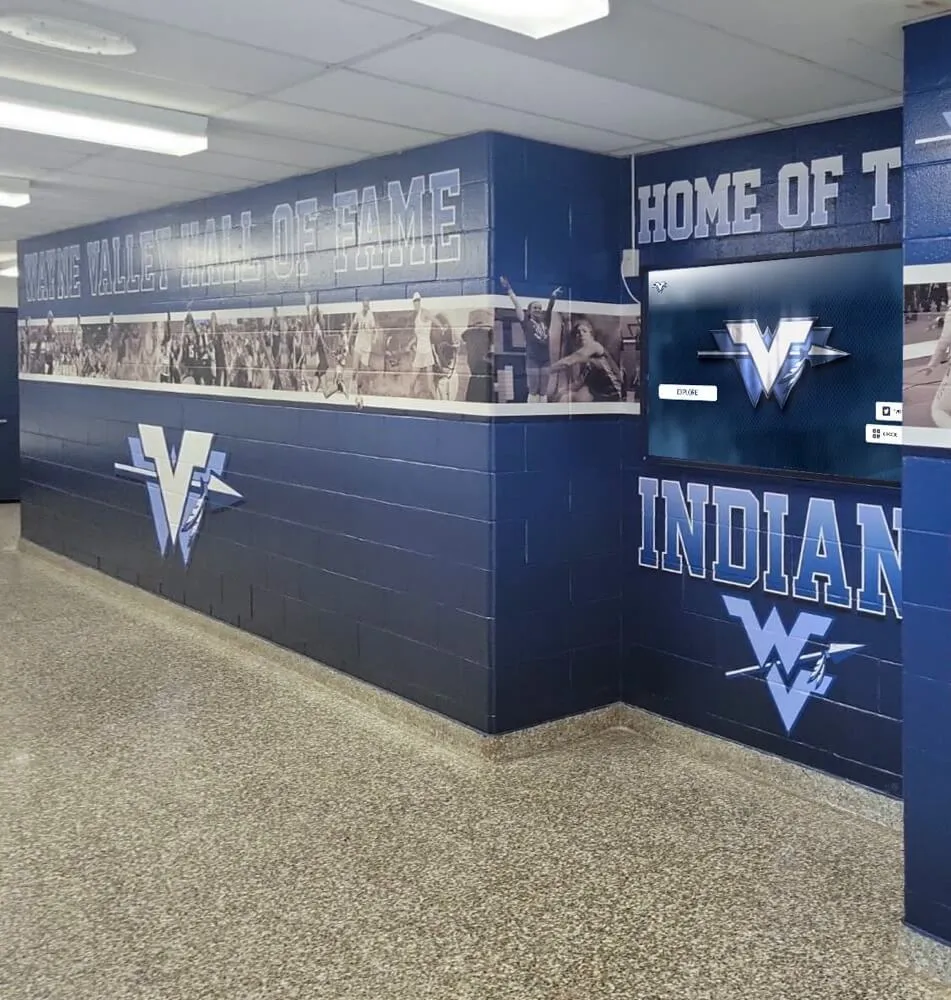
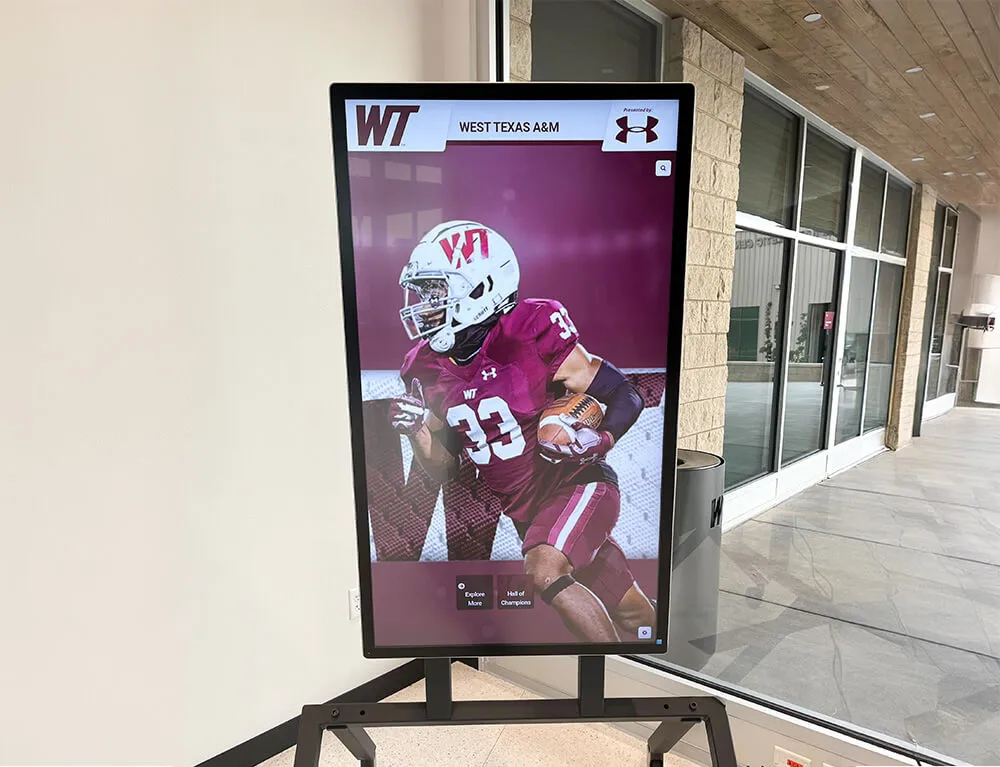
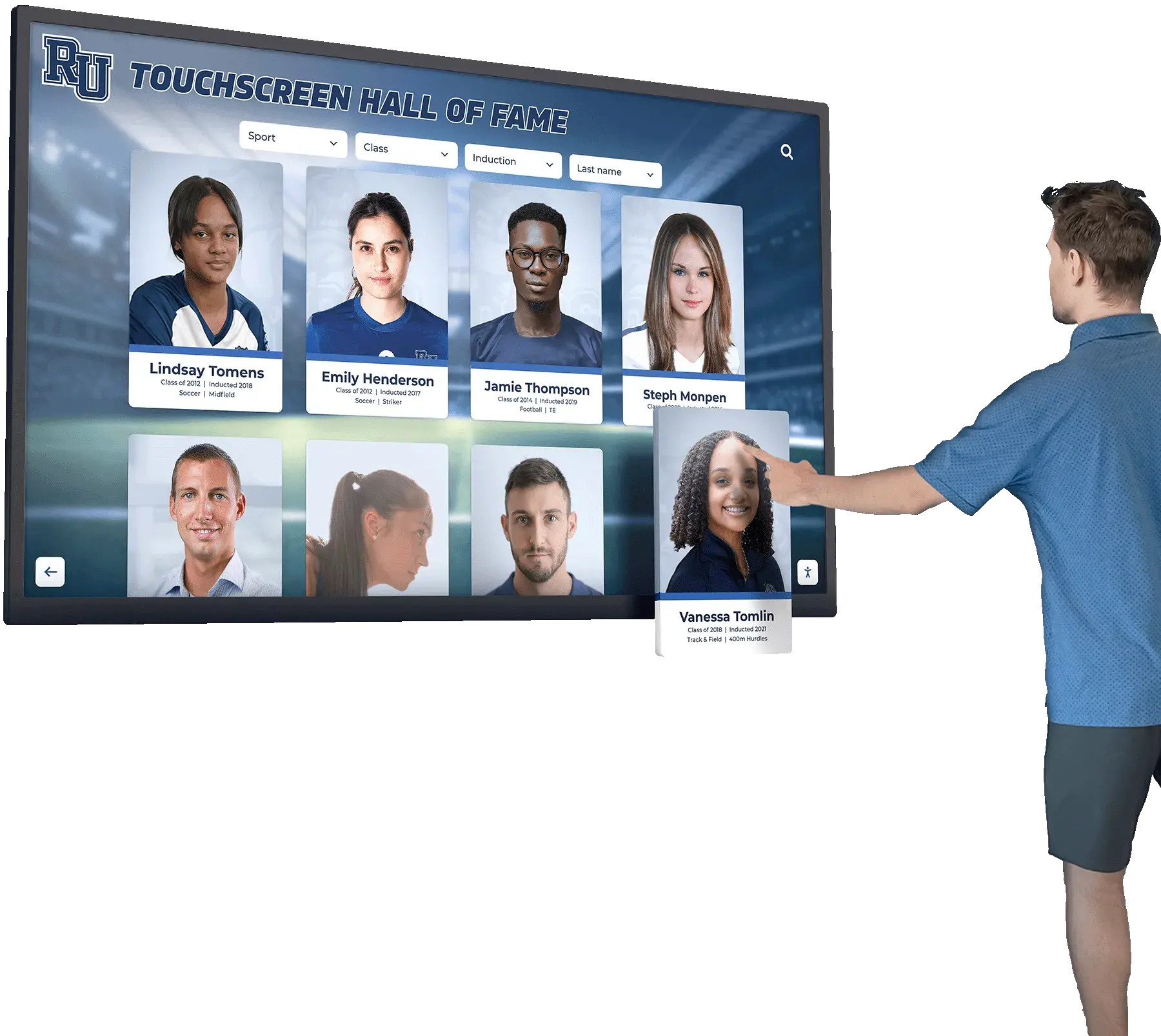
Every school year, talented students across the country design remarkable STEM projects and achieve outstanding results in engineering competitions—creating innovative solutions to real-world problems, building sophisticated robots that compete nationally, conducting groundbreaking research, and demonstrating the kind of creative problem-solving that defines tomorrow’s scientific and technological leaders. These student achievements represent countless hours of design work, iterative prototyping, scientific methodology, collaborative teamwork, and the dedication that transforms concepts into functioning solutions.
