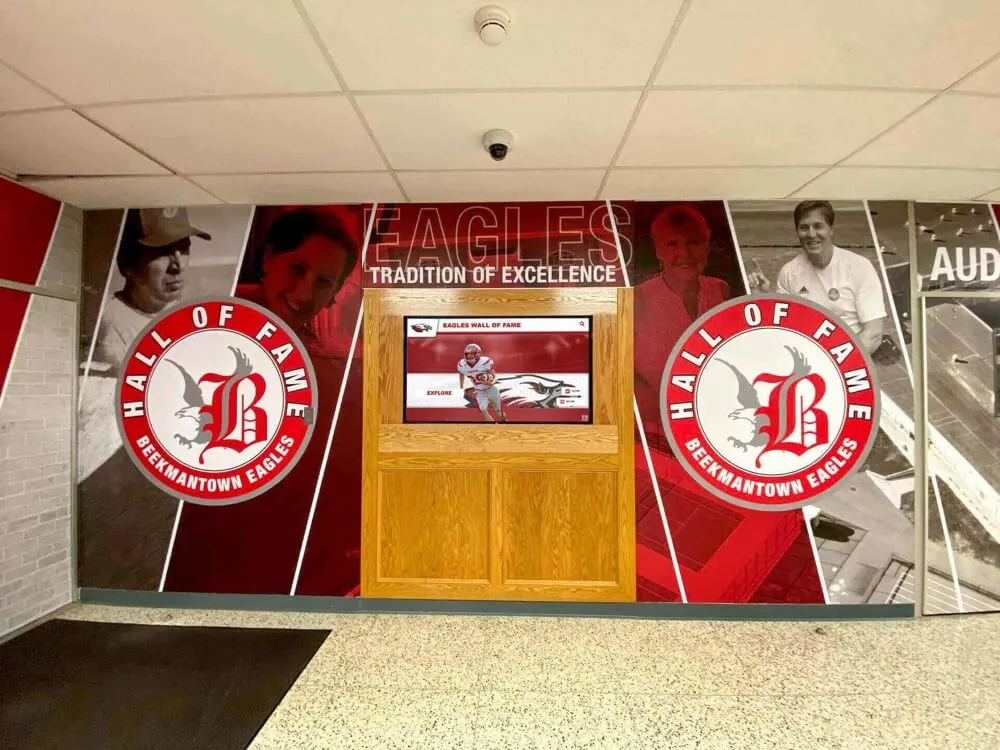
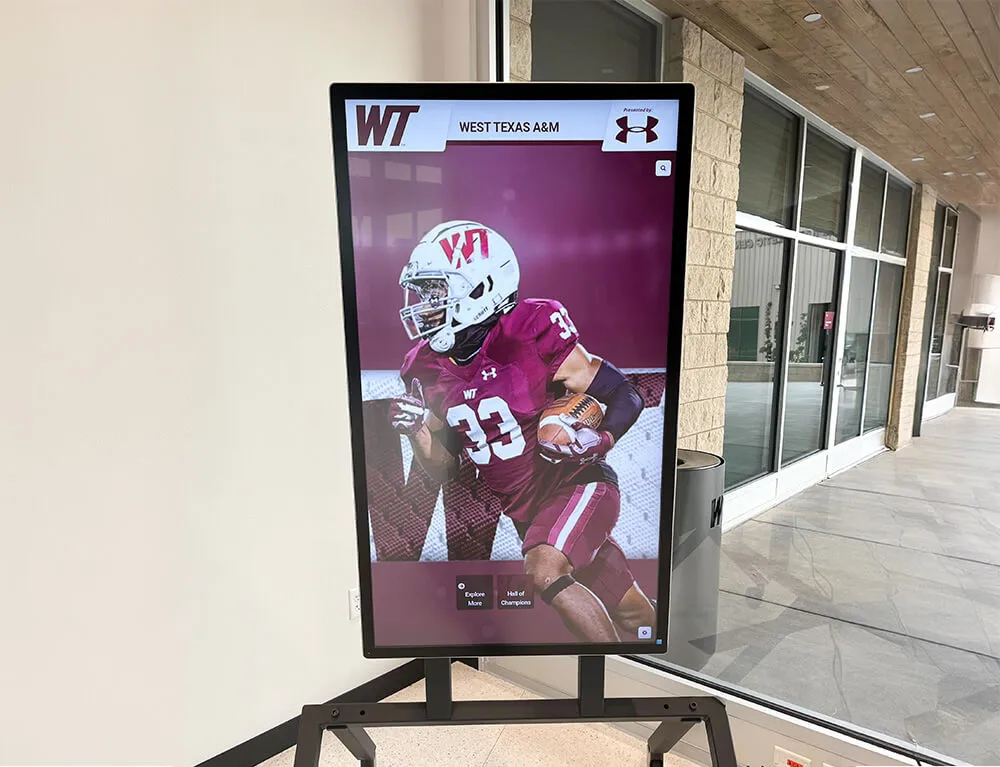
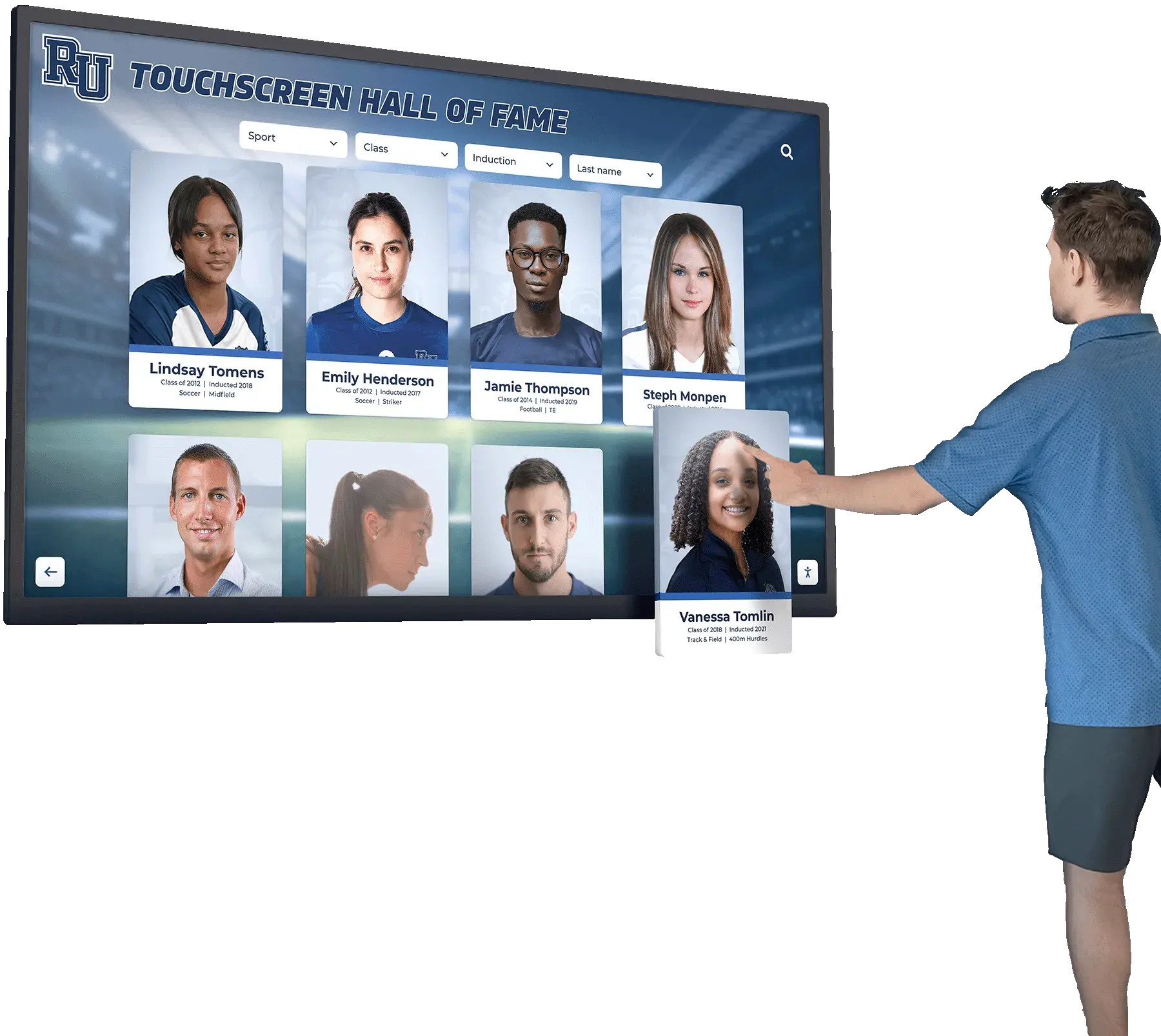
A hall of fame represents one of the most enduring forms of recognition across human culture—a permanent tribute to exceptional achievement that transcends individual moments and preserves excellence for future generations. From ancient civilizations honoring heroes in monuments to modern institutions celebrating distinguished members, the fundamental purpose remains constant: recognizing extraordinary accomplishment while inspiring others to pursue their own paths to excellence.
