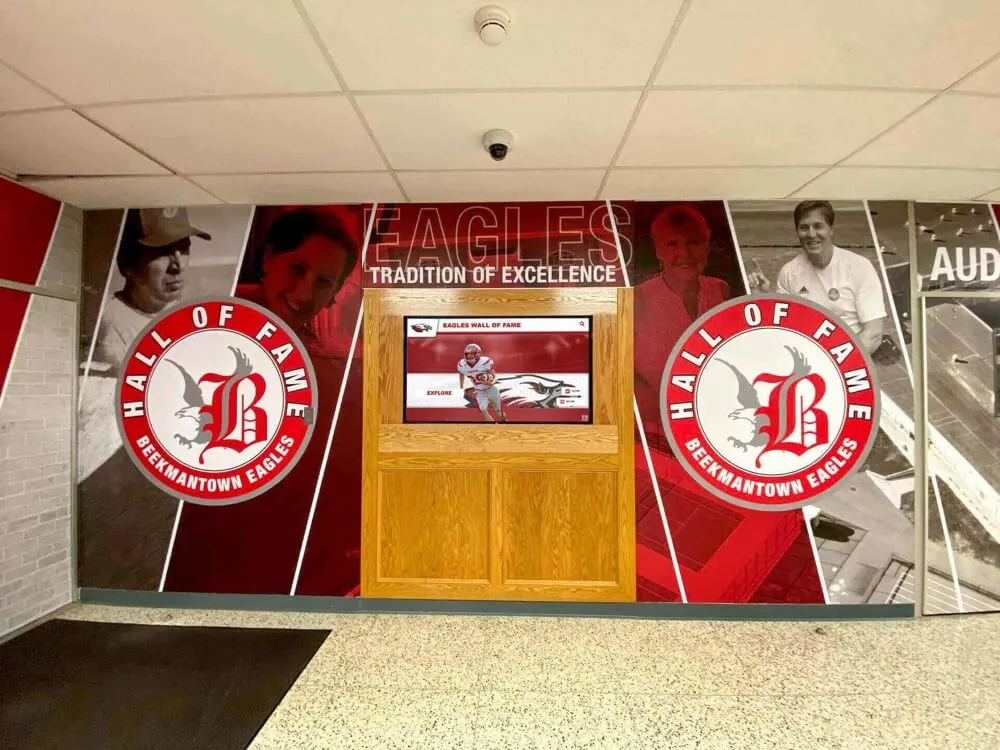
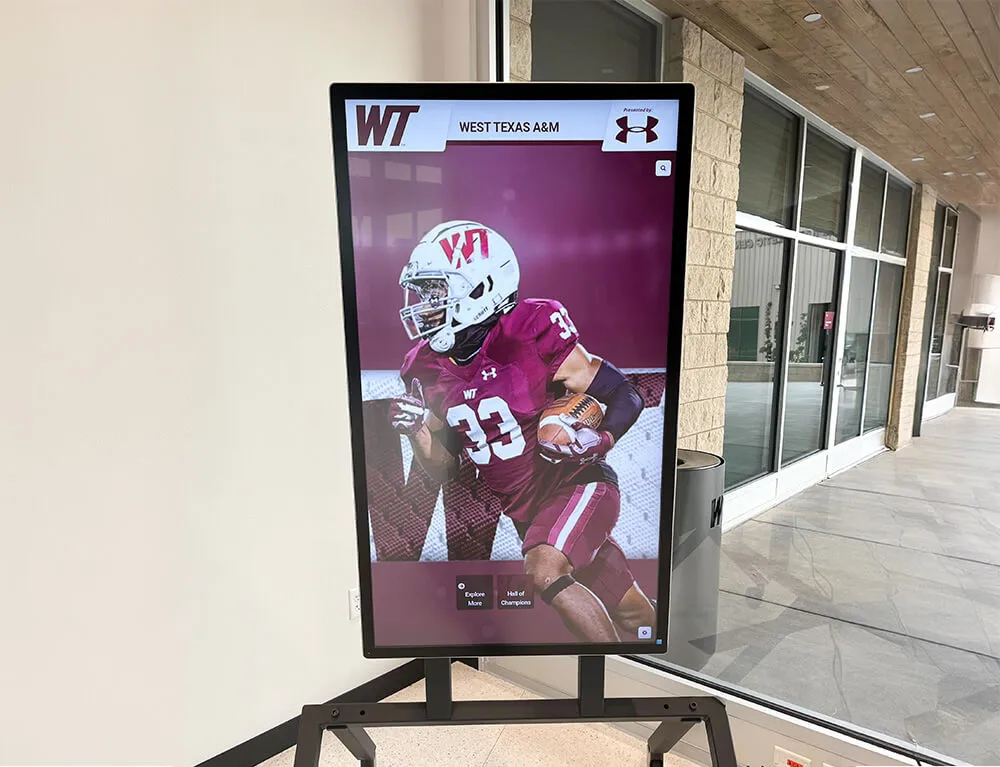
Educational institutions have long recognized that celebrating academic achievement serves purposes far beyond simple acknowledgment. A well-designed Hall of Achievement creates visible inspiration for students, builds institutional pride, honors intellectual excellence, and demonstrates that schools value achievement across all domains—not just athletics. Yet many schools struggle to showcase academic accomplishments effectively, often due to space constraints, outdated display methods, or lack of systematic recognition processes.
Hall of Achievement programs represent strategic investments in academic culture, establishing formal recognition that academic excellence matters as much as athletic success or artistic accomplishment. These programs create tangible proof that intellectual effort leads to meaningful recognition, inspire current students through role models who achieved academic distinction, preserve institutional history of scholastic excellence, strengthen community pride in educational quality, and demonstrate school commitment to comprehensive student development.
Why Academic Recognition Matters More Than Ever
In an era where schools face increasing pressure to demonstrate educational quality and student outcomes, comprehensive Hall of Achievement programs provide visible evidence of scholastic excellence. When implemented thoughtfully through platforms like Rocket Alumni Solutions, these recognition systems motivate students, engage families, and showcase institutional commitment to academic achievement while honoring individuals who demonstrated exceptional intellectual dedication.
Understanding Hall of Achievement vs. Hall of Fame
While related concepts, Hall of Achievement and Hall of Fame programs serve distinct purposes and recognize different accomplishment types within educational communities.
Defining Academic Achievement Recognition
Hall of Achievement programs specifically celebrate scholastic accomplishments, academic honors, and intellectual excellence separate from athletic or extracurricular recognition.
Academic Focus and Distinction: Traditional halls of fame often emphasize athletic achievement, sometimes overshadowing academic excellence despite schools’ primary educational missions. Dedicated Hall of Achievement recognition corrects this imbalance by creating equivalent prominence for scholarly accomplishments including valedictorians and salutatorians, National Merit Scholars and semifinalists, perfect attendance records spanning years, academic competition champions in math, science, debate, and other intellectual domains, scholarship recipients earning significant merit-based awards, and graduates admitted to highly selective universities.

