do people who majored in biology do?” or “Where do graduates work in Chicago?” Natural language interaction makes career exploration more accessible than complex search interfaces require.
Predictive analytics might identify students at risk of disengagement and proactively suggest career examples aligned with their demonstrated interests and strengths, using positive career futures to maintain educational motivation.
Virtual and Augmented Reality Integration
Immersive technologies create experiential career exploration beyond static profiles.
Virtual reality career experiences might allow students to “visit” alumni workplaces virtually, experiencing day-in-the-life simulations of various professions, interacting with virtual work environments, and gaining visceral understanding of career contexts that text and photos cannot fully convey.
Augmented reality applications could overlay career information on physical spaces—pointing smartphones at athletic facilities might show professional athletes who trained there, viewing science labs could highlight researchers who conducted early experiments in those spaces.
Integration with Learning Management Systems
Deep integration between career pathways and educational platforms creates seamless connections between learning and career preparation.
Career-connected assignments might require students to interview alumni, analyze career pathways in fields they’re studying, or complete research projects incorporating real-world professional context provided through alumni connections.
Automated career modules integrated into courses could present relevant alumni examples during appropriate curriculum moments—featuring healthcare professionals during anatomy units, showcasing engineers during physics lessons, highlighting journalists during media literacy instruction.
Digital portfolios connecting student work to professional expectations help students understand quality standards in various fields and document their developing capabilities in formats valued by colleges and employers.
Overcoming Common Implementation Challenges
Institutions launching career pathways programs typically encounter similar obstacles that proven strategies address.
Limited Alumni Contact Information
Many schools lack current contact information for significant portions of alumni populations, particularly older graduates or those who moved without notifying institutions.
Social Media Research: Platforms like LinkedIn, Facebook, and Instagram enable alumni discovery even without direct contact information. Searching class year groups, location-based communities, or employer networks often locates graduates who then provide direct contact preferences.
Class Representative Networks: Identify engaged alumni from each graduating class who maintain informal networks with classmates. These representatives can facilitate outreach, encourage participation, and help locate hard-to-find graduates.
Phased Approach Starting with Recent Graduates: Begin with the past 5-10 years of graduates whose information remains current and who likely remember the institution positively. Build database gradually rather than attempting comprehensive coverage immediately.
Community Partnerships: Local chambers of commerce, professional organizations, and employers may include alumni who never updated school contact information. Partnership enables alumni discovery through professional rather than personal networks.
Low Alumni Participation Rates
Even when contact information exists, many alumni don’t respond to participation requests or submit information.
Multiple Outreach Channels: Single email requests often go unnoticed. Combine email, social media messages, phone calls, postal mail, and in-person requests at events to increase touchpoints and reach alumni through preferred communication methods.
Simplified Submission Processes: Lengthy, complex forms discourage participation. Streamline information requests to essential fields, offer partial profiles when alumni won’t complete comprehensive forms, and enable incremental submission where alumni provide basic information initially and add details later.
Clear Value Propositions: Communicate specifically what participation accomplishes—inspiring students, demonstrating program value, connecting with current students as mentors, building professional networks with fellow alumni. Concrete benefits motivate participation more than vague appeals.
Recognition and Appreciation: Thank participating alumni publicly through newsletters, social media, or events. Acknowledgment demonstrates that contributions matter and encourages continued engagement and peer participation.
Resource Constraints for Ongoing Maintenance
Career pathways require sustained content management that competes with limited staff time and competing priorities.
Student Involvement: Engage students in research, outreach, content creation, and maintenance as learning experiences that develop research, communication, and project management skills while distributing workload.
Alumni Self-Service Portals: Enable alumni to update their own profiles through secure systems requiring only staff approval rather than data entry. This distributed model maintains currency with minimal administrative burden.
Volunteers and Service Organizations: Alumni association volunteers, parent groups, or community service organizations might adopt career pathways as ongoing service projects providing necessary labor for sustained maintenance.
Prioritized Updates: Establish tiered maintenance approaches—critical updates happen immediately, important updates quarterly, comprehensive reviews annually. Realistic expectations prevent paralysis from attempting perfection that resources cannot support.
Career Pathways Supporting Specific Institutional Goals
Different schools emphasize career pathways for distinct strategic purposes requiring tailored implementations.