Yet creating an effective hall of fame program involves far more than simply listing names on a wall or displaying trophies in a case. The most successful recognition programs thoughtfully balance multiple objectives including honoring past achievement appropriately, inspiring current participants through tangible role models, preserving institutional history and traditions, building community pride and identity, and maintaining credibility through fair selection processes.
Why Hall of Fame Programs Matter More Than Ever
In an era of instant digital communication and fleeting social media recognition, permanent hall of fame displays serve critical functions that temporary acknowledgment cannot match. They demonstrate that excellence matters enough to commemorate permanently, create physical or digital spaces where communities gather around shared values, preserve detailed achievement documentation that would otherwise fade, inspire aspiring individuals through concrete success examples, and build lasting connections between past legends and future generations.
Modern digital recognition solutions like those from Rocket Alumni Solutions enable organizations to create comprehensive hall of fame programs that combine the gravitas of traditional recognition with interactive capabilities and unlimited capacity impossible with physical-only approaches.
The History and Evolution of Hall of Fame Recognition
Understanding how recognition traditions evolved helps organizations create programs that honor heritage while embracing modern capabilities.
Ancient Origins of Permanent Recognition
Recognition of exceptional individuals extends back to humanity’s earliest civilizations through practices demonstrating that honoring excellence represents a fundamental human impulse across cultures and eras.

Ancient Greece and Rome: Greek city-states erected statues and monuments honoring Olympic champions, military heroes, and distinguished citizens in prominent public spaces. Roman civilization continued these traditions, creating elaborate monuments, triumphal arches, and inscribed records commemorating military victories and civic achievements. These physical tributes served multiple purposes—honoring individuals, inspiring citizens through exemplary models, and reinforcing community values about what accomplishments deserved celebration.
Medieval Recognition Traditions: Medieval societies honored distinguished members through heraldic systems, knightly orders, and guild membership recognition. Coats of arms communicated family achievement across generations. Chivalric orders like the Order of the Garter created exclusive recognition for exemplary service. These formalized systems established precedents for structured selection processes, eligibility criteria, and ceremonial induction practices still reflected in modern hall of fame programs.
19th Century Institutionalization: The concept of dedicated “halls of fame” as distinct recognition institutions emerged in the 1800s. New York University commissioned a “Hall of Fame for Great Americans” in 1900, creating the first use of this specific terminology. This pioneering installation established patterns including selection by distinguished committees, commemorative busts and plaques, public accessibility, and periodic induction ceremonies that influenced subsequent programs worldwide.
Modern Hall of Fame Development
The 20th century witnessed explosive growth in hall of fame programs across every domain of achievement including sports, entertainment, business, science, and civic leadership.
Baseball Hall of Fame (1939): The National Baseball Hall of Fame in Cooperstown, New York became the template for athletic recognition worldwide. Its combination of museum exhibits, permanent inductee plaques, stringent selection criteria, and annual induction ceremonies established patterns copied across virtually every sport. The credibility generated by thoughtful selection processes and the tourism impact of physical installations demonstrated hall of fame programs’ potential institutional and economic value.
Proliferation Across Domains: Following baseball’s success, virtually every professional sport established hall of fame recognition—basketball, football, hockey, soccer, tennis, golf, track and field, and countless others. Beyond athletics, halls of fame emerged recognizing achievement in music (Rock and Roll Hall of Fame), business (various industry halls of fame), science and technology, broadcasting, education, military service, and local community contributions. This expansion demonstrated universal recognition needs across all human achievement domains.
Educational Institution Adoption: Schools, universities, and educational organizations increasingly established hall of fame programs throughout the late 20th and early 21st centuries. These institutions recognized that formal recognition programs served multiple objectives including alumni engagement, student inspiration, fundraising support, recruitment enhancement, and institutional history preservation. Educational halls of fame evolved from primarily athletic focus toward comprehensive recognition spanning academic achievement, artistic accomplishment, civic leadership, and professional success.
Resources on best school hall of fame walls demonstrate how educational institutions adapted traditional recognition concepts to serve specific institutional needs while incorporating modern technology capabilities.
The Digital Revolution in Hall of Fame Recognition
Twenty-first century technology transformed recognition possibilities while preserving core hall of fame principles.

Physical Space Limitations Overcome: Traditional hall of fame installations faced inevitable capacity constraints—only finite plaques fit on available walls, only so many trophies display in cases, and physical expansion required significant construction investment. Digital recognition systems eliminated these limitations entirely. A single touchscreen display could accommodate thousands of inductee profiles. Web-based platforms provided unlimited growth capacity. Organizations no longer faced impossible choices about removing older recognition to accommodate new honorees or limiting inductions based on physical space rather than achievement merit.
Multimedia Storytelling Capabilities: Physical plaques communicate basic information—names, years, perhaps brief achievements. Digital systems enable comprehensive storytelling through high-resolution photographs, video highlights and interviews, audio recordings, extensive biographical narratives, career statistics and documentation, links to related content, and interactive timelines showing achievement progression. This rich multimedia creates emotional connection and deep engagement impossible with traditional static displays.
Remote Accessibility and Social Sharing: Physical hall of fame installations serve only those who visit specific locations. Digital recognition extends globally—alumni can explore their induction from anywhere, families share achievements with distant relatives, recruiters research institutional excellence remotely, and social media amplifies recognition visibility exponentially beyond physical visitors. This expanded accessibility multiplies engagement and impact dramatically.
Real-Time Updates and Maintenance: Adding recognition to physical displays requires ordering plaques, scheduling installation, and completing physical modifications—processes taking weeks or months and costing hundreds of dollars per inductee. Digital systems enable instant updates through simple content management. New inductees appear immediately, information corrections happen in minutes, and content enhancements require no physical labor. Long-term maintenance costs drop dramatically while responsiveness increases substantially.
Types of Hall of Fame Programs Across Institutions
Hall of fame programs serve diverse organizations with recognition needs tailored to specific contexts and objectives.
Athletic Halls of Fame
Sports recognition represents the most common hall of fame category across high schools, colleges, professional organizations, and community leagues.
High School Athletic Recognition: Secondary schools establish halls of fame honoring distinguished student-athletes, championship teams, coaching legends, and athletic program milestones. These recognition systems serve current athletes by showcasing achievable excellence pathways, engage alumni through continued acknowledgment decades after graduation, and build school pride celebrating comprehensive athletic traditions. Resources on high school alumni hall of fame displays explore implementation strategies specifically relevant to secondary education contexts.
College and University Athletic Programs: Collegiate athletic departments maintain halls of fame recognizing All-Americans, professional athletes who competed collegiately, championship teams, coaching legends, and athletic administrators who built programs. University athletic recognition balances multiple sports, ensuring Olympic sports receive equal visibility alongside revenue programs while celebrating both athletic performance and academic excellence. Guidance on college athletics hall of fame programs addresses unique challenges of multi-sport recognition in higher education contexts.