Yet despite their significance, many STEM project accomplishments and engineering competition successes receive minimal lasting recognition compared to athletic achievements. A robotics team winning a state championship earns brief announcements before being forgotten, while football championships receive permanent trophy display and ongoing celebration. Science fair winners get certificates tucked away in drawers, while all-conference athletes see their names permanently displayed in school hallways. Outstanding engineering design projects gather dust in storage rooms after judging concludes, never receiving the ongoing visibility that could inspire future innovators.
Why Recognizing STEM Projects and Engineering Excellence Matters
Student STEM projects and engineering competition achievements deserve prominent, permanent recognition that celebrates their creativity, validates their design thinking, and inspires younger students to pursue similar innovation. When schools systematically showcase these accomplishments through comprehensive displays, they build cultures where scientific inquiry and engineering excellence receive acknowledgment equal to any other achievement. Solutions like Rocket Alumni Solutions enable schools to create engaging recognition programs that preserve STEM project documentation, competition successes, and design portfolios permanently while inspiring the next generation of innovators.
The Recognition Gap for Student STEM Innovation
Walk through most high school facilities and an uncomfortable disparity becomes immediately apparent. Athletic trophy cases span entire hallways, championship banners hang prominently in gymnasiums, record boards celebrate decades of competitive excellence, and halls of fame feature legendary athletes with comprehensive career documentation. These visible celebrations serve important purposes—honoring achievement, motivating current participants, building program pride, and creating lasting institutional memory.
Yet walk through those same schools’ science labs, engineering classrooms, or technology spaces, and recognition often consists of temporary bulletin board displays, brief announcements quickly forgotten, participation certificates with no permanent visibility, and project work dismantled or discarded shortly after competitions conclude. This recognition imbalance communicates unintended but powerful messages about which accomplishments schools genuinely value, despite mission statements emphasizing academic excellence and 21st-century skill development.
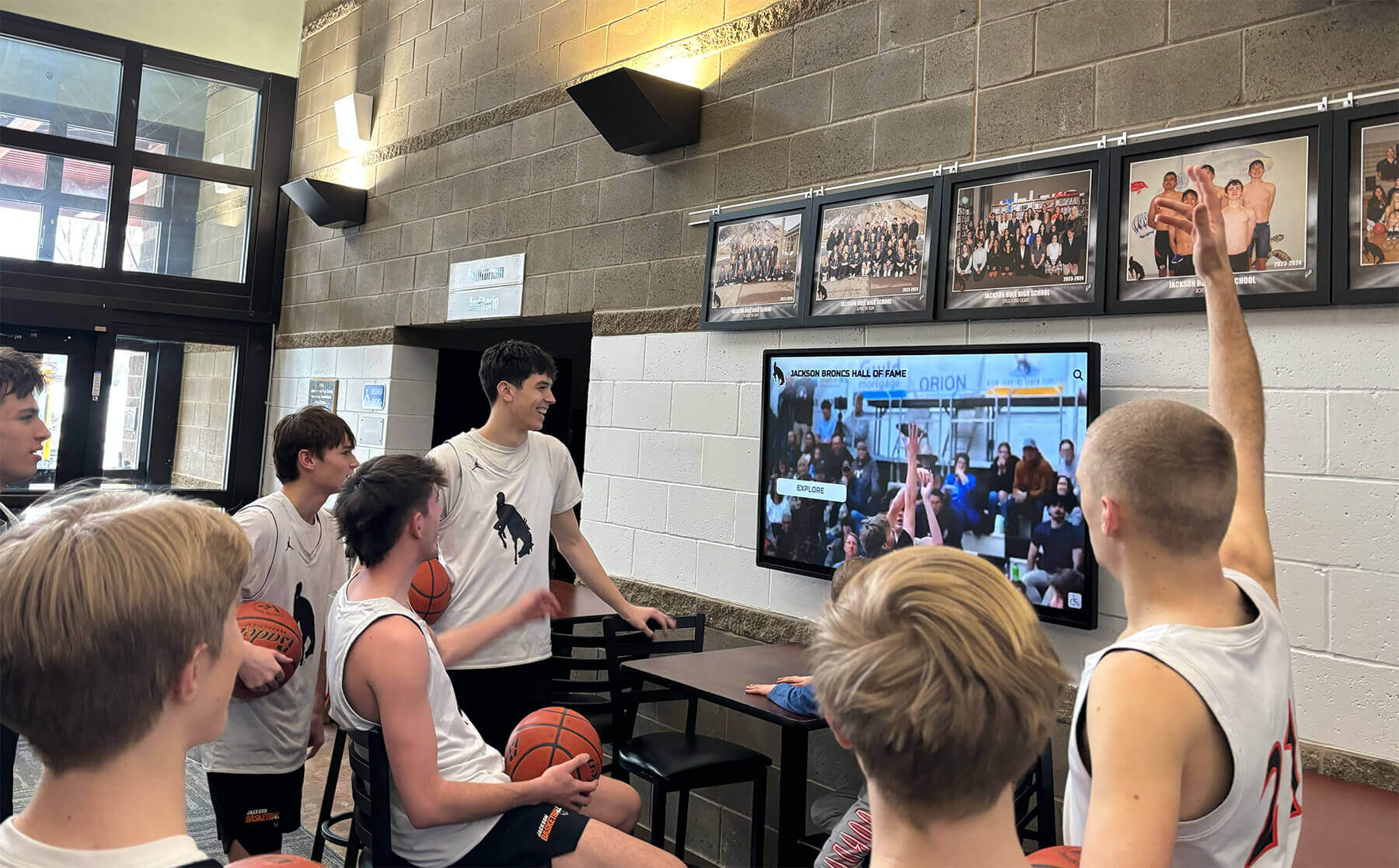

Understanding the Consequences of Inadequate STEM Recognition
When student STEM projects and engineering competition successes go largely unrecognized, several negative outcomes emerge that undermine program goals and student motivation:
Reduced STEM Participation: Students naturally gravitate toward activities where they observe peers receiving meaningful recognition and celebration. Visible athletic recognition attracts participants demonstrating institutional value, while absent STEM recognition suggests these accomplishments merit less attention. This disparity directly impacts enrollment in optional STEM courses, robotics team participation, science fair involvement, and engineering club membership.