Balanced Recognition Philosophy: Schools implementing both athletic halls of fame and academic halls of achievement communicate powerful messages about institutional values. Equivalent physical prominence, investment, and celebration for academic and athletic recognition demonstrates that schools genuinely value intellectual achievement as highly as sports success. This balanced approach inspires academically-focused students who may not participate in athletics while reinforcing that comprehensive excellence spans multiple domains.
Research on highlighting student accomplishments demonstrates that schools emphasizing diverse achievement types experience higher overall student engagement, improved academic performance, and stronger community pride compared to institutions focusing recognition narrowly on single domains.
Achievement Categories Typically Recognized
Comprehensive Hall of Achievement programs honor diverse forms of academic excellence reflecting multiple pathways to scholastic distinction.
Academic Performance Recognition includes graduates achieving highest academic honors (valedictorians, salutatorians, summa cum laude), students maintaining exceptional GPAs across multiple years, perfect attendance records demonstrating sustained commitment, and academic improvement awards recognizing remarkable growth trajectories. These performance-based recognitions reward consistent effort and dedication over time rather than single test scores or momentary achievements.
Competition and Contest Excellence celebrates students who compete successfully at state, national, or international levels in academic domains including mathematics competitions (MATHCOUNTS, AMC, USAMO), science olympiads and research competitions, debate and forensics championships, spelling bees and geography competitions, writing contests and journalism awards, and technology competitions like robotics or coding challenges. Competition success demonstrates exceptional preparation, skill, and ability to perform under pressure—valuable attributes deserving recognition.
Scholarship and Higher Education Recognition honors students earning significant merit-based scholarships, National Merit Scholarship Program recognition at all levels, acceptance to highly selective colleges and universities, students earning full academic scholarships, and recipients of prestigious awards like Presidential Scholars. These honors reflect achievement recognized beyond the school by external organizations and institutions validating accomplishment significance.
Subject-Specific Excellence recognizes outstanding achievement in particular academic disciplines through departmental awards for highest achievement in mathematics, science, English, history, world languages, arts, or other subjects, perfect scores on standardized subject tests, publication of student research or creative works, and recognition by professional organizations in specific fields. Subject-specific honors acknowledge depth of expertise and passion for particular intellectual domains.
Understanding comprehensive frameworks for student awards recognition programs helps schools develop balanced systems celebrating diverse achievement types while maintaining high standards ensuring recognition remains meaningful.
The Strategic Value of Academic Recognition Programs
Hall of Achievement programs deliver measurable benefits extending far beyond simply making students feel appreciated—they fundamentally shape school culture, motivation patterns, and educational outcomes.
Inspiring Academic Excellence Through Role Models
Visible recognition of past achievers creates aspirational examples motivating current students toward higher academic performance.
Personalized Inspiration Through Relatability: When students discover Hall of Achievement inductees who share similar backgrounds, interests, or challenges, motivation increases dramatically. A first-generation student sees previous first-generation graduates earning National Merit recognition and prestigious university acceptances. An English language learner explores past ELL students who became valedictorians. Students facing learning disabilities discover previous students with similar challenges who achieved academic distinction through persistence and support. These personalized connections inspire far more effectively than generic motivational messaging.
According to educational research, schools implementing comprehensive academic recognition report average improvements of 15-25% in honor roll qualification rates and 30-45% increases in academic competition participation within three years of program launch. These improvements stem from increased visibility of academic achievement paths, peer influence as recognition becomes socially valued, family engagement in supporting academic pursuits, and student belief that exceptional achievement is attainable rather than impossible.
Documentation of Achievement Pathways: Comprehensive profiles showing inductees’ complete academic journeys help students understand that excellence develops through sustained effort. Seeing specific study habits, courses, teachers, and activities that contributed to achievement provides actionable guidance rather than vague inspiration. Students learn that today’s top scholars once faced similar challenges, making exceptional academic performance feel attainable through concrete steps rather than innate talent alone.
Strategies for student engagement in modern schools reveal how recognition programs serve as foundations for broader academic motivation initiatives delivering sustained improvement in educational outcomes.
Strengthening School Pride and Institutional Identity
Academic recognition programs build community pride while communicating institutional values clearly to stakeholders.

Community Pride in Educational Quality: Comprehensive academic recognition provides tangible evidence of educational excellence that parents, community members, and stakeholders can see and appreciate. During open houses, prospective family visits, and community events, Hall of Achievement displays demonstrate institutional commitment to intellectual development and provide objective proof of academic quality. Unlike claims about educational excellence, recognized achievements represent verifiable, concrete evidence of scholastic outcomes.
Institutional Values Communication: Schools investing equivalent resources in academic recognition as athletic recognition send powerful messages about what they genuinely value. Physical prominence, ceremony quality, and ongoing attention to academic halls of achievement communicate that intellectual excellence matters as much as any other achievement domain. This values alignment attracts families prioritizing academics while reinforcing culture emphasizing comprehensive excellence.
Research on building school pride demonstrates that institutions with balanced recognition across athletics, academics, and arts experience stronger community engagement, improved retention rates, and enhanced reputation compared to schools emphasizing single achievement domains while neglecting others.
Enhancing Recruitment and Reputation
Hall of Achievement programs serve strategic recruitment and marketing objectives by demonstrating educational quality through concrete evidence.
Prospective Family Confidence: During campus tours and admissions events, comprehensive academic recognition reassures prospective families about educational quality and college preparation. Parents and students see graduates achieving National Merit recognition, earning acceptances to prestigious universities, winning academic competitions, and receiving substantial scholarships—objective evidence validating institutional claims about academic excellence. This confidence influences enrollment decisions particularly among families prioritizing academic rigor and college readiness.
Staff Recruitment and Retention: Accomplished educators seek schools genuinely valuing academic achievement beyond rhetoric. Comprehensive Hall of Achievement recognition demonstrates institutional commitment attracting high-quality teachers, strengthens staff pride in institutional affiliation and achievement, provides teachers with visible examples of impact on student success, and creates positive work environment where intellectual development receives appropriate recognition. These factors improve both educator recruitment and retention in competitive employment markets.
Resources on how recognition solutions build community belonging explore how academic recognition programs contribute to comprehensive school culture supporting student success, staff satisfaction, and institutional effectiveness simultaneously.
Designing Effective Hall of Achievement Programs
Successful academic recognition requires thoughtful program design addressing selection criteria, nomination processes, content development, and display formats ensuring long-term sustainability and community respect.
Establishing Fair Selection Criteria
Credible recognition programs require transparent, consistent standards that community members understand and trust as fair and meaningful.
Achievement Threshold Setting: Criteria should remain appropriately selective—maintaining standards that make induction genuinely meaningful—while accessible enough that students see achievement as possible through hard work. Common approaches include recognizing top percentage of graduating class (top 5% or 10%), specific GPA thresholds (4.0 or above on weighted scale), National Merit recognition at any level, state or national competition placement (top 3 or top 10), and significant merit scholarship awards (full tuition or above). Clear numerical standards provide objectivity while enabling consistent evaluation across years.