College Preparation and Four-Year University Placement
Schools prioritizing four-year college enrollment emphasize pathways showing educational progression beyond high school.
Feature extensive college destination information including universities attended, majors pursued, graduate schools, and academic achievements. Create searchable databases enabling students to explore alumni at institutions they’re considering. Highlight diverse paths within college-going trajectories including transfers, major changes, and graduate education choices.
Connect educational choices to career outcomes by showing how specific majors, double majors, or graduate programs prepared alumni for eventual careers. This connection helps students understand that college serves as preparation for professional life rather than representing ultimate goal itself.
Career and Technical Education Outcomes
CTE programs demonstrate value through employment success in trained fields, industry credential attainment, and skill development leading to self-sufficient careers.
Showcase graduates working in skilled trades, healthcare technical roles, business occupations, and technical fields. Feature starting salaries, advancement potential, credential pathways, and ongoing skill development. Highlight graduates who become business owners, managers, or industry leaders demonstrating that CTE pathways offer advancement equivalent to four-year degree routes.
Document industry partnerships, apprenticeship opportunities, and employer relationships that connect students to career entry. Show alumni working at well-known employers or successful local businesses that students recognize and respect.
Supporting Underrepresented Student Populations
Career pathways prove particularly valuable for first-generation college students, underrepresented minorities, low-income students, and others who may lack family networks providing career guidance and role models.
Prioritize featuring alumni from similar backgrounds so students see that people like them succeed in professional careers. This representation matters tremendously for students who might not personally know professionals in many career fields.
Highlight non-traditional paths including community college transfers, adult learners, career changers, and those who overcame obstacles. These narratives demonstrate that multiple routes lead to success and that challenges don’t determine outcomes. Understanding student engagement strategies helps institutions support all students effectively.
Feature alumni who give back to communities, maintain cultural connections, or work in fields serving underrepresented populations. This recognition validates that success doesn’t require abandoning heritage or community but can support strengthening both.
Integrating Career Pathways With Comprehensive School Recognition
Career pathways function most effectively when integrated into broader recognition ecosystems celebrating diverse achievement types.
Schools implementing comprehensive digital recognition platforms can showcase academic achievements, athletic success, arts accomplishments, community service contributions, and career outcomes through unified systems. This integration creates complete pictures of student development from enrollment through professional life.
Unified platforms enable powerful connections—linking athletic achievements to sports careers, academic awards to research positions, performing arts recognition to entertainment industry success, and service projects to nonprofit sector careers. These connections help students understand how school experiences prepare for specific professional paths.
Conclusion: Career Pathways as Strategic Investment
Interactive career pathways boards represent far more than technology installations or alumni databases. They embody institutional commitments to student success extending beyond graduation, transparency about educational outcomes, and relationship maintenance with alumni who provide evidence of program effectiveness.
Schools implementing comprehensive career recognition discover multiple returns on investment: students develop clearer career goals and increased motivation, families gain confidence in educational choices through outcome evidence, alumni feel valued and increase engagement with institutions, and administrators obtain documentation demonstrating program effectiveness for accountability requirements.
Success requires commitment beyond initial implementation—ongoing alumni outreach, regular content updates, strategic promotion ensuring students actually engage with displays, and continuous improvement based on usage data and stakeholder feedback. Institutions treating career pathways as living programs rather than static installations achieve greatest impact.
Modern solutions from providers like Rocket Alumni Solutions deliver comprehensive capabilities specifically designed for educational career recognition. These platforms combine intuitive content management accessible to non-technical staff, professional display options for physical and web-based access, advanced search and filtering enabling meaningful exploration, rich multimedia support creating engaging content, and integrated analytics tracking engagement and effectiveness.
Every student deserves to envision possibilities for their futures, every graduate’s success deserves acknowledgment demonstrating institutional impact, and every school merits tools showcasing the outcomes that justify continued community support. Interactive career pathways boards provide the comprehensive recognition infrastructure enabling these goals while supporting college and career readiness that prepares students for meaningful professional lives.
Ready to showcase your students’ career success? Explore how interactive career pathways boards can transform your college and career guidance, strengthen alumni relationships, and demonstrate the real-world outcomes that matter to all stakeholders. From college commitments to professional achievements, comprehensive career recognition tells the complete story of educational impact that numbers alone cannot capture.