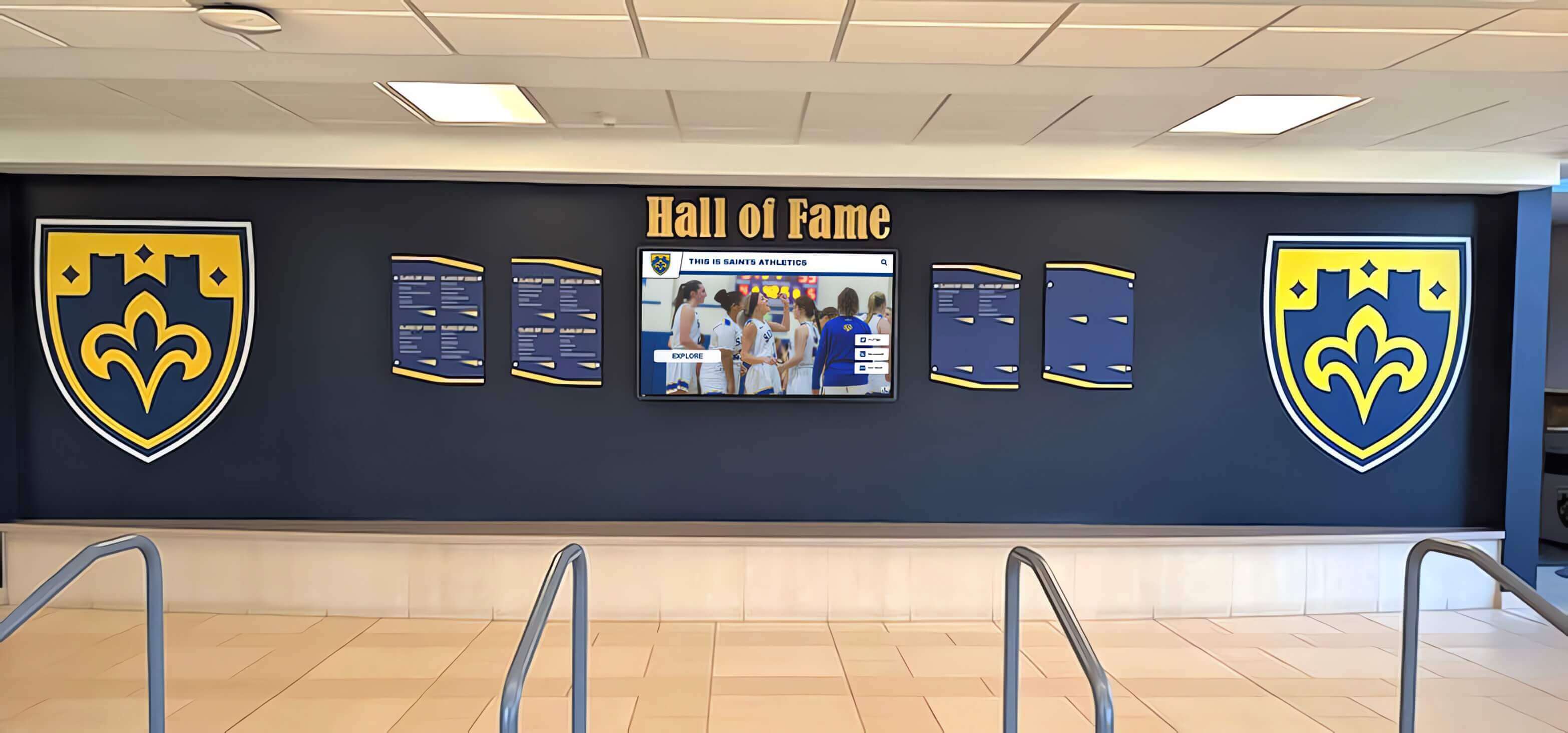

Professional League Recognition: Major professional sports leagues maintain prestigious national halls of fame that represent career achievement pinnacles. These highly selective programs establish rigorous criteria including performance statistics, championship success, awards and honors, career longevity, and character standards. Professional halls of fame often incorporate museum components, generate tourism revenue, and create major media events around annual induction ceremonies.
Youth and Community Sports Organizations: Local leagues, recreational programs, and community sports organizations increasingly establish recognition programs honoring volunteers, coaching contributors, outstanding participants, and program milestones. These grassroots programs build organizational identity, recognize sustained commitment from community members, and create visibility enhancing program reputation and recruitment.
Academic and Alumni Halls of Fame
Comprehensive institutional recognition extends beyond athletics to celebrate diverse forms of excellence and contribution.
Distinguished Alumni Recognition: Educational institutions honor graduates who achieved exceptional professional success, demonstrated exemplary civic leadership, made significant philanthropic contributions, or brought distinction to their alma mater through accomplishments in any field. These programs inspire current students through diverse role models while strengthening alumni engagement and supporting fundraising initiatives. Resources on creating an alumni hall of fame provide implementation frameworks for schools and universities.
Academic Excellence Halls of Fame: Some institutions specifically recognize academic achievement through valedictorians and salutatorians, National Merit Scholars, perfect attendance records, or academic competition champions. These programs communicate that institutions value intellectual achievement as highly as athletic excellence while creating visible inspiration for academically-focused students. Approaches to recognizing valedictorians offer specific strategies for academic recognition programs.
Faculty and Staff Recognition: Educational institutions recognize distinguished educators, administrators, and support staff who made exceptional contributions through teaching excellence, research impact, program innovation, or sustained service. These programs honor internal community members whose work enables student success while reinforcing institutional values about what contributions matter most.
Professional and Industry Halls of Fame
Career field recognition celebrates excellence within specific professions, industries, or vocational domains.
Industry-Specific Recognition: Virtually every professional field maintains hall of fame programs including business and entrepreneurship, medicine and healthcare, engineering and technology, arts and entertainment, journalism and media, military and public safety, and trade and skilled professions. These domain-specific programs establish field-relevant criteria, recognize contributions advancing entire professions, and inspire practitioners through exemplary career models.
Company and Organizational Halls of Fame: Individual companies establish internal recognition programs honoring employees who demonstrated exceptional performance, embodied organizational values, achieved significant tenure, or contributed innovations advancing business success. Corporate halls of fame build organizational culture, recognize sustained contribution, and create retention incentives demonstrating that companies value long-term excellence.
Community and Civic Halls of Fame
Local recognition programs celebrate community members whose contributions improved civic life and quality of place.

Community Service Recognition: Cities, towns, and community organizations honor residents who demonstrated extraordinary volunteer leadership, made significant philanthropic contributions, advanced social justice and inclusion, or improved community quality of life through sustained service. These programs celebrate unsung heroes whose contributions might otherwise go unrecognized while reinforcing community values about citizenship and service. Frameworks for honoring community accomplishments provide strategies for civic recognition programs.
Military and Veterans Recognition: Communities establish halls of honor recognizing military service members who served with distinction, demonstrated extraordinary valor, achieved significant rank or command, or contributed to veteran support upon returning to civilian life. These programs preserve military service history while honoring sacrifice and commitment. Resources on military wall of honor installations address unique considerations for veteran recognition.
Essential Elements of Effective Hall of Fame Programs
Successful recognition systems share common characteristics ensuring credibility, sustainability, and meaningful impact.
Clear Selection Criteria and Processes
Transparent standards establish program credibility while ensuring selection decisions withstand community scrutiny.
Achievement Thresholds: Effective programs define specific accomplishments warranting consideration including performance statistics or records, awards and honors received, championship participation or success, career longevity and sustained excellence, and post-career impact or contributions. Criteria should remain appropriately selective—maintaining high standards that make induction genuinely meaningful—while accessible enough that deserving individuals have realistic paths to recognition.
Character and Values Standards: Beyond pure achievement, most credible programs require exemplary conduct and character alignment with institutional values. This prevents recognition of individuals whose behavior might embarrass organizations regardless of their accomplishments. Character standards should be clearly articulated, consistently applied, and documented to protect selection integrity.
Waiting Periods: Most programs establish minimum time periods between achievement completion and hall of fame eligibility—commonly 5-10 years for athletes after retirement, or 10-15 years after graduation for alumni. These waiting periods allow achievement significance to become clear, enable post-career accomplishments to inform selection, and ensure programs recognize sustained excellence rather than momentary success.
Nomination Processes: Structured nomination systems balance accessibility with thoroughness through open nomination windows accepting community submissions, standardized forms requesting comprehensive information, multiple nomination sources ensuring diverse candidate pools, and transparent communication about processes and timelines. Resources on hall of fame selection criteria explore best practices for fair, credible nomination and selection systems.