Multiple Achievement Pathways: Effective programs recognize that academic excellence manifests through diverse accomplishments beyond GPA alone. Systems honoring various achievement types ensure students with different strengths find recognition pathways including high cumulative GPA, exceptional single-year or final-semester achievement, competition and contest success, scholarship and honor program recognition, research publication or presentation, and significant academic improvement trajectories. Multiple pathways prevent programs from becoming exclusive clubs accessible only through specific achievement types while recognizing diverse forms of intellectual excellence.
Character and Conduct Standards: Beyond academic metrics, most credible programs require exemplary behavior ensuring recognized students represent role models appropriate for younger students to emulate. Character standards should address academic integrity (no significant cheating or plagiarism incidents), general conduct alignment with school behavioral expectations, positive peer relationships and collaborative approaches, and respect for teachers, staff, and community members. These standards protect program credibility while ensuring recognition celebrates not just intelligence but complete individuals demonstrating values schools seek to cultivate.
Guidance on creating comprehensive recognition programs provides frameworks for developing selection criteria that community members respect as fair, transparent, and appropriately rigorous while remaining attainable through genuine effort.
Nomination and Selection Processes
Structured approaches ensure comprehensive candidate identification and consistent evaluation maintaining program credibility.
Nomination Source Diversity: Effective programs gather candidates through multiple channels preventing oversight of deserving students including automatic consideration of students meeting specific GPA or honor thresholds, teacher and counselor nominations recognizing students who may not reach automatic thresholds but