Lost Role Models and Inspiration: Younger students exploring potential interests desperately need visible examples of peers succeeding in various fields. Athletic walls of fame provide these role models in abundance—students can identify athletes who preceded them, understand achievement pathways, and envision themselves following similar trajectories. Without equivalent STEM recognition, students may never realize that peers with similar backgrounds excel in science and engineering fields.
Undervalued Student Effort: Successful STEM projects require sustained intellectual effort, technical skill development, and dedicated persistence comparable to athletic training. Students spend countless hours researching problems, designing solutions, building prototypes, testing iterations, documenting processes, and preparing presentations. When this substantial investment goes unrecognized while athletic training receives prominent celebration, students and families question whether academic STEM pursuits receive appropriate institutional value.
Weakened Innovation Culture: Schools aiming to strengthen STEM programs discover that recognition systems powerfully signal what institutions genuinely value beyond published mission statements. Prominent STEM recognition creates environments where innovation, design thinking, and scientific inquiry feel central to school identity rather than secondary interests pursued by small groups without broader visibility or appreciation.
According to the National Science Foundation, the United States faces critical shortages of STEM-qualified professionals across industries from engineering and technology to healthcare and environmental science. Schools play vital roles in cultivating interest and persistence in STEM fields, and recognition programs represent powerful tools for building cultures where scientific and engineering excellence receives celebration matching its importance to students’ futures and national workforce needs.
Defining STEM Project Excellence Worth Celebrating
Effective recognition programs celebrate diverse forms of STEM innovation and engineering achievement rather than focusing exclusively on major competition victories or single project types. Comprehensive approaches acknowledge varied accomplishment forms, creating multiple pathways ensuring students with different strengths experience meaningful recognition.
Individual STEM Project Recognition
Science Fair Achievement and Research Excellence
Science fairs represent foundational opportunities for students to conduct independent research, apply scientific methodology, and communicate findings. Recognition should celebrate multiple dimensions of science fair participation:
- School-level science fair winners demonstrating strong project design and execution
- Regional science fair qualifiers advancing beyond initial competition rounds
- State science fair placements showing excellence among broader competitive fields
- International Science and Engineering Fair (ISEF) participation and awards
- Specialized science fair categories including biology, chemistry, physics, environmental science, and engineering
- Research quality regardless of placement when projects demonstrate exceptional methodology
- Long-term research projects spanning multiple years showing sustained investigation
Schools should document complete project details including research questions, methodologies employed, findings and conclusions, practical applications, photographs of project displays, and student reflections about their research process. Classroom project recognition programs demonstrate how comprehensive documentation preserves achievement details that make recognition meaningful and educational for viewers.
Engineering Design and Innovation Competitions
Engineering competitions challenge students to design solutions addressing real-world problems through systematic design processes, requiring creativity, technical knowledge, and iterative development:
- FIRST Robotics Competition team achievements and robot design excellence
- VEX Robotics competitions at local, state, and national levels
- Science Olympiad engineering events including bridges, vehicles, and devices
- National Engineering Design Challenge participation and recognition
- Regional and state engineering competitions sponsored by professional organizations
- Patent applications for student inventions demonstrating genuine innovation
- Engineering portfolio competitions showcasing design thinking processes
Recognition should include robot photographs and videos demonstrating capabilities, engineering notebooks documenting design iterations, technical drawings and CAD models showing design sophistication, team photographs celebrating collaborative achievement, competition placement and award documentation, and descriptions explaining engineering principles applied. Digital recognition platforms enable showcasing dynamic content like robot performance videos impossible to display through traditional static recognition approaches.

Coding and Computer Science Competitions
As technology increasingly shapes every industry, student coding accomplishments and computer science competition success deserve prominent recognition:
- Programming competition placements including USA Computing Olympiad
- Hackathon participation and project awards
- Congressional App Challenge winners and state finalists
- Cybersecurity competition success including CyberPatriot
- Game development competition entries and recognition
- Website and application development projects addressing real needs
- Open source contributions and collaborative coding projects
Document project functionality through screenshots and demonstrations, technical documentation explaining code architecture, problem statements showing what applications solve, user testimonials when projects serve real communities, and student reflections about development challenges overcome. Many students pursuing computer science careers point to early coding competition experiences as pivotal moments—recognition preserving these achievements validates their importance.
Mathematics Competitions and Problem-Solving Excellence
Mathematical competitions demonstrate analytical thinking, problem-solving prowess, and intellectual persistence worthy of celebration:
- MATHCOUNTS chapter, state, and national competition results
- American Mathematics Competitions performance and advancement
- Math Olympiad participation and problem-solving achievement
- State and regional mathematics competitions
- Math modeling competitions applying mathematics to real-world problems
- Perfect scores on advanced mathematics assessments
- Sustained excellence in mathematics coursework and advanced sequences
Mathematics achievement often receives less visible recognition than applied STEM fields, yet mathematical thinking underlies all scientific and engineering accomplishment. Comprehensive STEM recognition ensures mathematical excellence receives acknowledgment equal to projects producing physical artifacts.
Team-Based STEM Achievement
Beyond individual recognition, successful STEM programs emphasize collaborative achievement reflecting how professional science and engineering work actually occurs:
Robotics Team Success and Design Excellence
Robotics programs combine mechanical engineering, electrical systems, programming, and strategic thinking through collaborative team competition:
- FIRST Robotics Competition regional championships and world championship participation
- VEX Robotics state and national tournament success
- Team awards recognizing design excellence, innovation, and engineering documentation
- Sustained program success across multiple competition seasons
- Rookie year achievements by newly-formed teams
- Engineering notebook awards and design process documentation
- Gracious professionalism and mentor/community impact recognition
Robotics teams often include 20-30 students fulfilling specialized roles from mechanical design and electrical engineering to programming, business planning, and community outreach. Comprehensive recognition acknowledges all contributors rather than only visible student operators, celebrating the complete team effort required for competitive success.
Science Bowl and Quiz Bowl Teams
Academic competitions testing scientific knowledge, quick thinking, and collaborative problem-solving demonstrate intellectual excellence:
- Regional Science Bowl championships and national competition participation
- Physics, chemistry, and biology specialized bowl competitions
- Science Olympiad team placements and event medals
- State and national academic competition advancement
- Sustained team success across multiple competition years
Quiz bowl formats emphasize quick recall and collaborative problem-solving distinct from individual research projects, representing different but equally valuable forms of STEM excellence worthy of recognition.

Collaborative Research and Group Engineering Projects
Some of the most impactful student work emerges from sustained collaborative efforts:
- Multi-student research teams conducting comprehensive investigations
- Community-based research projects addressing local issues
- School-industry partnership projects with authentic client relationships
- Grant-funded student research receiving external validation
- Cross-curricular projects integrating STEM with other disciplines
- Environmental monitoring and long-term data collection initiatives
Collaborative project recognition should clearly identify all contributors, specify individual roles and responsibilities, document team collaboration processes, and celebrate collective achievement alongside individual contributions. This approach models professional scientific and engineering practice where credit appropriately flows to teams rather than only individual leaders.
Essential Components of Effective STEM Recognition Programs
Successful recognition programs share fundamental characteristics distinguishing truly motivational systems from token acknowledgment generating minimal impact on culture or participation.
Comprehensive Documentation and Project Archives
Detailed Achievement Records
STEM recognition becomes meaningful when viewers understand what accomplishments actually represent, requiring thorough documentation beyond simple names and dates:
For individual students, include student name and graduation year, project titles with descriptive explanations, competition names and placement levels, achievement dates and circumstances, photographs showing projects and students, current pursuits for alumni demonstrating how STEM interests developed into careers, and detailed project descriptions explaining problems addressed and solutions developed.