Professional Display and Presentation
Recognition quality directly impacts program credibility and inductee satisfaction requiring professional presentation standards.
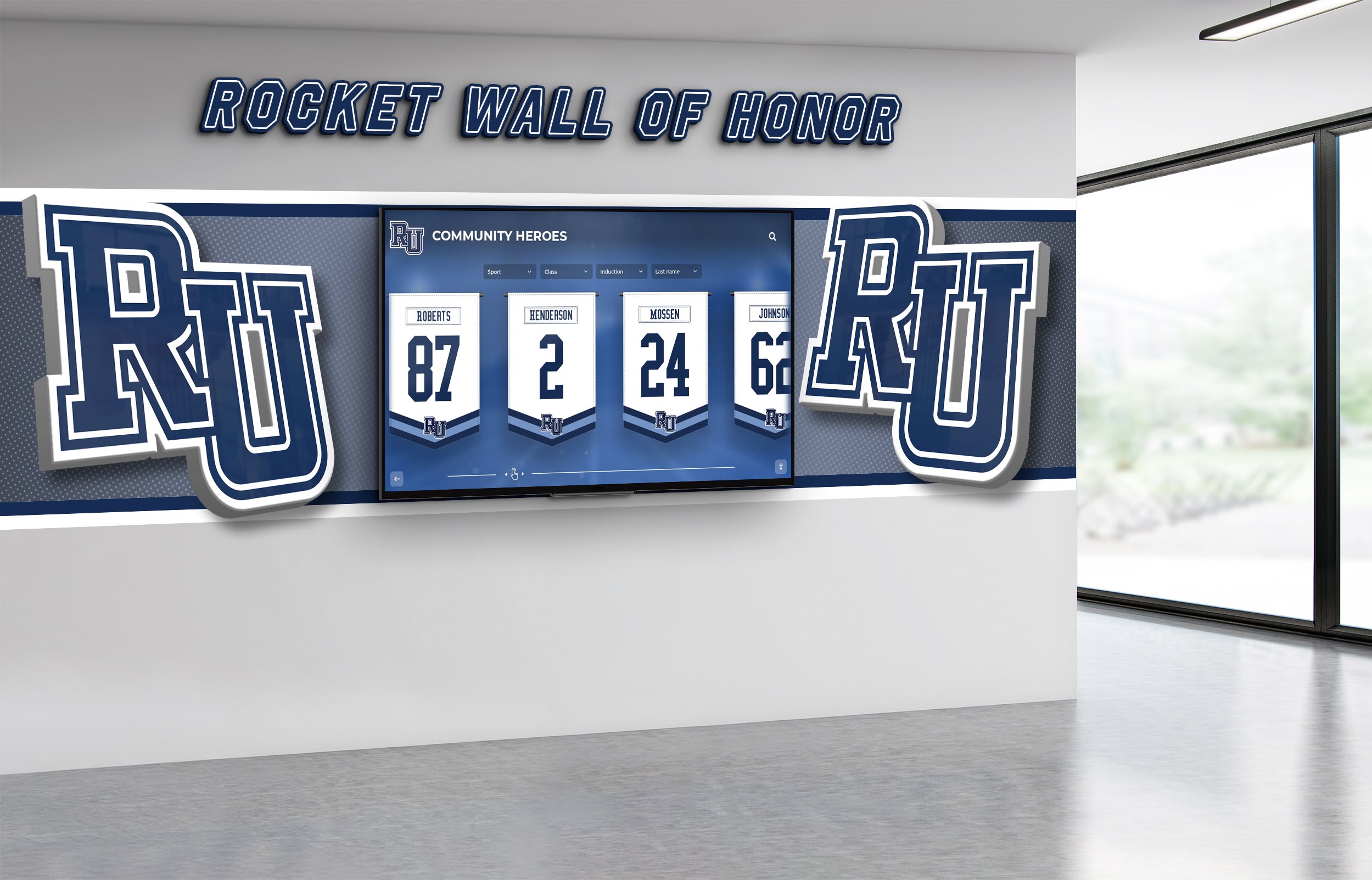

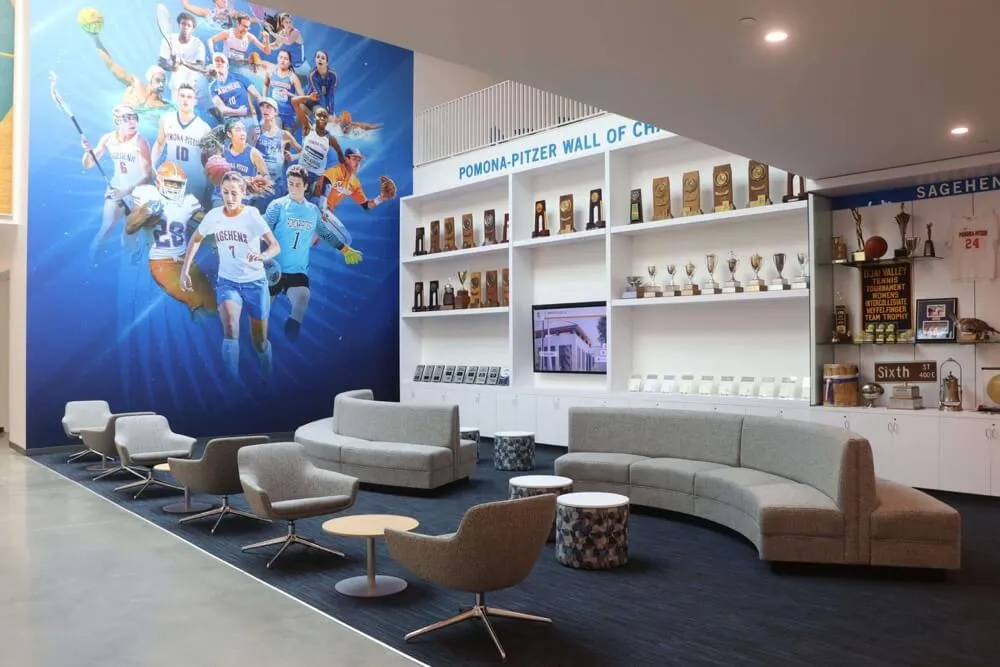
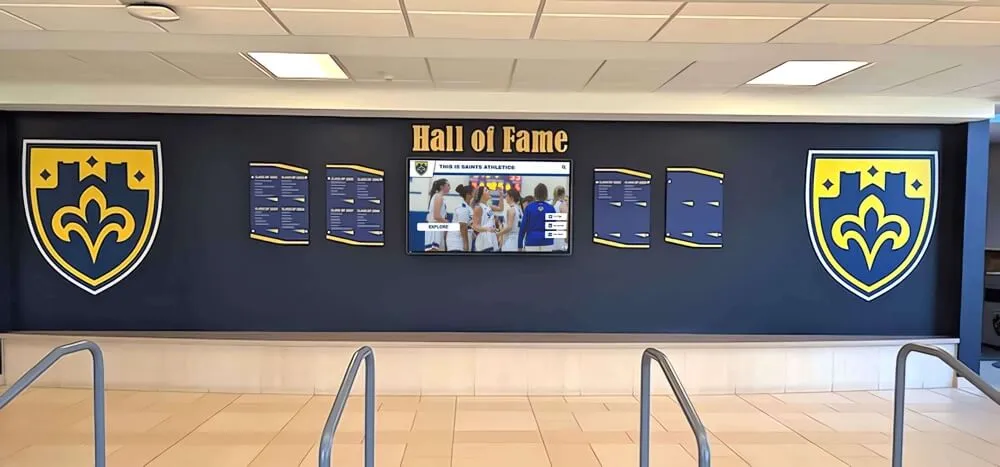
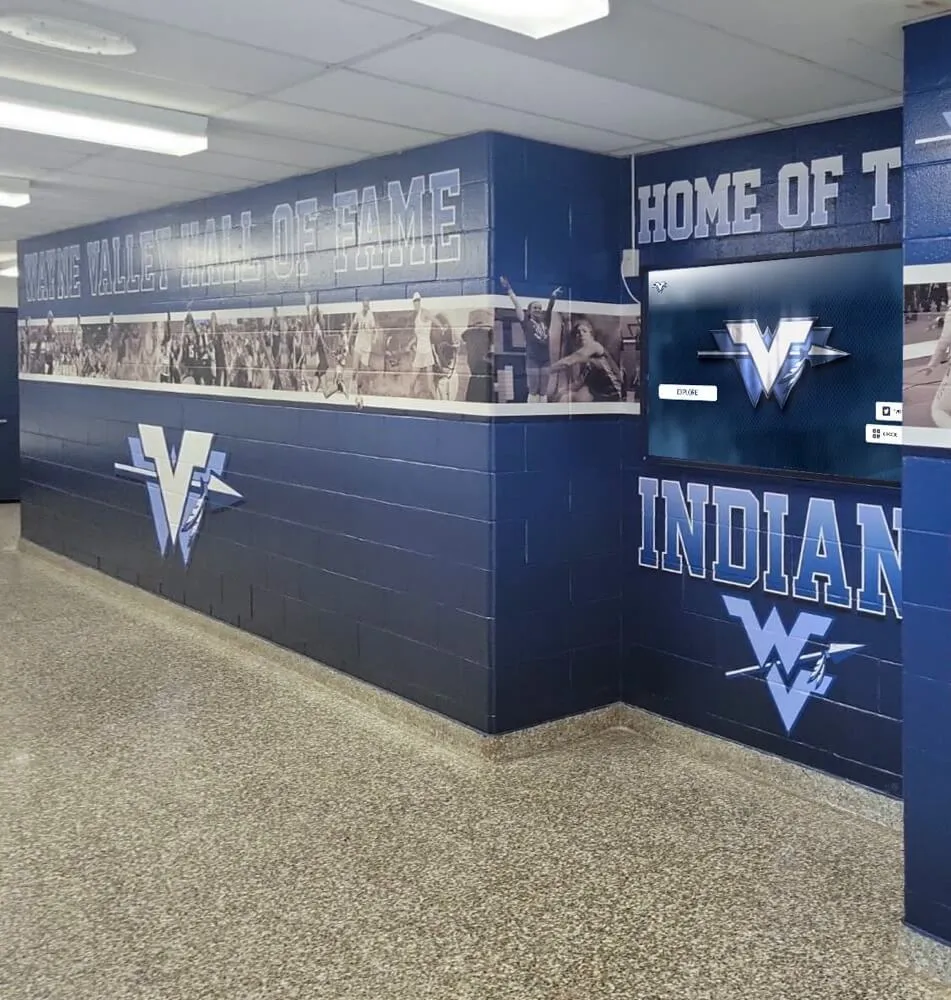
Traditional Physical Displays: Conventional recognition through engraved plaques, mounted photographs, trophy cases, and banner displays provides tangible permanence and familiar aesthetics. Physical recognition requires quality materials, professional installation, prominent placement, and ongoing maintenance ensuring continued professional appearance. While traditional displays face capacity limitations and update challenges, they convey formal dignity many stakeholders value highly.
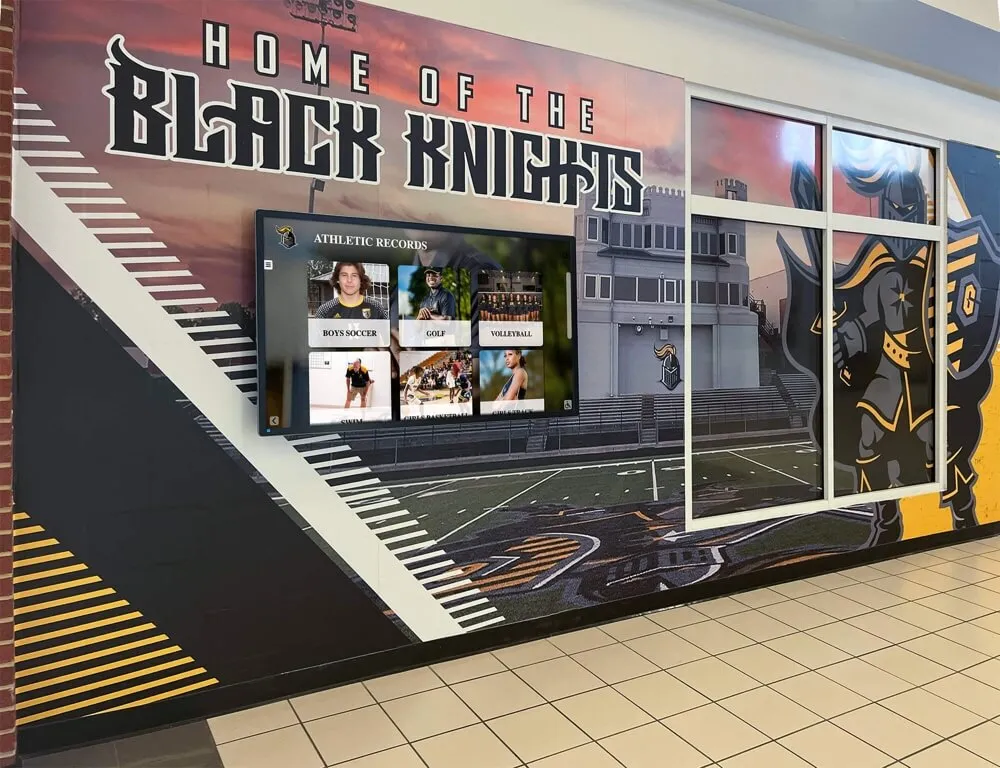
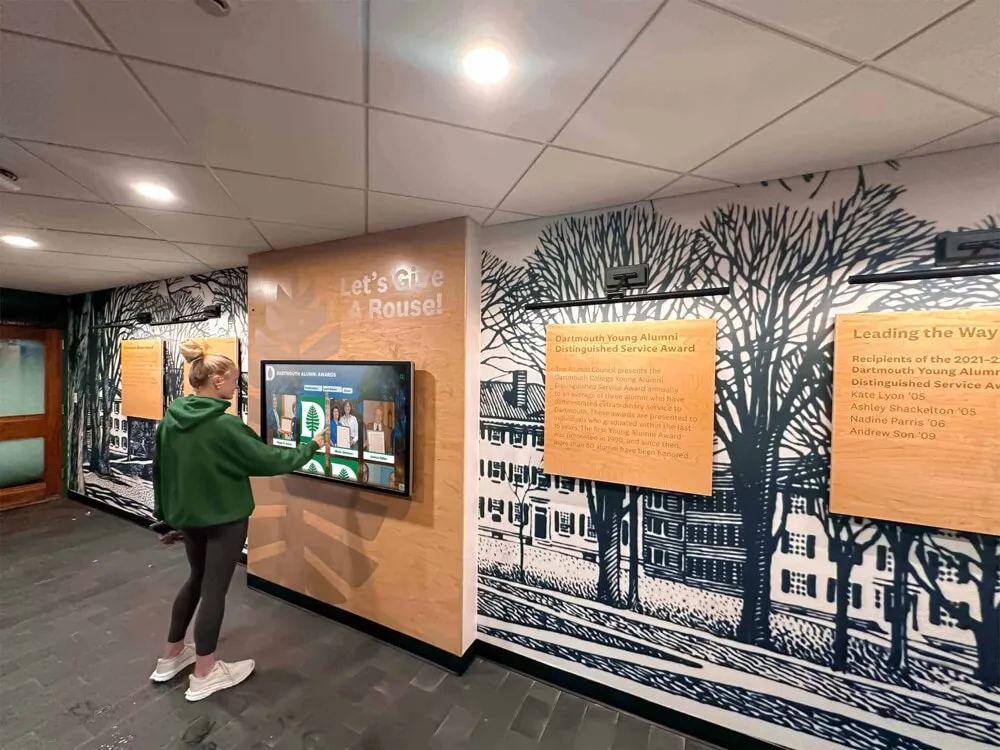
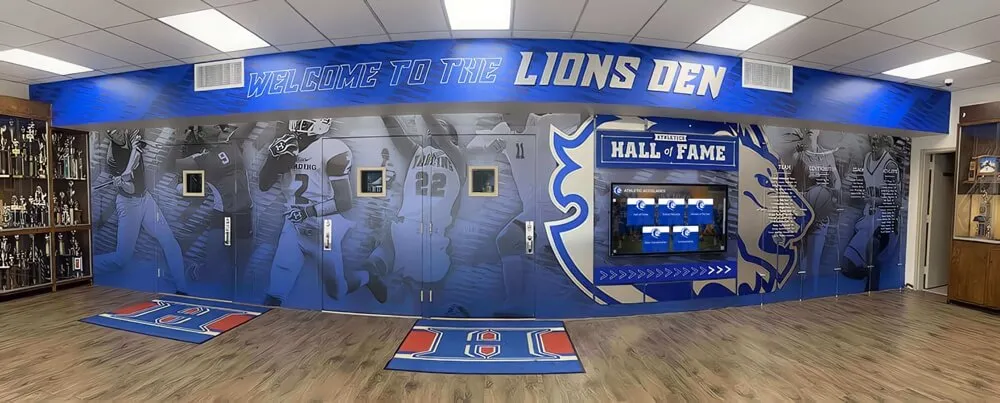
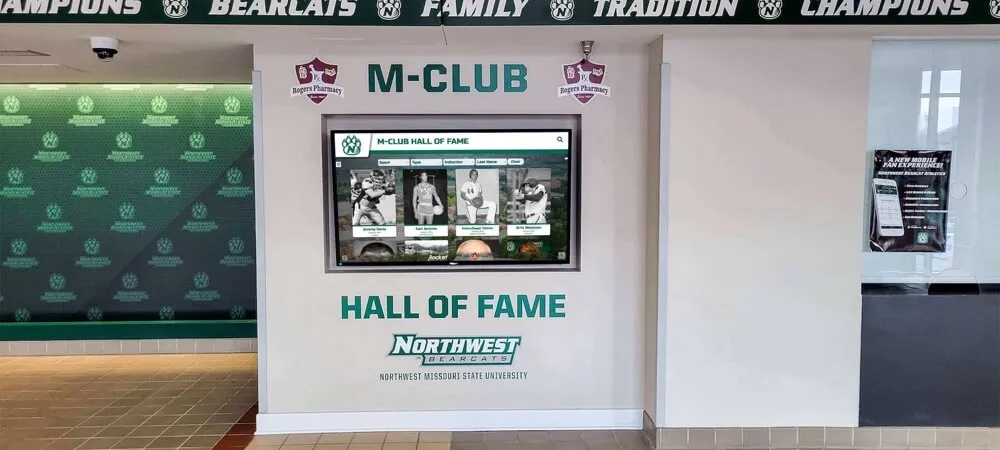
Digital Interactive Systems: Modern touchscreen displays and web platforms overcome physical limitations while adding capabilities including unlimited capacity for comprehensive recognition, rich multimedia storytelling through photos and videos, instant content updates without physical modifications, search and filtering enabling easy discovery, remote web access extending reach globally, and engagement analytics informing program improvement. Digital systems require higher initial investment but typically prove more cost-effective long-term while delivering superior functionality. Guidance on touchscreen hall of fame technology helps organizations evaluate digital recognition options.
Hybrid Approaches: Many successful programs combine selective traditional displays for highest-profile inductees with comprehensive digital systems accommodating unlimited recognition. This balanced strategy satisfies traditionalists while solving practical limitations through modern technology, often representing optimal solutions for organizations with diverse stakeholder preferences.
Compelling Content and Storytelling
Recognition effectiveness depends more on content quality than display technology or physical materials.
Comprehensive Profile Elements: Effective inductee recognition includes biographical background and context, detailed achievement documentation, career progression narratives, personal reflections and quotes, photographic and video content, connections to related achievements, and appropriate historical context. Comprehensive profiles honor inductees appropriately while creating engaging content that inspires audiences through concrete, relatable examples. Resources on storytelling through digital recognition provide frameworks for developing compelling narratives.
Professional Writing Standards: Recognition content should employ active voice and dynamic language, provide specific examples over vague praise, maintain consistent length and structure ensuring equitable treatment, use accessible vocabulary engaging diverse audiences, and balance formal respect with engaging readability. Professional content development demonstrates institutional commitment to honoring inductees appropriately while maximizing engagement effectiveness.