demonstrate exceptional characteristics, self-nominations with required documentation enabling students to advocate for their achievements, parent and community nominations supplementing institutional knowledge, and systematic transcript review ensuring no qualifying student is inadvertently omitted. Multiple sources create comprehensive candidate pools rather than relying on institutional memory or limited perspectives alone.
Evaluation Committee Composition: Diverse selection committees ensure balanced assessment including faculty representatives from multiple academic departments, counseling staff with comprehensive student knowledge, administration members providing institutional perspective, community representatives offering external viewpoints, and when appropriate, student representatives contributing peer perspective. Committee diversity prevents individual bias from dominating decisions while bringing varied expertise to candidate evaluation. Clear term limits maintain continuity while regularly adding fresh perspectives.
Documentation and Transparency: Maintaining clear records and communication supports long-term program credibility through written evaluation rubrics scoring candidates consistently against established criteria, documentation of selection rationales preserving institutional memory, transparent communication about selection timelines and processes, and feedback mechanisms enabling community input about criteria or processes when appropriate. These practices demonstrate systematic rigor generating community confidence in recognition integrity.
Display Formats for Academic Recognition
How schools present Hall of Achievement recognition significantly impacts visibility, engagement, accessibility, and long-term sustainability. Understanding available options helps institutions choose approaches aligned with objectives and resources.
Traditional Physical Recognition Methods
Classic display formats maintain symbolic permanence and formal dignity some schools and stakeholders value highly for academic recognition.