For teams, document complete team rosters acknowledging all contributors, team photographs showing collaborative nature, robot or project photographs and videos, technical documentation including engineering notebooks, competition performance statistics and progression, coach and mentor recognition, and multi-year team histories showing sustained excellence.
Context matters tremendously—viewers unfamiliar with specific competitions need information about competition size and selectivity, achievement rarity and historical significance, advancement pathways and qualification requirements, technical challenges overcome, and real-world applications of projects and innovations. Academic recognition programs that invest in rich documentation create far more engaging and educational displays than minimal name-and-date listings.
Visual Documentation Best Practices
High-quality visual content brings STEM achievements to life in ways text alone cannot match:
- Project Display Photos: Capture complete science fair displays showing visual presentation quality and project scope
- Action Shots: Photograph students actively engaged with projects, robots competing, or presenting to judges
- Process Documentation: Include behind-the-scenes images showing project development, prototyping, and iteration
- Award Ceremony Photos: Preserve memorable moments when students receive recognition at competitions
- Detail Images: Showcase specific technical elements demonstrating engineering sophistication or innovative design features
- Team Photos: Capture complete teams celebrating successes together
Professional-quality photography dramatically enhances recognition impact while demonstrating institutional commitment to comprehensive celebration. Many schools designate parent volunteers or student photographers specifically to document STEM competition events ensuring adequate visual assets for recognition displays.
Accessible Organization and Intuitive Navigation
Logical Categorization Systems
Organize STEM recognition enabling visitors to easily find content matching their interests:
- By Competition Type: Separate sections for science fairs, robotics competitions, mathematics contests, coding challenges, engineering design competitions
- By Discipline: Categories for biology, chemistry, physics, mathematics, computer science, engineering, environmental science
- By Achievement Level: Tiers including national recognition, state competition success, regional achievement, school-level excellence
- By Year: Chronological organization showing program development over time
- By Team or Individual: Separate sections acknowledging collaborative versus individual achievement
Thoughtful organization prevents overwhelming visitors with undifferentiated information while helping specific audiences quickly locate relevant content. Students interested in robotics can immediately find relevant achievements, prospective families can assess program strengths across disciplines, and alumni can locate their own historical accomplishments.
Search and Filter Capabilities
For digital recognition platforms, robust search functionality dramatically enhances accessibility:
- Name search locating specific students across all competitions and years
- Keyword search finding projects addressing particular topics or technologies
- Date range filtering showing achievements during specific time periods
- Competition type filtering isolating specific event categories
- Combined filters enabling precise queries like “robotics teams 2020-2025 with state championship appearances”
Interactive exploration transforms passive viewing into active engagement where students discover role models with interests matching their own aspirations. AP Scholar recognition programs demonstrate how searchable databases enable personalized recognition experiences impossible with static displays.
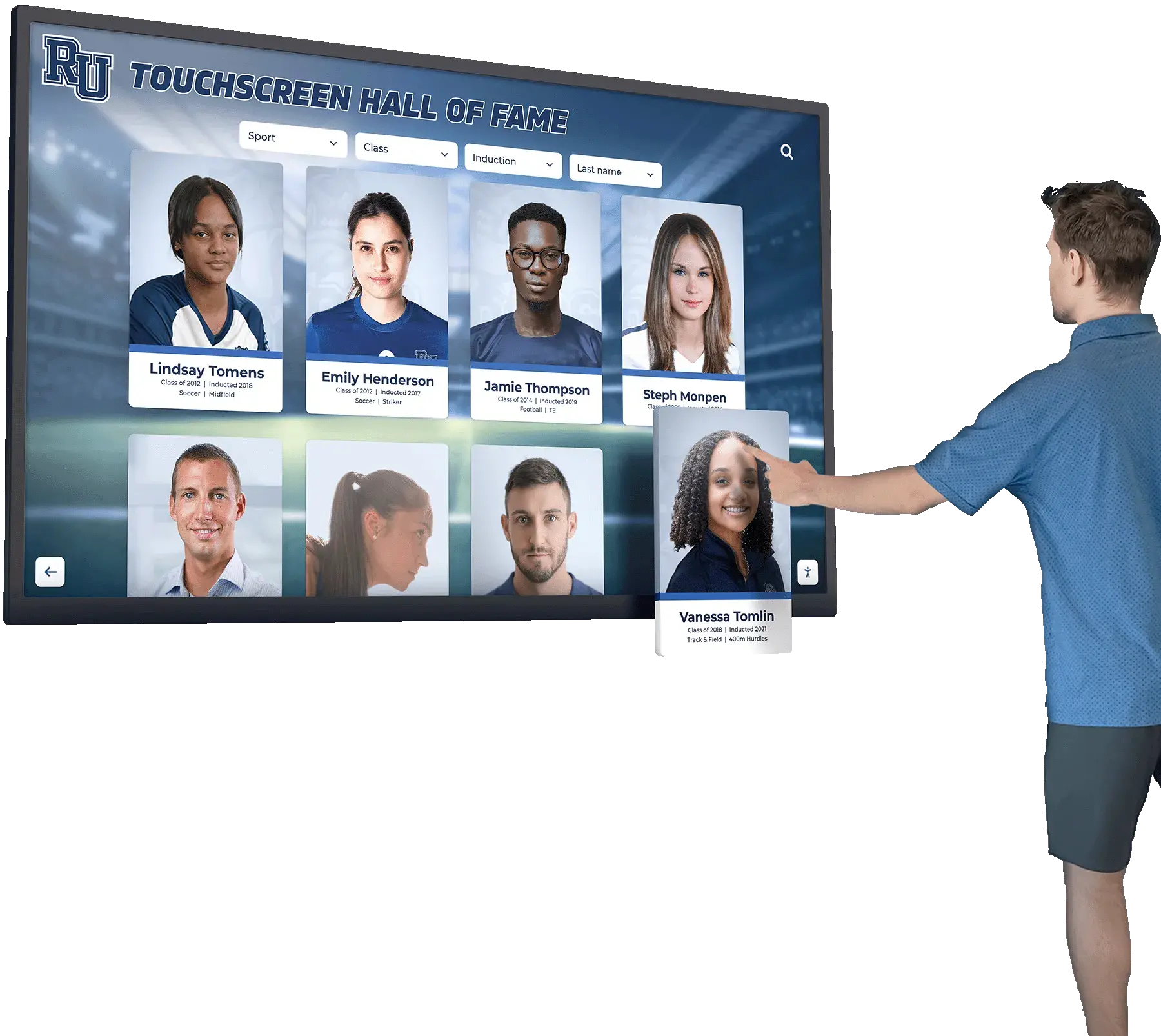
Educational Value Beyond Simple Celebration
Learning Opportunities Through Recognition
Effective recognition displays educate viewers beyond simply listing achievements:
- Scientific Concept Explanations: Brief overviews explaining scientific principles investigated in research projects
- Engineering Design Process Documentation: Illustrations showing how students progressed from problem identification through prototyping to final solutions
- Competition Format Descriptions: Explanations helping viewers understand what specific competitions involve and what success requires
- Technical Vocabulary Definitions: Accessible language making specialized STEM content understandable to general audiences
- Career Connection Information: Links between student projects and professional careers in related fields
- Next Steps for Interested Students: Resources and guidance for students wanting to pursue similar paths
Educational elements transform recognition walls from backward-looking celebration into forward-looking inspiration actively encouraging STEM engagement. When middle school students exploring interests view high school science fair projects with accessible explanations, they can envision themselves conducting similar research, making recognition instrumental in recruitment and pathway development.