Multimedia Integration: When technology permits, rich media dramatically enhances recognition through action photographs showing inductees during peak performance, video highlights capturing memorable achievements, audio interviews sharing personal reflections, historical documents providing context, and interactive timelines showing career progressions. Multimedia creates emotional connection impossible with text-only recognition while accommodating diverse learning preferences among audiences.
Sustainable Operations and Maintenance
Long-term program success requires systematic operations ensuring consistent activity and continuous relevance.
Annual Operating Cycles: Sustainable programs establish predictable rhythms including fall planning and committee formation, winter nomination periods accepting submissions, spring selection and announcement, summer preparation developing new inductee content, and fall induction ceremonies celebrating achievements. Regular cycles maintain program momentum while distributing workload sustainably preventing burnout among volunteer or staff administrators.
Content Update Protocols: Recognition remains relevant through regular maintenance adding new inductees annually, enhancing existing profiles with updated information, rotating featured content ensuring diverse visibility, correcting errors promptly when identified, and expanding historical coverage systematically. Established protocols ensure updates happen consistently rather than sporadically when someone remembers.

Budget Sustainability: Effective programs secure ongoing funding through institutional budget allocation, alumni or booster contributions, corporate sponsorships providing annual support, endowments generating investment income, or event fundraising around induction ceremonies. Initial implementation requires significant investment, but ongoing operations need sustainable funding models ensuring programs remain active long-term rather than launching enthusiastically then languishing due to resource constraints.
Modern Technology Solutions for Hall of Fame Programs
Digital recognition systems transformed what’s possible while making comprehensive programs achievable for organizations previously constrained by physical limitations and budget realities.
Interactive Touchscreen Displays
Physical kiosk installations provide prominent on-site recognition with engaging interactive capabilities.
Hardware Components: Commercial-grade touchscreen displays (typically 43-75 inches), dedicated computer modules running recognition software, secure mounting and enclosures protecting equipment, professional cable management ensuring clean appearance, and reliable network connectivity enabling content updates. Commercial equipment designed for continuous operation proves essential—consumer displays fail quickly under constant use in public spaces.