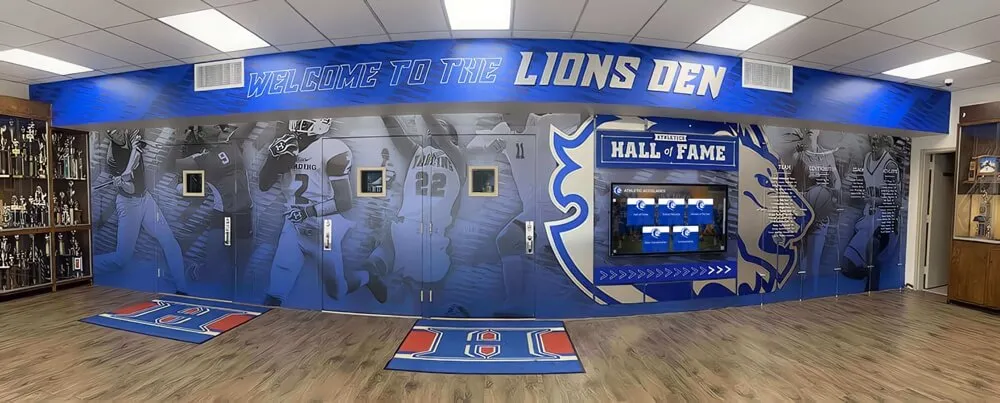
Engraved Plaques and Boards: Traditional recognition through wall-mounted plaques featuring inductee names, graduation years, and specific achievements communicates formal institutional acknowledgment. These displays typically cost $50-150 per inductee for professional engraving and materials, with installation adding additional expenses. Physical plaques convey permanence and dignity particularly meaningful to families and honored students themselves.
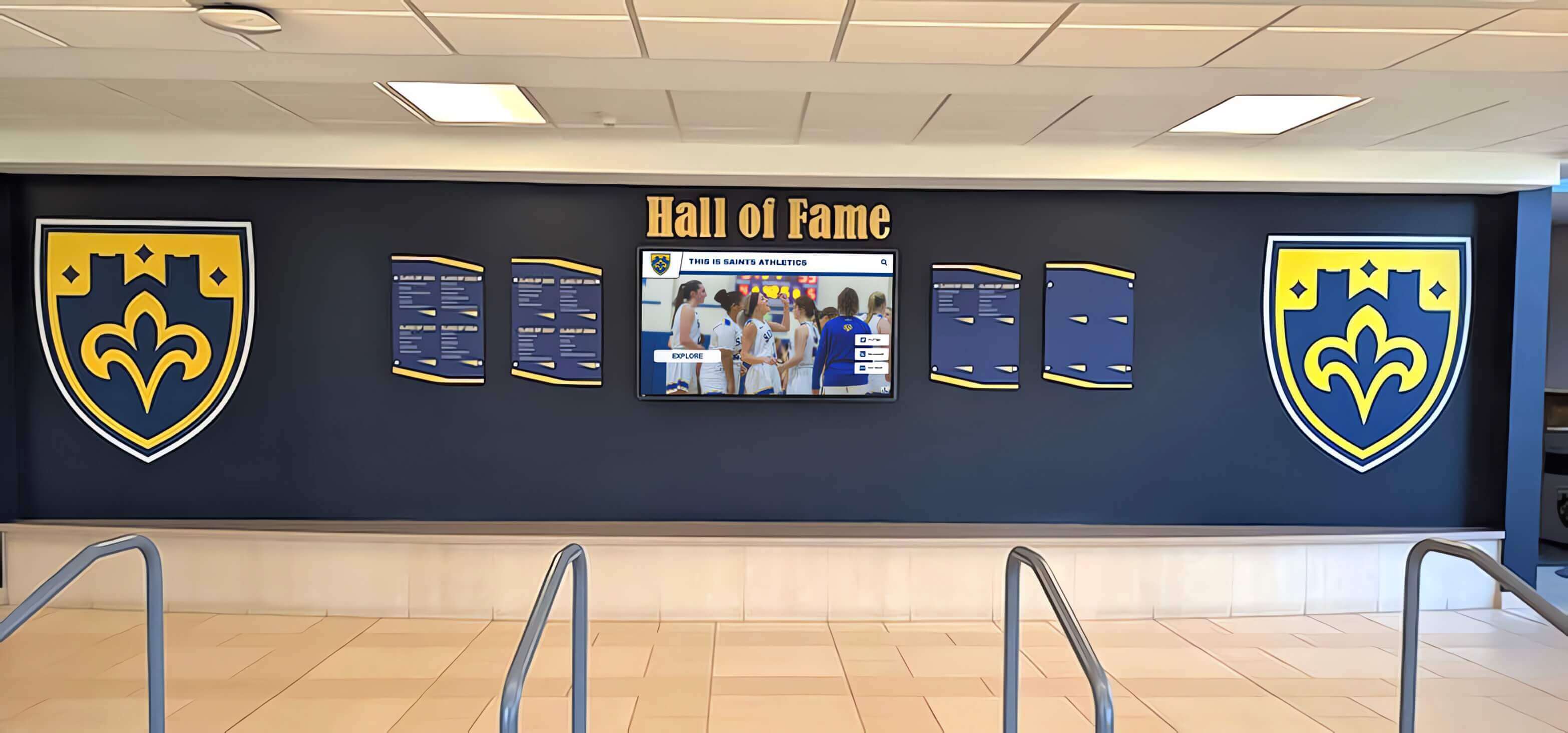

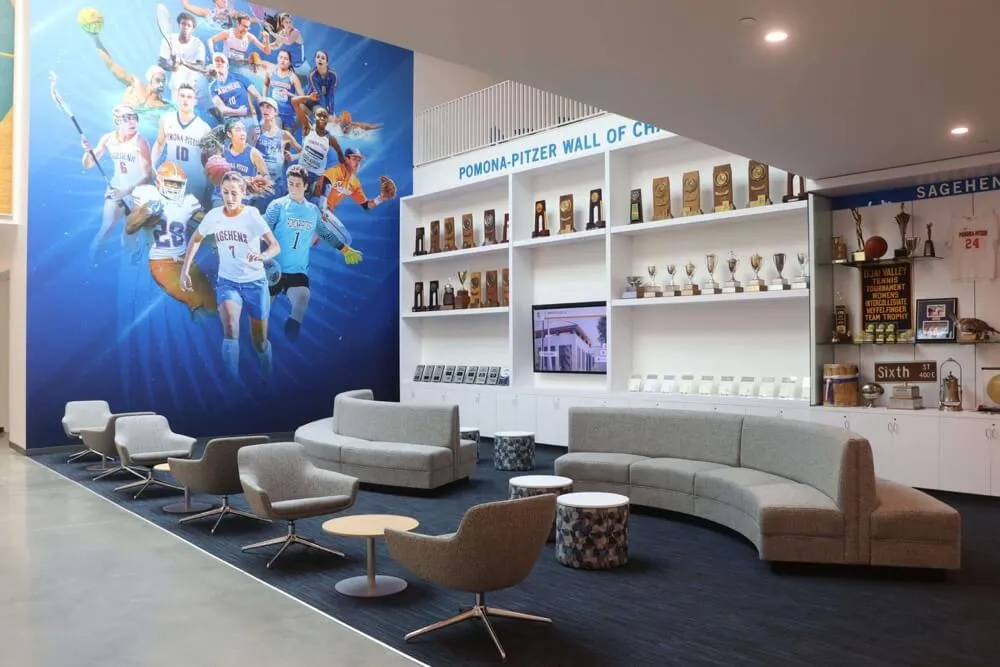
Display Case Recognition: Three-dimensional cases showcase physical evidence of achievement including original certificates and award documentation, academic competition trophies and medals, scholarship notification letters, acceptance letters from prestigious universities, published student research or creative works, and photographs of inductees at academic events. Display cases create impressive visual impact while enabling tangible connection to actual achievements rather than just names on walls.
Limitations of Physical-Only Approaches: Despite symbolic value, traditional recognition faces significant constraints including finite physical capacity forcing difficult decisions as more students achieve recognition annually, high per-inductee costs for materials, engraving, and professional installation, update delays requiring physical production and mounting new plaques, limited information capacity beyond basic names and achievements, no search functionality for finding specific inductees, geographic restriction limiting visibility to campus visitors only, and ongoing maintenance requirements including cleaning, damage repair, and periodic refurbishment.
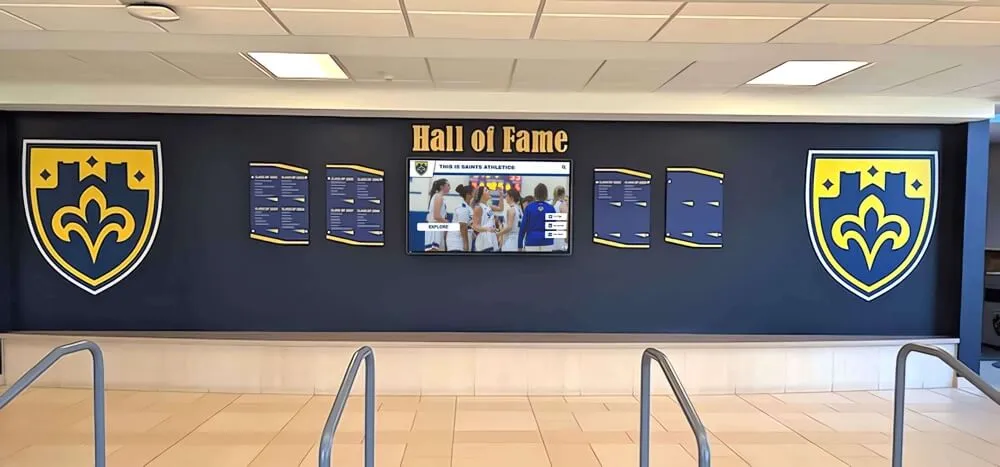
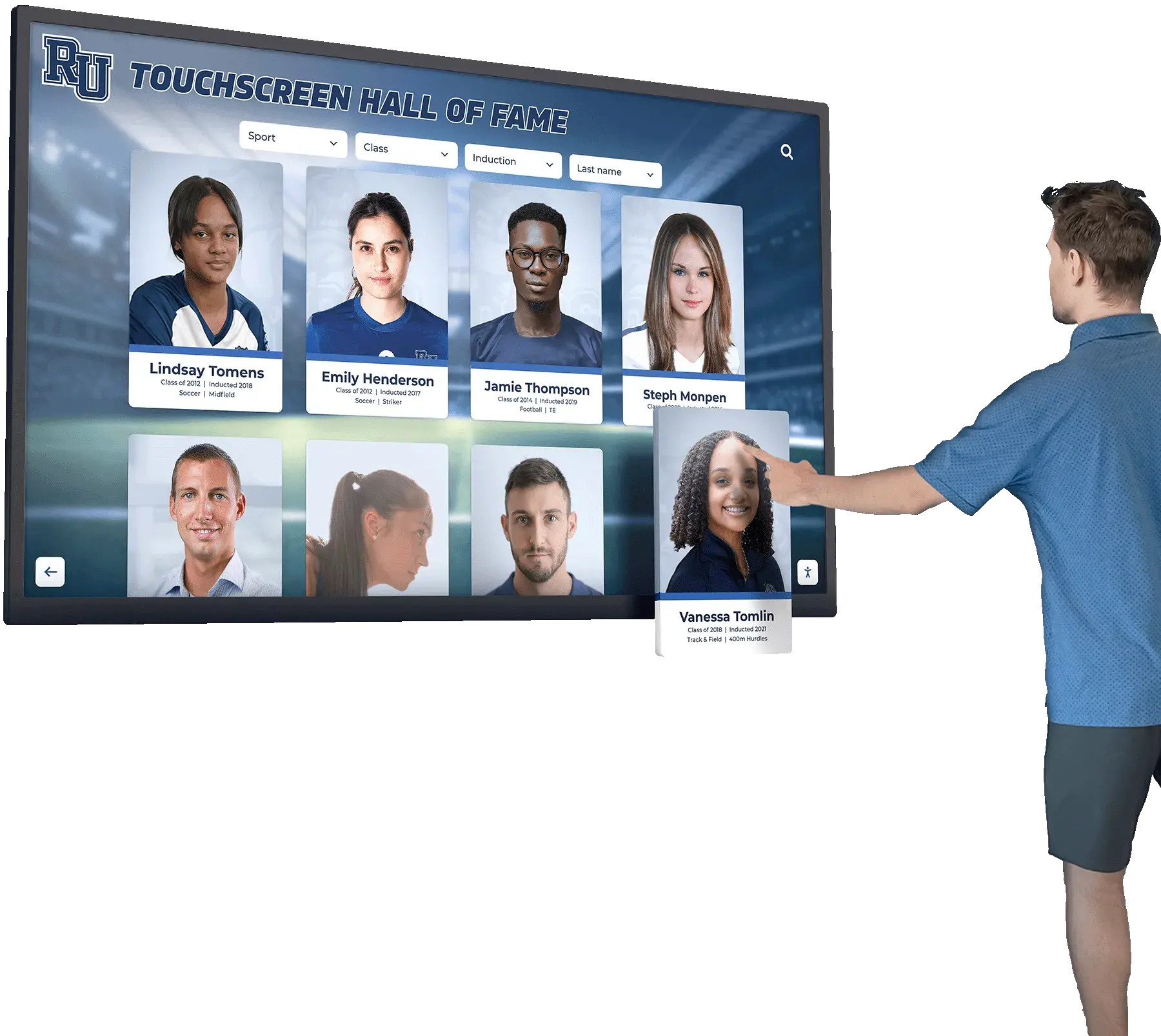
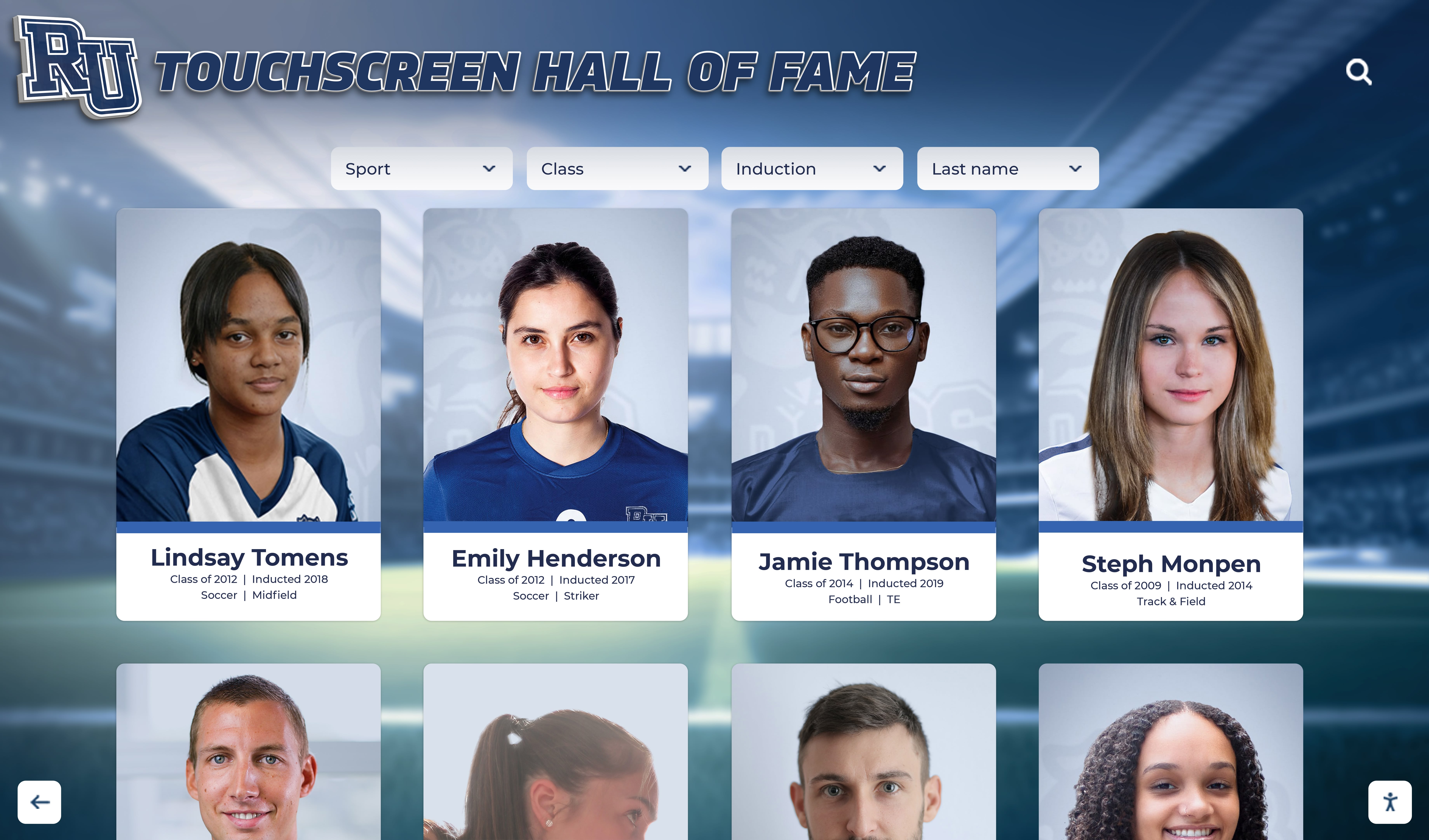
Digital Interactive Hall of Achievement Systems
Modern technology addresses every limitation of traditional approaches while introducing capabilities impossible with physical-only displays.