Role Model Accessibility and Inspiration
Help diverse students envision themselves in STEM fields through intentional recognition design:
- Demographic Diversity: Ensure recognition highlights achievements by students across all demographic groups, directly combating stereotypes about who belongs in STEM
- Achievement Pathway Documentation: Show how recognized students developed expertise from beginner to advanced levels, making success feel accessible rather than dependent on innate genius
- Student Reflections: Include first-person accounts where students describe their STEM journey, initial interests, challenges overcome, and what drove their persistence
- Failure and Iteration Stories: Normalize struggle and revision by documenting how projects evolved through multiple unsuccessful attempts before success
- Accessible Next Steps: Provide concrete guidance about joining robotics teams, entering science fairs, or accessing resources rather than leaving interested students uncertain about participation pathways
Effective role modeling requires intentional design ensuring all students see achievers reflecting diverse identities and backgrounds. Research consistently demonstrates that representation matters profoundly in STEM persistence, particularly for students from groups historically underrepresented in scientific and engineering fields.
Implementation Strategies: Creating Comprehensive STEM Recognition
Successfully recognizing diverse STEM projects and engineering competition achievements requires systematic planning ensuring displays effectively celebrate accomplishment while remaining sustainable and manageable for teachers and administrators.
Assessment and Planning Phase
Inventory Existing STEM Achievements
Begin by documenting what already exists across your institution over recent years:
- Compile science fair participation and placement records at school, regional, state, and national levels
- Gather robotics competition results including event placements, awards, and advancement history
- Collect mathematics competition results and individual student achievements
- Document coding competition participation and project awards
- Identify independent research projects, publications, or patent applications
- Survey teachers for notable student projects deserving recognition beyond formal competitions
- Contact alumni pursuing STEM careers to document how school experiences influenced their pathways
Comprehensive inventories often reveal substantial achievement depth when no centralized recognition previously existed. Many schools discover decades of excellent accomplishments essentially forgotten because no system preserved institutional memory beyond individual teacher recollections.
Define Recognition Scope and Criteria
Establish clear boundaries for what qualifies for inclusion:
- Minimum Achievement Levels: Determine whether to include all science fair participants, only regional qualifiers, or exclusively state and national achievers
- Competition Categories: Specify which competitions merit inclusion beyond major events like ISEF, FIRST Robotics, and Science Olympiad
- Time Period: Decide whether to include comprehensive history, past decade, or only recent years
- Team Recognition Approach: Clarify how team achievements will be documented—complete rosters, team highlights, or featured individual roles
- Project Quality Thresholds: For non-competition projects, establish evaluation criteria ensuring recognition maintains meaningful standards
Clear scope prevents later confusion and inconsistency while ensuring recognition feels appropriately selective without being impossible to achieve. Many programs establish tiered recognition with stringent criteria for highest honors while creating accessible pathways for broader participation acknowledgment.

Engage Stakeholders in Planning
Build broad ownership supporting long-term sustainability:
- STEM Teachers: Science, mathematics, technology, and engineering instructors know student achievements and can provide comprehensive achievement lists
- School Administrators: Administrative support ensures adequate resources and prominent placement
- Students: Current STEM students provide perspective on what recognition feels meaningful and motivational
- Families: Parents of recognized students often contribute photographs, project documentation, and support
- Alumni: Former students can provide career updates and reflect on how recognition influences persistence
- Community Partners: Industry professionals and university partners can validate achievement significance and provide external perspective
Diverse perspectives ensure recognition programs serve multiple purposes while building coalition supporting ongoing investment and maintenance.
Content Development and Gathering
Compile Comprehensive Achievement Data
Systematically gather information about recognized accomplishments:
- Student names, graduation years, and current status (for alumni)
- Detailed project titles and descriptions explaining what students investigated or designed
- Competition names, dates, and placement levels with context about selectivity
- Award titles and issuing organizations demonstrating external validation
- Team rosters identifying all contributors to collaborative projects
- Supporting documentation including research abstracts, engineering notebooks, or technical specifications
- Verification confirming achievement accuracy to maintain recognition program credibility
Thorough data collection creates valuable institutional records while ensuring accurate, complete recognition. Many schools designate specific staff members responsible for STEM achievement tracking, creating systematic processes ensuring accomplishments are captured immediately rather than requiring difficult historical reconstruction.
Gather High-Quality Visual Assets
Collect professional-quality imagery enhancing recognition impact:
- Project display photographs showing complete science fair exhibits
- Robot photos and videos demonstrating design and competitive performance
- Student portraits showing individuals and teams with their creations
- Competition event photography capturing participation moments
- Award ceremony images preserving recognition memories
- Process documentation photos showing project development progression
- Technical detail images demonstrating engineering sophistication
Invest time in photography quality—professional-looking images dramatically enhance overall recognition presentation. Consider engaging parent volunteers with photography skills, student media classes, or even professional photographers for major competition events. Student project showcase programs that prioritize visual documentation create far more engaging displays than text-heavy alternatives with minimal imagery.
Develop Educational Context Content
Create explanatory materials helping viewers understand achievement significance:
- Competition Descriptions: Brief overviews explaining what specific competitions involve, participation requirements, and recognition levels
- Scientific Concept Summaries: Accessible explanations of key principles investigated in research projects
- Engineering Design Process Documentation: Diagrams or narratives showing how students progressed from problems to solutions
- Achievement Statistics: Data providing context about rarity—“Only 3% of participants advance to nationals”—helping viewers appreciate accomplishments
- Career Connection Information: Links between student projects and professional opportunities in related fields
- Resources for Interested Students: Guidance about how other students can pursue similar achievements
Rich context transforms recognition from simple celebration into educational experiences actively promoting STEM engagement and pathway development.
Technology Solutions for Comprehensive STEM Recognition
Traditional physical recognition approaches struggle with STEM project documentation inherently multimedia and documentation-intensive. Modern digital platforms provide ideal solutions matching how students actually conducted and documented their innovative work.
Digital Recognition Display Advantages
Unlimited Capacity for Comprehensive Recognition
Physical recognition space constraints force impossible choices about which achievements deserve display and which must be excluded or archived. A single trophy case might accommodate 50 plaques. A bulletin board displays perhaps 20 photographs. These limitations mean schools can only recognize small fractions of worthy achievements.