Software Capabilities: Purpose-built platforms provide intuitive content management requiring no technical expertise, searchable databases enabling instant name lookups, filtered browsing by achievement type or era, multimedia support for photos and videos, featured content rotation keeping displays fresh, analytics tracking engagement patterns, and user-friendly public interfaces accessible to all ages. Comprehensive guides on touchscreen kiosk software help organizations evaluate platform options.
Physical Placement Strategy: Location dramatically impacts engagement through high-traffic areas maximizing visibility, appropriate viewing heights meeting accessibility standards, environmental considerations including lighting and temperature, and thematic appropriateness for recognition context. Strategic placement ensures recognition receives attention rather than being relegated to forgotten corners where minimal engagement occurs.
Web-Based Virtual Halls of Fame
Online platforms extend recognition beyond physical locations enabling global accessibility.
Remote Access Benefits: Web-based recognition serves alumni unable to visit physically, prospective students researching institutional excellence, families sharing achievements with distant relatives, media researching stories and information, and social networks amplifying recognition visibility. Remote accessibility multiplies engagement exponentially beyond those visiting physical locations while serving alumni anywhere in the world.
Search Engine Visibility: Well-designed web platforms generate organic traffic through search engine optimization around inductee names, achievement keywords, and institution-related queries. This discoverability brings recognition to broader audiences while supporting recruitment, reputation management, and alumni relations objectives. Resources on online hall of fame websites explore platform design and optimization strategies.
Social Media Integration: Web-based systems facilitate easy sharing on social networks, create shareable graphics celebrating individual inductees, enable direct linking to specific profiles, and support promotional campaigns around induction announcements. Social integration extends recognition reach while creating ongoing engagement opportunities between major program events.

Hybrid Digital and Physical Approaches
Combined strategies leverage advantages of both physical presence and digital capabilities.
Many successful programs maintain selective traditional recognition—signature plaques or trophy displays for highest-profile inductees—while adding digital systems providing unlimited capacity, comprehensive content, and remote accessibility. This hybrid approach satisfies stakeholders valuing physical permanence while solving practical limitations through modern technology. QR codes on physical displays linking to expanded digital content create seamless integration between physical and digital recognition elements.