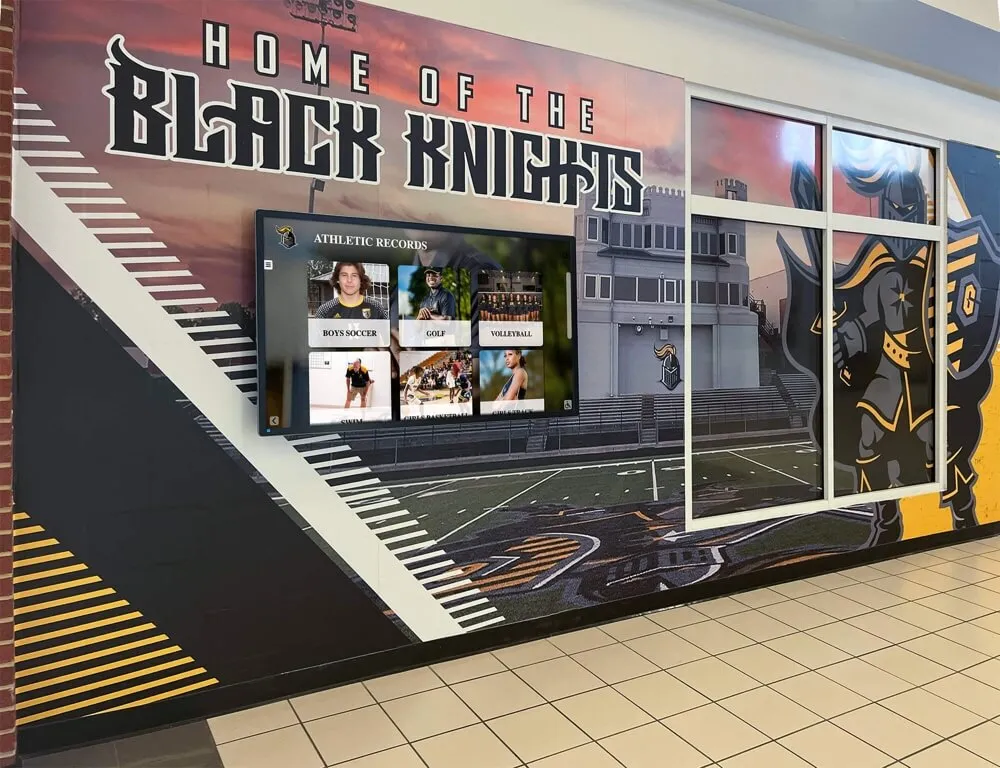
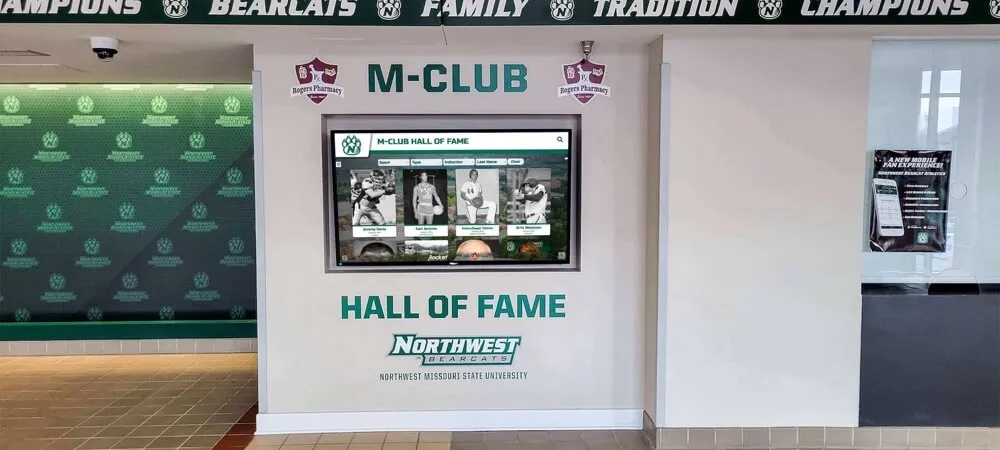
Unlimited Recognition Capacity: Digital systems accommodate hundreds or thousands of academic achievement profiles without physical space constraints. A single touchscreen display provides access to comprehensive recognition limited only by content development rather than wall space. This unlimited capacity means every deserving student receives appropriate recognition regardless of how many others achieved distinction in previous years. Schools never face decisions about removing old recognition to accommodate new inductees or limiting annual induction numbers based on space rather than achievement merit.
Rich Multimedia Storytelling: Digital profiles support extensive content including professional photography showing students during academic achievements, video interviews where inductees share advice and reflect on journeys, quotes about favorite teachers or formative experiences, detailed biographical narratives describing specific accomplishments, achievement documentation through certificates and awards, college choice information and scholarship details, current occupation updates for graduated inductees, and career progression showing how academic achievement translated to professional success.

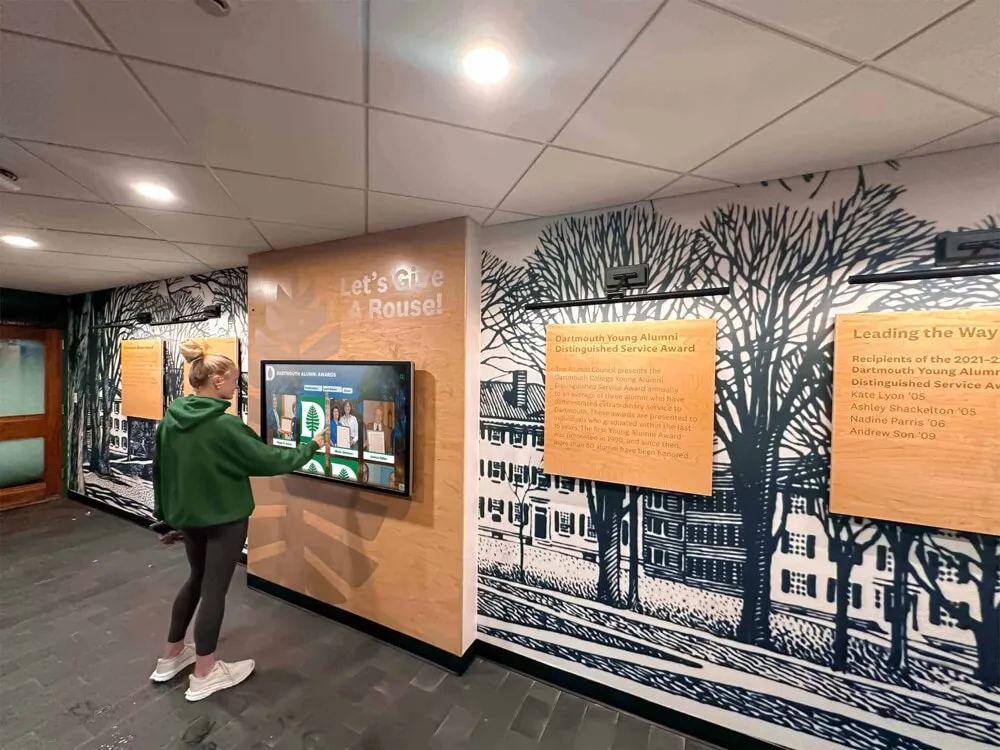
Interactive Discovery and Engagement: Robust search enables finding specific inductees instantly by name, graduation year, achievement type (valedictorian, National Merit, competition winner), college attended, scholarship type, or academic subject area. Browsing tools allow chronological exploration showing recognition by decade or year, category-based organization by achievement domain, featured content rotation highlighting diverse accomplishments and underrepresented achievement types, and related profile suggestions encouraging extended exploration. These discovery capabilities generate extended engagement—visitors spend significantly more time exploring digital recognition compared to viewing static displays.