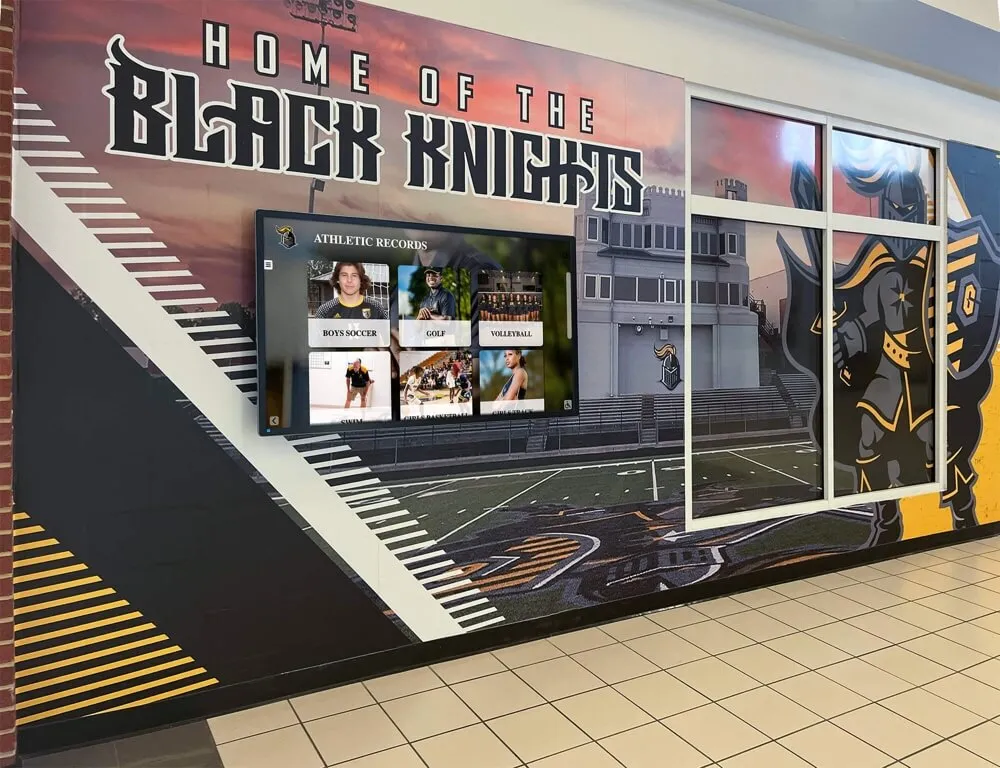
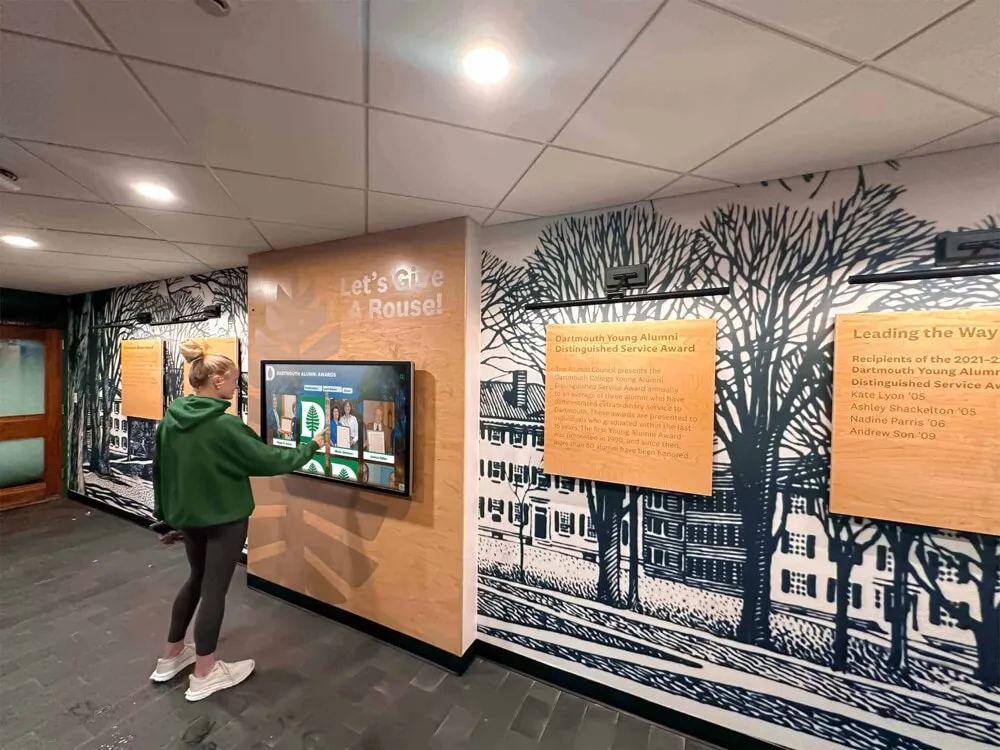
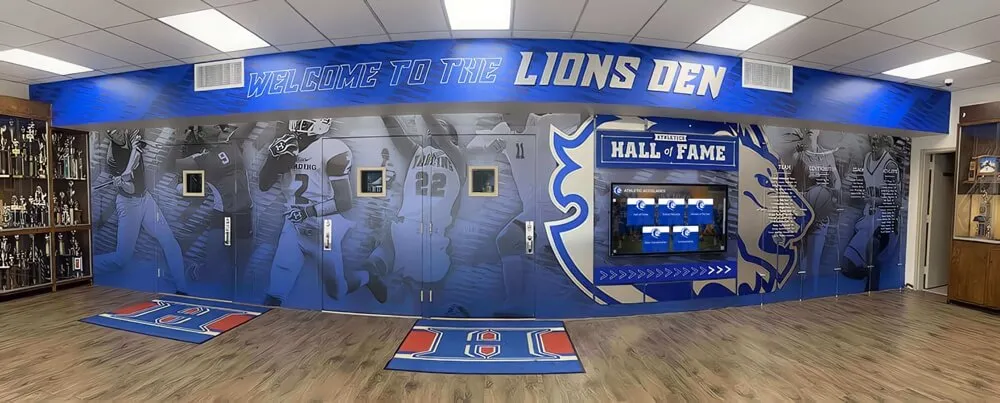
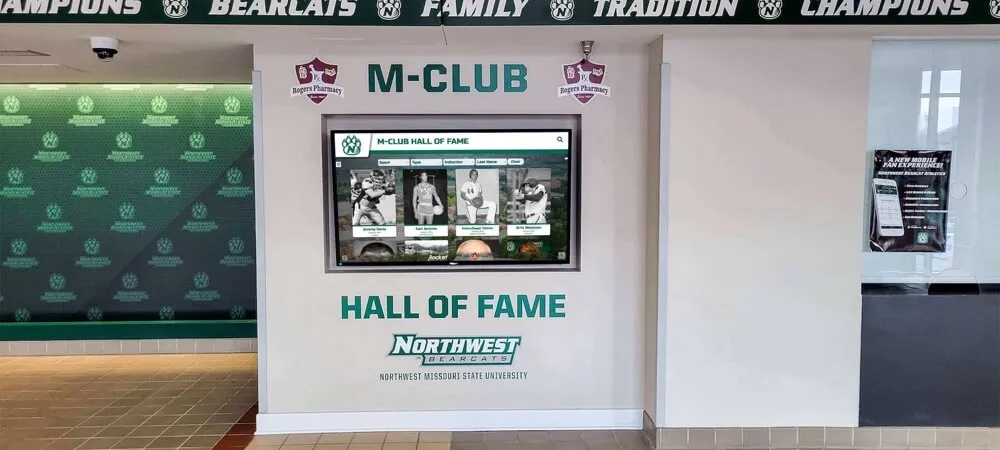
Digital recognition platforms eliminate space constraints entirely. A single 55-inch touchscreen display can showcase unlimited projects—hundreds of science fair entries, complete robotics team histories spanning decades, comprehensive mathematics competition results, extensive coding project portfolios—all accessible through intuitive interfaces requiring minimal physical space while providing virtually unlimited digital capacity.
This unlimited capacity proves transformative for STEM recognition because projects generate substantial documentation. A single science fair entry might include project photographs, research abstract, methodology description, findings summary, student reflection, judge comments, and award documentation. Traditional displays can show perhaps a photograph and name; digital platforms present complete project documentation preserving achievement details that make recognition educational and inspirational.
Solutions like Rocket Alumni Solutions enable schools to include unlimited photos, videos, technical documentation, and descriptive text for every recognized achievement. This comprehensive approach ensures newer accomplishments don’t force removing older recognition—complete historical archives remain permanently accessible while featured content spotlights recent successes.
Rich Multimedia Presentation
STEM projects increasingly incorporate multimedia documentation including process videos, robot performance footage, digital design files, interactive demonstrations, and photographic documentation sequences showing iterative development. Traditional static displays cannot accommodate these formats effectively.
Digital recognition displays excel at presenting multimedia content matching how students actually documented their work:
- Video Integration: Showcase robot competition performances, science fair presentation recordings, time-lapse project development sequences, and student reflection videos
- Image Galleries: Present comprehensive photo collections showing multiple project aspects, development progression, and team collaboration
- Technical Documentation: Display engineering notebooks, research posters, CAD models, and design specifications
- Interactive Elements: Enable viewers to explore project details, zoom into technical images, and access supplementary materials
Multimedia capabilities transform how schools celebrate STEM achievement by presenting projects with depth impossible through traditional recognition approaches. Digital storytelling for student achievement demonstrates how video and interactive content creates emotional engagement that static displays cannot match.

Instant Updates Without Production Costs
Traditional recognition requires physical production—engraved plaques, printed photographs, professionally-mounted displays—creating ongoing costs and update friction. Adding new recognition means purchasing materials, scheduling installation, and physically modifying displays. This friction often results in recognition becoming outdated as busy administrators delay updates due to cost and effort involved.