Implementing Your Hall of Fame Program: Step-by-Step Guide
Organizations creating new recognition programs benefit from systematic approaches addressing all implementation dimensions from initial planning through sustained operations.
Phase 1: Planning and Foundation (Months 1-3)
Comprehensive planning prevents common pitfalls while establishing sustainable foundations.
Define Clear Objectives: Articulate specific purposes including primary goals (inspiration, engagement, preservation, recruitment), target audiences and their needs, success metrics enabling evaluation, and integration with other organizational initiatives. Clear objectives inform all subsequent decisions about criteria, format, budget allocation, and operational priorities.
Engage Diverse Stakeholders: Involve representatives including alumni or member communities, leadership and administration, development and fundraising staff, facilities and IT departments, students or current participants, and donor or sponsor representatives. Early engagement builds support, generates valuable input, identifies concerns before they become obstacles, and creates ownership supporting long-term sustainability.
Assess Resources Realistically: Evaluate available budget for implementation and operations, staff capacity for content development and management, physical space for displays if applicable, technical infrastructure for digital systems, and timeline given other organizational priorities. Resource constraints don’t preclude recognition programs—they inform appropriate scale and phasing enabling success within realistic parameters rather than overambitious plans destined to fail.
Research and Benchmark: Review successful programs at comparable organizations, identify best practices applicable to your context, learn from others’ mistakes and successes, and adapt proven approaches rather than reinventing unnecessarily. Numerous organizations have successfully implemented halls of fame—learning from their experiences accelerates your success while avoiding common pitfalls.
Phase 2: Criteria Development and Selection Systems (Months 2-4)
Fair, transparent processes establish credibility essential for program acceptance and longevity.
Draft Eligibility Requirements: Establish waiting periods between achievement and eligibility, define participation or membership requirements, articulate character and conduct standards, and specify achievement thresholds warranting consideration. Document criteria clearly enabling community understanding of recognition standards while providing selection committees with concrete evaluation frameworks.
Create Nomination Processes: Develop standardized nomination forms requesting comprehensive information, establish annual nomination windows with clear deadlines, communicate processes through multiple channels ensuring broad awareness, and accept nominations from diverse sources preventing committee blind spots. Open, accessible nomination systems ensure deserving candidates receive consideration rather than limiting recognition to committee members’ personal knowledge.
Form Selection Committees: Recruit diverse members representing varied perspectives, establish clear term limits preventing stagnation, develop conflict of interest policies ensuring integrity, and provide committee members with training on criteria and evaluation processes. Committee composition directly impacts selection credibility—diverse, respected members following transparent processes generate community confidence in recognition decisions.

Document Decision Frameworks: Create evaluation rubrics scoring nominees consistently, establish voting procedures and thresholds, develop documentation systems maintaining institutional memory, and plan communication strategies for announcements and notifications. Structured frameworks ensure consistent application of criteria across all candidates and years while creating records enabling future committees to understand historical selection rationales.
Phase 3: Display and Technology Selection (Months 3-5)
Strategic technology choices balance functionality, budget, stakeholder preferences, and long-term sustainability.
Evaluate Display Options: Compare traditional physical recognition, modern digital interactive systems, hybrid approaches combining both, and web-based platforms emphasizing remote access. Each approach offers distinct advantages and limitations regarding capacity, content richness, maintenance requirements, and cost profiles. Understanding best platforms for building virtual hall of fame helps organizations make informed technology decisions.
Assess Budget Implications: Calculate total cost of ownership including initial hardware and software investment, installation and integration expenses, content development time and resources, ongoing licensing and support fees, and future expansion capabilities. Long-term analysis often reveals that digital systems achieving cost parity with traditional approaches within 5-7 years while delivering dramatically superior functionality justify higher initial investments.
Select Vendors and Partners: Research providers serving similar organizations, request demonstrations and reference checks, evaluate support quality and responsiveness, verify vendor stability and long-term viability, and negotiate clear terms for implementation, training, and ongoing service. Vendor selection ranks among the most consequential decisions—poor choices create frustration and limit program potential regardless of budget or planning quality.
Plan Physical Installation: Identify optimal locations maximizing visibility, verify electrical and network infrastructure, design mounting and enclosure specifications, coordinate with facilities for professional installation, and ensure accessibility compliance meeting all requirements. Thoughtful installation planning prevents expensive modifications correcting initial mistakes while ensuring recognition receives the prominent, professional presentation inductees deserve.
Phase 4: Content Development (Months 4-7)
Comprehensive profile creation represents the most time-intensive implementation phase determining ultimate recognition quality.
Research Historical Achievements: Review archives and institutional records, interview longtime staff and community members, examine yearbooks and publications, contact alumni for information and materials, and verify facts across multiple sources. Historical research requires sustained effort but creates recognition foundations honoring past excellence appropriately while preserving institutional memory that would otherwise fade.
Develop Initial Recognition Pool: Rather than attempting complete historical coverage immediately, strategic approaches begin with recent inductees for whom information is readily available, then systematically expand backward through earlier eras. Launching with 20-40 profiles creates immediate impact while establishing content development processes enabling efficient ongoing expansion.
Create Compelling Profiles: Write engaging narratives honoring achievements, select high-quality photographs representing inductees well, develop or obtain video content when feasible, organize information using consistent structure, and implement quality control ensuring accuracy and professional presentation. Profile quality directly determines recognition effectiveness—comprehensive, well-written content honors inductees appropriately while engaging audiences effectively. Strategies for creating engaging video content for digital hall of fame enhance multimedia recognition capabilities.

Establish Sustainable Workflows: Document content development processes enabling multiple contributors, create templates ensuring consistency, develop approval procedures maintaining quality standards, and plan annual cycles for new inductee addition. Sustainable workflows prevent volunteer or staff burnout while ensuring programs maintain consistent content quality across years and decades.
Phase 5: Launch and Promotion (Months 7-8)
Strategic launches generate awareness establishing recognition importance while building engagement patterns supporting long-term success.
Plan Induction Ceremonies: Schedule events around dates maximizing attendance, invite all inductees and their families, incorporate speeches and presentations, engage media for publicity coverage, and create memorable experiences honoring inductees appropriately. Ceremonies serve multiple purposes—recognizing achievements publicly, generating community awareness and excitement, and establishing annual traditions that become anticipated events.
Execute Marketing Campaigns: Announce program launch through multiple channels, create social media content featuring inductees, generate press releases for media coverage, produce printed materials and signage, and engage alumni networks promoting recognition. Sustained promotional efforts ensure entire community knows about recognition rather than displays languishing with minimal awareness beyond those who stumble upon them accidentally.
Conduct Soft Launch Testing: Before public launch, invite select stakeholders for preview access, gather feedback about functionality and content, identify technical issues requiring resolution, verify all systems work reliably, and make refinements based on testing. Soft launches prevent public embarrassment from easily correctable problems while demonstrating responsiveness to stakeholder input.
Celebrate Publicly and Prominently: Host unveiling events with institutional leadership present, recognize inaugural inductees with appropriate ceremony, demonstrate interactive features encouraging exploration, and generate enthusiasm establishing recognition as important institutional priority. High-profile launches communicate that organizations take recognition seriously while creating initial engagement momentum supporting sustained success.
Measuring Success and Continuous Improvement
Effective programs evaluate performance systematically and adapt based on data and feedback ensuring ongoing relevance and impact.
Key Performance Indicators
Quantifiable metrics demonstrate program value to stakeholders while identifying improvement opportunities.
Engagement Metrics: For digital systems, track total interactions and viewing sessions, average time spent exploring content, most-viewed profiles identifying popular content, search patterns showing discovery behaviors, and trends over time indicating sustained or declining interest. Engagement data demonstrates recognition value while informing content and feature priorities.
Program Growth Indicators: Monitor annual nominations and inductee additions, historical content expansion rate, total recognition pool growth, diversity across achievement categories, and comparison against program goals. Growth metrics show whether programs maintain momentum or stagnate after initial enthusiasm fades.
Alumni Relations Impact: Measure giving participation changes among recognized alumni, overall alumni engagement rate shifts, event attendance including induction ceremonies, inquiry and outreach volume increases, and qualitative feedback from alumni about recognition appreciation. Recognition programs should demonstrably strengthen alumni relationships—measuring these outcomes validates program investment.