Web Accessibility and Remote Viewing: Modern recognition systems extend beyond physical campus locations through responsive websites accessible from any device enabling families to share recognition remotely, mobile companion apps providing portable access during campus events, social media integration enabling easy sharing of individual achievements, and QR code connections linking physical spaces to expanded digital content. This accessibility multiplies engagement exponentially—recognized students share achievements with extended family worldwide, alumni revisit their recognition years after graduation, and prospective families explore academic culture before visiting campus.
Analytics Informing Program Optimization: Digital systems generate valuable data revealing which achievement types generate most interest, popular search terms showing how visitors discover content, session duration indicating engagement depth, time-based patterns showing peak usage periods, and demographic information about who accesses recognition. These insights inform content development priorities, promotional strategies, and program refinements impossible with traditional displays offering no feedback about viewer engagement.
Solutions like digital wall of achievement demonstrate how technology creates comprehensive, engaging recognition programs honoring academic excellence appropriately while remaining easily updatable as new achievements emerge annually.
Hybrid Implementation Strategies
Many successful programs combine selective traditional recognition with comprehensive digital systems, balancing symbolic permanence with practical functionality.
Strategic Hybrid Approaches might include maintaining signature physical plaques for highest-profile achievements like valedictorians and National Merit Scholars, adding digital touchscreens providing unlimited capacity for comprehensive recognition of all honor students, integrating QR codes on physical plaques linking to expanded digital profiles with additional photos and details, and ensuring web accessibility for alumni and community members regardless of physical display format. This balanced strategy honors tradition while solving practical limitations through modern technology, often satisfying stakeholders preferring physical permanence while enabling comprehensive recognition digital systems make possible.
Content Development for Academic Profiles
Recognition value depends on content quality, not just existence. The best Hall of Achievement programs tell complete, engaging stories rather than presenting minimal information.
Essential Profile Elements
Comprehensive profiles should include specific information creating complete pictures of achievements, journeys, and advice for current students.
Basic Biographical Information: Standard elements providing context including full name and preferred name format, graduation year establishing historical context, photograph showing student during school years (yearbook photo, academic event, or formal portrait), current city and state showing post-graduation trajectory, and when applicable, current occupation demonstrating how academic achievement translated to professional success. Basic information enables quick identification while situating achievement within broader institutional history.
Academic Achievement Documentation: Specific accomplishments warranting recognition including cumulative GPA and class rank quantifying performance, specific honors (valedictorian, salutatorian, honor graduate), National Merit Program recognition at any level, academic competition success with specific placements and competitions, scholarship details including scholarship names and amounts, college acceptance information particularly for highly selective institutions, and advanced coursework documentation like AP courses and scores or dual enrollment participation. Specific details demonstrate achievement depth while providing inspiration and guidance for current students pursuing similar paths.

Formative Experiences and Influences: Context helping students understand achievement development including favorite teachers or classes that proved particularly influential, extracurricular activities complementing academic pursuits, study strategies or approaches that contributed to success, challenges overcome demonstrating persistence and resilience, and peer or mentor relationships supporting academic development. This contextual information makes extraordinary achievement feel attainable by showing concrete factors contributing to success rather than attributing excellence to innate talent alone.
Advice and Reflections for Students: First-person content creates authentic connections including advice for current students pursuing academic excellence, reflections on what they wish they had known during school years, thoughts on balancing academics with other life dimensions, messages about values or principles guiding their educational approach, and expressions of gratitude toward teachers, families, or others who supported their success. Personal narratives humanize achievements making honored students relatable role models rather than distant, unreachable examples.
Writing Principles for Engaging Recognition
Effective profile writing balances formality appropriate for honoring distinguished achievements with accessibility engaging diverse audiences.
Active Voice and Dynamic Language: Profiles should use action verbs and engaging syntax rather than passive, bureaucratic language. “Sarah mastered challenging AP coursework while competing nationally in mathematics competitions” engages more effectively than “coursework was completed by Sarah and competitions were participated in.” Dynamic writing makes achievements come alive rather than reading like résumé bullet points.
Specific Examples Over Vague Praise: Rather than general statements like “outstanding student” or “remarkable achievement,” compelling profiles provide concrete details: “maintained 4.8 weighted GPA while taking 12 AP courses and scoring 5 on all exams” or “placed first in state science olympiad three consecutive years, advancing to national competition twice.” Specific information gives audiences clear understanding of actual accomplishment scope while demonstrating achievement depth and significance.
Accessible Vocabulary: Profiles should avoid jargon or technical terminology making content inaccessible to general audiences. When technical terms prove necessary for accuracy (specific scholarship program names, standardized test acronyms), brief explanations ensure understanding. Recognition serves students, families, and community members—writing should engage all audiences effectively without requiring specialized knowledge to comprehend achievement significance.
Resources on storytelling through digital recognition provide frameworks for developing compelling narratives that honor achievements authentically while inspiring and engaging diverse audiences effectively.
Implementing Your Hall of Achievement Program
Successful academic recognition results from systematic planning addressing program foundation, selection processes, content development, technology selection, and ongoing management.
Phase 1: Program Foundation and Planning (Months 1-2)
Comprehensive planning prevents common pitfalls while establishing strong program foundations supporting long-term success.
Stakeholder Engagement and Objective Setting: Involve diverse perspectives early ensuring broad support including academic department chairs understanding subject-specific excellence, counseling staff with comprehensive student knowledge, administration providing institutional priorities and resources, technology staff addressing implementation requirements, and parent representatives offering family perspectives. Engage stakeholders to define clear objectives including primary purposes (student motivation, institutional pride, recruitment support), target audiences (current students, prospective families, alumni, community), success metrics for program evaluation, and timeline considering other institutional priorities.

Resource Assessment and Budget Planning: Realistic evaluation of available resources prevents underinvestment or unsustainable commitments including budget for initial implementation (displays, technology, content development), ongoing operational funding (annual updates, maintenance, content expansion), staff capacity for program management and content creation, physical space for displays if using traditional or hybrid approaches, and technical infrastructure supporting digital systems including network connectivity and support. Understanding best platforms for virtual hall of fame helps schools make informed decisions about technology investments and long-term costs.
Criteria Development and Documentation: Establish clear, transparent standards community members understand and trust including specific achievement thresholds warranting recognition, multiple achievement pathways recognizing diverse excellence forms, character and conduct expectations ensuring appropriate role models, nomination and evaluation processes ensuring fair, comprehensive candidate identification, and documentation practices maintaining institutional memory and process credibility across years.
Phase 2: Content Collection and Profile Development (Months 2-4)
Systematic content development ensures manageable, sustainable profile creation supporting program launch and ongoing growth.