Digital platforms enable immediate additions through cloud-based content management without physical production costs. When students achieve new recognition, administrators can add comprehensive documentation within minutes from any location. Recognition remains continuously current rather than becoming outdated between infrequent update cycles.
Instant update capability proves particularly valuable for STEM recognition because many competitions occur throughout school years. Robotics competitions happen autumn through spring. Science fairs run winter through spring. Mathematics competitions occur fall and winter. Coding challenges are year-round. Traditional recognition requiring production delays means weeks or months pass between achievement and recognition—dramatically reducing motivational impact compared to near-real-time acknowledgment digital platforms enable.
Analytics and Engagement Tracking
Digital recognition systems provide valuable data about how viewers interact with content:
- Interaction frequency showing which projects generate most engagement
- Search patterns revealing what visitors seek when exploring recognition
- Time spent viewing different content types
- Popular navigation pathways through achievement archives
- Demographic engagement data when combined with sign-in features
Analytics enable continuous improvement by revealing what recognition content resonates most effectively, which organizational approaches work best, and how displays could be enhanced to maximize educational impact and student inspiration.
Web-Based Accessibility Extending Recognition Impact
Physical displays serve on-campus audiences effectively, but web-based recognition platforms extend project visibility to families, college admissions representatives, potential employers, prospective students, and global audiences far beyond school buildings:
- Family Access: Parents and extended family can explore student projects regardless of geographic location, particularly important for families unable to attend school events
- College Applications: Students can share specific project links with college admissions offices demonstrating achievement depth beyond application constraints
- Employer Portfolio Building: Projects become accessible portfolios demonstrating capabilities to potential employers or internship sponsors
- Alumni Engagement: Former students can revisit their school projects years after graduation, maintaining connections to institutions
- Prospective Family Recruitment: Families considering enrollment can explore program quality and student achievement understanding exactly what opportunities exist
- Community Awareness: Local community members and partner organizations can engage with student work appreciating program excellence
Web accessibility proves particularly valuable for STEM program recruitment. Prospective students considering robotics team participation, science fair involvement, or engineering course enrollment can explore current program achievements understanding exactly what they could learn, create, and accomplish.
Ensuring Equity in STEM Recognition Programs
STEM recognition programs must intentionally address equity ensuring all students see achievement pathways rather than systems inadvertently favoring those with existing advantages.
Recognizing Diverse Achievement Pathways
Multiple Recognition Categories
Create varied achievement categories ensuring students with different strengths experience acknowledgment:
- Competition Success: Traditional competition placements from local through national levels
- Research Excellence: High-quality investigations regardless of competition participation
- Design Innovation: Creative solutions demonstrating novel approaches even without top placements
- Sustained Excellence: Consistent STEM coursework achievement and advanced sequence completion
- Growth and Improvement: Significant development from baseline showing dramatic progress
- Leadership and Mentorship: Contributions building STEM program culture and supporting peers
- Community Application: Projects addressing local needs or serving authentic audiences
Diverse categories ensure students who may not win major competitions still receive acknowledgment for meaningful STEM engagement and accomplishment.
Addressing Access Barriers
Resource Equity Considerations
Consider whether recognition criteria assume access to resources not equally available:
- Competition Fees: Science fair entry fees, robotics team registration costs, mathematics competition charges create financial barriers
- Transportation Requirements: Competitions requiring travel may be inaccessible for families without transportation or unable to afford travel costs
- Time Demands: Activities requiring substantial after-school or weekend commitment may exclude students with work or family responsibilities
- Equipment Access: Projects requiring expensive materials, specialized equipment, or technology may be impossible for students lacking personal resources
- Summer Programs: Recognition emphasizing participation in costly summer enrichment programs privileges students from wealthy families
When recognition depends heavily on opportunities not accessible to all students, programs inadvertently privilege advantaged students while excluding those with equal ability but fewer resources. Schools serious about equity ensure recognition pathways exist requiring only effort, talent, and commitment rather than family wealth.

Proactive Opportunity Expansion
Address access barriers directly rather than accepting them as inevitable:
- Fee Assistance Programs: Eliminate financial barriers to competition participation through school funding or booster support
- Transportation Provision: Arrange school-provided transportation to competitions ensuring accessibility
- Equipment Lending Libraries: Establish lending programs for materials, tools, and technology needed for projects
- Extended Access Hours: Provide after-school and weekend access to facilities, equipment, and teacher mentorship
- Free STEM Activities: Ensure robust school-based STEM opportunities requiring no additional family investment
Equity-focused schools recognize that removing barriers expands not just recognition opportunity but actual STEM participation and skill development, directly addressing persistent achievement gaps.
Cultural Responsiveness in Recognition
Representation Matters
Ensure diverse students see themselves in recognition:
- Intentional Demographic Balance: Monitor recognition distribution across student demographics, investigating causes when disparities appear
- Highlighting Underrepresented Achievement: Feature accomplishments by students from groups historically underrepresented in STEM fields
- Culturally Relevant Projects: Value investigations and innovations addressing issues significant to diverse communities
- Multilingual Accessibility: Provide recognition content in languages spoken by school families when appropriate
- Diverse Role Model Presentation: Ensure recognition showcases varied pathways avoiding reinforcement of stereotypes about who belongs in STEM
When students from particular backgrounds rarely see recognition for peers reflecting their identities, implicit messages suggest STEM fields may not welcome certain groups. Intentionally highlighting diverse achievers directly combats these damaging perceptions.
Maintaining and Growing STEM Recognition Over Time
Sustainable recognition requires ongoing attention ensuring displays remain current, accurate, and continue serving motivational purposes effectively.
Establishing Update Workflows
Regular Recognition Addition Processes
Create systematic approaches ensuring new achievements receive timely acknowledgment:
- Quarterly Reviews: Scheduled assessments identifying recent accomplishments deserving recognition
- Competition Season Updates: Immediate additions following major competition events while achievements remain fresh
- Teacher Nomination Systems: Simple processes enabling STEM teachers to flag notable projects throughout school years
- Student Self-Nomination: Allowing students to submit their own accomplishments with supporting documentation
- Annual Comprehensive Audits: End-of-year reviews ensuring no significant achievements were missed
Recognition timing significantly impacts motivational value. Immediate acknowledgment following achievement carries far greater impact than delayed recognition months later when accomplishment feels distant. Digital systems enable near-real-time updates impossible with traditional physical displays requiring production and installation delays.
Quality Maintenance and Enhancement
Preserve recognition program value through ongoing attention:
- Error Corrections: Promptly fix discovered mistakes maintaining accuracy and credibility
- Profile Enhancements: Add additional context, improved images, or supplementary documentation to existing recognition
- Alumni Updates: Contact recognized students after graduation gathering career information demonstrating how STEM interests developed
- Content Reorganization: Adjust organizational structures as recognition grows and usage patterns suggest improvements
- Technical Updates: Refresh technology, improve interfaces, and incorporate new capabilities enhancing user experience
Program Assessment and Continuous Improvement
Engagement and Impact Metrics
Evaluate recognition program effectiveness through systematic measurement:
- Participation Trends: Monitor STEM competition participation, science fair involvement, and optional course enrollment before and after recognition implementation
- Student Awareness: Survey students about recognition program awareness and perceived motivational impact
- Display Interaction Data: Track touchscreen usage patterns, popular content, and engagement duration for digital displays
- Demographic Participation: Monitor whether recognition and program participation become more diverse and inclusive over time
- Alumni Outcomes: Follow recognized students’ college majors, career choices, and continued STEM engagement
While attribution proves difficult, monitoring outcomes alongside recognition implementation helps assess whether programs contribute to desired STEM culture strengthening and participation growth.
Stakeholder Feedback Collection
Gather qualitative perspectives beyond quantitative metrics:
- Student focus groups exploring how recognition influences motivation, risk-taking, and STEM identity development
- Teacher observations about cultural shifts, student conversations about recognition, and apparent impacts on classroom dynamics
- Family surveys assessing satisfaction with recognition approaches and perceived institutional commitment to STEM
- Alumni reflections about recognition’s role in their STEM persistence and career development
- Community partner feedback about program visibility and institutional STEM reputation
Qualitative feedback often reveals recognition impacts that metrics miss, providing valuable guidance for program refinement and enhancement.