Recruitment and Reputation Effects: Track prospective student or member awareness of recognition, media coverage frequency and reach, social media engagement and sharing, community perception surveys, and citation in recruitment materials. Recognition enhances organizational reputation—quantifying these effects demonstrates broader institutional value beyond internal engagement alone.
Resources on measuring ROI of digital alumni recognition provide frameworks for comprehensive program evaluation connecting recognition investment to measurable organizational outcomes.
Continuous Enhancement Strategies
Successful programs evolve continuously rather than remaining static after launch.
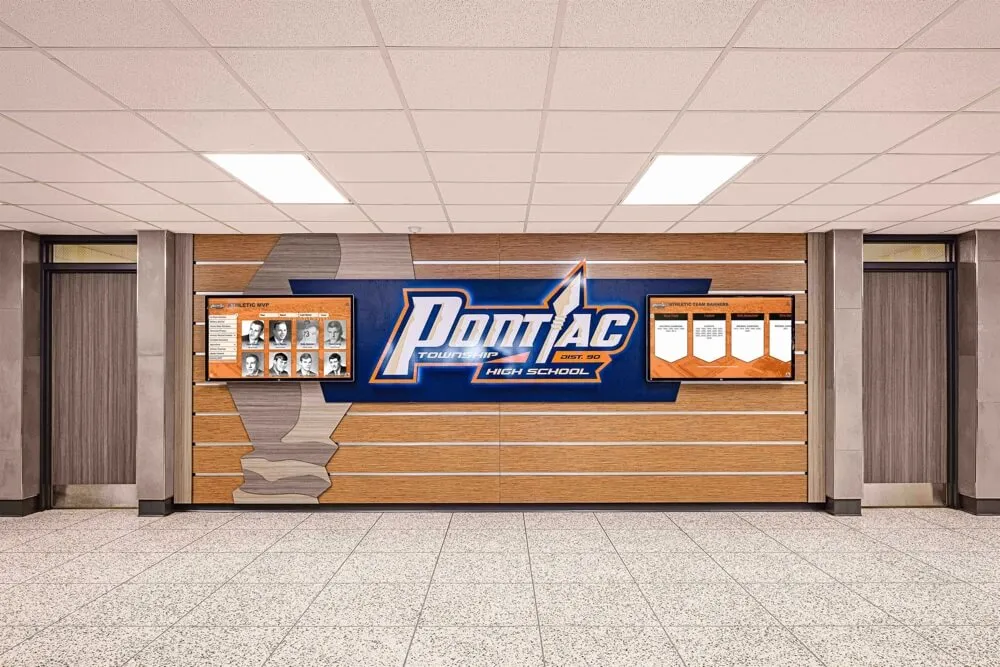

Regular Content Additions: Maintain momentum through annual inductee classes, systematic historical expansion, periodic profile enhancements, and featured content rotation. Continuous additions provide reasons for repeat engagement while demonstrating that programs remain active rather than abandoned after enthusiastic launches.
Technology Upgrades: Plan for periodic refreshes including software platform updates, hardware replacement as equipment ages, feature enhancements based on usage patterns, and integration with new systems. Technology should improve continuously—programs using decade-old systems appear neglected regardless of content quality.
Process Refinements: Adapt based on experience through criteria evolution addressing gaps or issues, nomination process improvements increasing participation, selection system adjustments improving fairness or efficiency, and event enhancement making induction ceremonies more impactful. No initial design proves perfect—successful programs learn from experience and improve systematically.
Community Feedback Integration: Systematically gather stakeholder input through user surveys, suggestion mechanisms, focus groups exploring specific topics, and informal conversation monitoring. Responsive adaptation to community feedback demonstrates that organizations value stakeholder perspectives while ensuring programs serve actual needs rather than assumed preferences.
Common Challenges and Practical Solutions
Organizations implementing hall of fame programs encounter predictable obstacles that proven approaches address effectively.
Limited Historical Information
Challenge: Many organizations discover incomplete records about past members complicate comprehensive historical recognition attempts.
Solutions: Conduct systematic archive research checking all available records, launch community-wide appeals requesting information and materials from those with long institutional memory, acknowledge documentation gaps transparently while inviting assistance filling them, and implement phased approaches beginning with well-documented recent achievements while expanding historically as information becomes available. Understanding digitizing yearbooks and historical records helps preserve and access institutional history systematically.
Selection Controversy and Perceived Bias
Challenge: Despite best intentions, selection decisions sometimes generate community concerns about fairness or favoritism.
Solutions: Maintain transparent criteria and processes documented publicly, ensure diverse selection committees representing varied perspectives, use written evaluation rubrics providing objective assessment frameworks, implement conflict of interest policies addressing committee member relationships with nominees, and communicate decision rationales when appropriate while respecting confidentiality. When concerns arise, address questions directly and professionally while maintaining process integrity.
Maintaining Long-Term Momentum
Challenge: Initial launch excitement often fades without strategic attention to sustained relevance and engagement.
Solutions: Establish regular operating cycles ensuring annual activity, continuously enhance content keeping recognition fresh, integrate with ongoing institutional events like reunions or fundraising campaigns, measure and communicate impact demonstrating program value, and ensure adequate resources preventing program neglect when priorities shift. Programs viewing recognition as ongoing commitment rather than one-time project achieve lasting impact.
Budget Constraints and Resource Limitations
Challenge: Financial and staffing constraints affect implementation scope and sustainability for many organizations.
Solutions: Implement phased approaches matching available resources, explore creative funding through alumni contributions or corporate sponsorships, engage volunteers for content research and development, select purpose-built platforms minimizing technical complexity, and conduct long-term cost analysis demonstrating that digital systems often achieve parity with ongoing physical recognition expenses. Many successful programs start modestly, demonstrate value, then expand as additional resources become available.
Conclusion: Building Recognition Legacies That Inspire Generations
Hall of fame programs represent powerful institutional tools for honoring excellence, inspiring achievement, preserving history, and building community pride. When thoughtfully designed and consistently maintained, recognition programs deliver lasting benefits extending far beyond simple acknowledgment of past accomplishment.
The most successful programs share common characteristics including clear criteria ensuring fairness and credibility, professional displays commanding respect and attention, compelling content honoring inductees appropriately while engaging audiences, sustainable operations maintaining program vitality long-term, and strategic integration with broader organizational objectives including engagement, fundraising, and reputation building.
For organizations beginning recognition programs, starting with solid foundations sets the stage for long-term success. Well-defined selection standards create credibility. Structured nomination processes ensure community participation. Realistic resource planning enables sustainable operations. Manageable initial scope allows demonstration of value supporting expansion over time.
Modern digital recognition solutions like those from Rocket Alumni Solutions offer particular advantages for organizations seeking comprehensive, flexible, cost-effective recognition. Unlimited capacity accommodates all deserving honorees without space constraints. Rich multimedia tells compelling stories honoring achievements appropriately. Instant updates eliminate physical modification costs and delays. Remote accessibility extends engagement globally beyond physical visitors. Analytics demonstrate program value quantitatively while informing continuous improvement.
Whether organizations choose traditional physical displays, cutting-edge interactive systems, hybrid approaches, or web-based platforms, the core principles remain constant: transparent selection processes, professional presentation standards, comprehensive content development, sustained operational commitment, and continuous adaptation based on experience and feedback.
Beyond immediate recognition purposes, effective hall of fame programs strengthen bonds connecting past, present, and future organizational community members. They demonstrate that institutions value excellence across diverse domains, inspire current participants to pursue their own paths to achievement, and create tangible connections between today’s members and accomplished predecessors who once occupied the same roles, facilities, and communities.
Organizations ready to create recognition programs can explore additional resources on interactive hall of fame systems, digital wall of fame benefits, and alumni recognition walls that maximize impact while creating manageable, sustainable programs honoring distinguished members for generations to come.
Hall of fame recognition honors the past, inspires the present, and shapes the future—preserving excellence for those yet to come while demonstrating that extraordinary achievement deserves permanent commemoration. The legends you honor today become the inspiration for tomorrow’s excellence, creating cycles of achievement that strengthen organizations and communities across generations.