Integrating STEM Recognition with Broader School Programs
STEM recognition creates maximum impact when strategically integrated with broader educational initiatives rather than functioning as isolated displays disconnected from daily school life.
Curriculum Connections
Active Learning Integration
Connect recognition to classroom experiences:
- Research Role Models: Have science classes examine recognized projects as exemplars of strong scientific methodology
- Engineering Design Study: Use documented projects to teach design thinking processes and iterative development
- Statistics and Data Analysis: Analyze achievement trends, competition results, and program growth patterns in mathematics classes
- Technical Writing: Study how recognized students described projects as models for effective scientific communication
- Goal Setting and Planning: Help students identify potential achievement pathways using recognition displays as inspiration
Curricular integration ensures recognition actively supports learning rather than simply celebrating past achievement separately from educational programming.
Advising and Pathway Development
Student Guidance and Support
Leverage recognition to shape student planning:
- Interest Exploration: Encourage advisors to discuss STEM recognition with students exploring potential pathways
- Course Selection: Highlight achievement pathways during course registration helping students understand how classes lead to opportunities
- Competition Introduction: Use recognition to recruit participants for robotics teams, science fairs, and mathematics competitions
- Mentor Connections: Link interested students with recognized alumni pursuing STEM careers
- Portfolio Development: Help students understand recognized work forms valuable content for college applications and scholarship competitions
Recognition becomes active recruitment and retention tool when integrated into advising rather than treated separately from academic planning and student support systems.
Community Engagement and Outreach
Building External Awareness
Leverage STEM recognition in external communication:
- Prospective Family Tours: Feature recognition prominently during school tours highlighting program excellence
- Community Events: Display recognition at open houses, STEM nights, and community celebrations
- Partnership Development: Share recognition with potential industry partners, university collaborators, and funding sources
- Media Coverage: Generate news stories about significant achievements and recognition program launches
- Social Media Promotion: Regularly feature recognized students and projects across school social platforms
- Alumni Engagement: Connect recognition to advancement efforts maintaining relationships with STEM career alumni
Visible STEM recognition strengthens school reputation, demonstrates program quality to prospective families, and builds community pride in student innovation and design excellence.
Budget Considerations and Implementation Costs
STEM recognition implementation requires financial investment, though costs vary dramatically based on scope, technology choices, and content development approaches.
Investment Requirements
Traditional Physical Recognition Systems
Basic recognition using conventional approaches:
- Bulletin Board Installations: $300-$1,000 for professional displays in science department areas
- Trophy Case Additions: $2,000-$6,000 for quality cases accommodating awards and small projects
- Wall-Mounted Plaque Systems: $4,000-$10,000 for professional installations with engraved recognition
- Project Display Cases: $1,500-$4,000 per case for protecting and showcasing physical artifacts
Traditional systems have lower initial costs but limited capacity, difficult updates, and accumulating expenses for new materials as recognition grows.
Digital Recognition Platforms
Modern touchscreen solutions enabling comprehensive recognition:
- Entry-Level Touchscreen Systems: $10,000-$18,000 for displays with basic mounting and software
- Mid-Range Professional Installations: $18,000-$35,000 including quality displays, professional mounting, and comprehensive software platforms
- Multi-Display Comprehensive Systems: $35,000-$70,000+ for schools creating extensive recognition networks
- Annual Software Subscriptions: $2,500-$10,000 for cloud-based content management, updates, and support
Digital systems carry higher initial investment but provide unlimited capacity, easy updates, rich multimedia capabilities, and elimination of ongoing material costs for recognition additions. Schools should evaluate total cost of ownership over 5-10 years rather than focusing exclusively on initial purchase price. Digital trophy case solutions often prove more cost-effective long-term than physical displays requiring continuous material purchases.
Content Development Investment
Professional services and staff time allocation:
- Photography and Media Collection: $2,000-$8,000 for professional documentation of projects and competitions
- Data Compilation and Verification: 150-300 staff hours researching and organizing achievement information
- Content Writing and Profile Creation: 100-200 hours developing project descriptions and contextual content
- Historical Research: 50-150 hours reconstructing older achievement records through archives and alumni contact
- Ongoing Maintenance: 2-5 hours monthly adding new achievements and maintaining currency
Content development represents substantial investment but creates lasting value as institutional knowledge preservation.
Funding Strategies
Grant Opportunities
External funding specifically supporting STEM initiatives:
- Federal STEM Education Grants: Department of Education programs supporting comprehensive STEM program development
- State Mathematics and Science Funding: State-level grants for STEM equipment, programs, and recognition
- Corporate STEM Initiative Grants: Technology and engineering companies supporting local school STEM programs
- Foundation Support: Private foundations funding education innovation and STEM pathway development
- University Partnership Funding: Higher education institutions supporting K-12 STEM pipeline programs
Many grant programs specifically support recognition components as parts of comprehensive STEM program development, particularly when proposals emphasize equity, access, and inspiration for underrepresented groups.
Community and Booster Support
Local fundraising and partner contributions:
- Parent-Teacher Organization Funding: PTO/PTA support for recognition as priority school improvement
- STEM-Specific Booster Organizations: Dedicated groups supporting science, robotics, and mathematics programs
- Business Partnerships: Local engineering firms, technology companies, or healthcare organizations sponsoring recognition
- Alumni Giving Campaigns: Former students contributing to STEM recognition honoring their own formative experiences
- Memorial and Honorific Naming: Recognition opportunities for donors through named displays or endowed programs
Compelling funding cases emphasize both celebrating existing excellence and investing in future program growth, participation expansion, and cultural transformation toward greater STEM emphasis.
Celebrating Innovation: Building STEM Culture Through Recognition
Creating comprehensive STEM project and engineering competition recognition represents far more than adding displays to school facilities—it demonstrates institutional commitment to valuing scientific inquiry, innovative design thinking, and engineering excellence with prominence equal to athletic achievement. When schools invest in professional, thorough STEM recognition, they send clear messages that innovation matters profoundly, creative problem-solving deserves celebration, intellectual accomplishment builds school identity and pride, diverse forms of STEM achievement receive acknowledgment, and student effort in challenging technical disciplines brings meaningful recognition.
These messages powerfully influence school culture, student motivation, program participation, family perceptions, and community understanding of institutional priorities. Recognition alone doesn’t create STEM excellence, but visible, prominent celebration of achievement contributes significantly to environments where scientific and engineering engagement feels valued, celebrated, and central to school identity.
The recognition approaches explored in this guide provide frameworks for celebrating student STEM projects and engineering competition success that honor innovative work while remaining sustainable, equitable, and aligned with educational goals. Modern digital recognition solutions like Rocket Alumni Solutions transform project celebration from temporary bulletin board displays into permanent, engaging showcases accessible to families, communities, and future students—preserving STEM achievements with prominence matching any athletic championship while inspiring the next generation of innovators, designers, engineers, and scientists.
Your students’ STEM achievements deserve recognition matching the significance of their accomplishments and the countless hours invested in design, prototyping, research, and competitive preparation. Whether they’re conducting groundbreaking research, building sophisticated robots, solving complex mathematical challenges, or designing innovative solutions to real-world problems, these young scientists and engineers represent your institution’s commitment to preparing tomorrow’s innovators. Celebrate them prominently, professionally, and permanently through recognition systems demonstrating that scientific and engineering excellence matters as much as any trophy or banner.
Ready to transform how your school celebrates STEM innovation and engineering excellence? Digital recognition displays provide purpose-built solutions specifically designed for comprehensive STEM achievement documentation, enabling schools to showcase unlimited projects with photos, videos, technical details, and student reflections in engaging formats that preserve accomplishments permanently while inspiring current and future students to pursue their own innovative excellence.