Initial Recognition Pool Strategy: Rather than attempting comprehensive historical coverage immediately, strategic approaches begin with current or recent graduates for whom information is readily available and most relevant to current students, then systematically expand backward through historical eras as resources allow. Many successful programs launch with 20-40 most recent distinguished graduates creating immediate impact while establishing content development processes, then add historical profiles systematically in subsequent years.
Efficient Content Collection Processes: Establish streamlined methods for gathering comprehensive information including direct outreach to recognized students requesting information, photos, and quotes, parent outreach supplementing student-provided information and collecting childhood photos, teacher and counselor interviews providing perspective on student characteristics and development, archival research checking institutional records for verification, and quality control review ensuring accuracy, consistency, and appropriate tone across all profiles.
Multimedia Asset Development: Beyond text, compelling recognition requires quality visual content through recent photograph collection showing students during school years, professional photo scanning from yearbooks ensuring quality digital copies, certificate and award documentation photographing evidence of specific achievements, and when possible, video interview recording where inductees share advice and reflections for current students.
Phase 3: Technology Selection and Display Implementation (Months 3-5)
For institutions choosing digital recognition, careful technology evaluation ensures platforms serve objectives effectively while fitting resources and capabilities.
Platform Evaluation Criteria: Essential considerations include content management ease for non-technical staff updating information regularly, user interface intuitiveness ensuring accessibility for all ages and abilities, total cost of ownership including hardware, software, licensing, support, and future updates, vendor reputation and support quality based on references and track record, scalability supporting future expansion without platform changes, and integration capabilities connecting with existing school systems when valuable. Platforms specifically designed for educational recognition like Rocket Alumni Solutions offer particular advantages through purpose-built features, K-12 and higher education experience, and support understanding institutional needs.
Hardware Selection and Installation: If implementing physical touchscreen displays, consider commercial-grade displays rated for continuous operation (not consumer models), minimum 4K resolution for professional presentation quality, appropriate screen size for viewing distance and space (commonly 43"-65" for most school installations), secure mounting with professional cable management, reliable touch technology supporting intuitive interaction, and appropriate placement in high-traffic areas maximizing visibility while meeting accessibility requirements.
Understanding touchscreen hall of fame systems helps schools make informed decisions about technology platforms, hardware specifications, and implementation approaches maximizing recognition effectiveness while fitting institutional contexts and budgets.
Phase 4: Launch and Promotion (Month 5-6)
Strategic launches generate awareness establishing recognition importance while building engagement patterns supporting long-term success.
Ceremony and Event Planning: Formal induction events honor achievements publicly while generating community awareness including invitations to all recognized students and families, speeches from school leadership emphasizing academic achievement importance, individual recognition moments for each inductee, media coverage generating publicity and community awareness, and memorable experiences honoring students appropriately. Ceremonies serve multiple purposes—recognizing achievements publicly, generating community excitement, and establishing annual traditions that become anticipated events.

Marketing and Communication Campaigns: Sustained promotional efforts ensure entire community knows about recognition including announcements through multiple channels (newsletters, social media, school announcements), press releases for local media coverage, social media content featuring individual inductees, printed materials and signage directing people to displays, and family outreach encouraging sharing and celebration. Comprehensive promotion ensures recognition receives attention rather than displays being overlooked by community members unaware of their existence.
Soft Launch Testing: Before public unveiling, invite select stakeholders for preview access gathering feedback about functionality, content quality, and user experience, identify technical issues requiring resolution before official launch, verify all systems work reliably, and make refinements based on testing. Soft launches prevent public embarrassment from easily correctable problems while demonstrating responsiveness to stakeholder input.
Maintaining Program Excellence Long-Term
Hall of Achievement programs require ongoing attention maintaining relevance, accuracy, and engagement across years as new students achieve recognition and institutional contexts evolve.
Annual Update Cycles
Sustainable programs establish predictable operating rhythms distributing workload managably while ensuring consistent activity.
Regular Induction Schedules: Establish annual cycles including fall planning and criteria review, winter nomination period accepting submissions, spring selection committee deliberations and decisions, summer inductee notification and content development, and fall ceremony or announcement celebrating new inductees. Regular cycles ensure programs maintain momentum rather than sporadic activity followed by dormancy undermining visibility and community engagement.
Content Expansion and Enhancement: Beyond adding new inductees, ongoing improvement includes gradually expanding historical coverage filling earlier eras, updating profiles for graduated inductees showing career progression demonstrating long-term impact of academic achievement, enhancing existing content with additional photos or updated information, and rotating featured content ensuring diverse visibility across all inductees. Continuous enhancement demonstrates active program management rather than abandoned initiatives.
Performance Monitoring and Improvement
Data-informed management ensures recognition programs continuously improve based on actual engagement patterns rather than assumptions.
Engagement Analytics Review: For digital systems, establish routines examining interaction data including monthly review of usage volume and trends, quarterly analysis identifying top-performing and underperforming content, annual comprehensive assessment of program impact on student achievement and engagement, and special analyses around specific events or promotional campaigns. Resources on measuring success of digital recognition provide frameworks for comprehensive program evaluation.
Stakeholder Feedback Collection: Complement quantitative analytics with qualitative insights through periodic surveys assessing satisfaction and gathering improvement suggestions from students, families, and staff, focus groups exploring specific questions about recognition preferences, suggestion mechanisms enabling ongoing community input, and regular touchpoints with recognized students gathering their perspectives on program impact. Qualitative feedback explains patterns in quantitative data while identifying enhancement opportunities analytics alone might miss.
Iterative Enhancement and Adaptation: Use insights to guide ongoing improvements including adding features addressing common user requests, enhancing content in underperforming categories through better writing or additional details, expanding popular achievement areas generating high interest, improving navigation based on observed usage patterns, and refreshing design maintaining contemporary aesthetics. Continuous improvement demonstrates institutional commitment while maximizing program effectiveness and impact.
Common Challenges and Practical Solutions
Schools implementing Hall of Achievement programs encounter predictable obstacles that proven approaches address effectively.
Balancing Recognition Breadth and Selectivity
Programs must remain selective enough that induction means something significant while broad enough that motivated students see achievement as attainable.
Solution Approaches: Establish clear achievement tiers creating multiple recognition levels—highest tier (Hall of Achievement) for truly exceptional accomplishment, middle tier (honor roll, dean’s list) for strong academic performance, and broad participation acknowledgment for effort and improvement. Multi-tier systems ensure students at all levels receive appropriate recognition while preserving special distinction for exceptional achievement. Define specific numerical thresholds providing objectivity and enabling students to understand exactly what achieving recognition requires. Create multiple pathway options so students with different strengths find viable routes to recognition.
Maintaining Equity Across Student Demographics
Recognition systems can inadvertently favor students from specific backgrounds or demographic groups unless actively designed for equity.
Equity-Focused Design: Analyze recognition data by demographic characteristics identifying potential bias in criteria or processes, ensure multiple achievement pathways prevent systems favoring specific student populations, consider socioeconomic factors in scholarship recognition (some students may not qualify for merit aid due to financial need-based awards), recognize improvement and growth trajectories alongside absolute achievement levels, and conduct regular equity audits making adjustments when data reveals disproportionate representation. Guidance on inclusive digital recognition programs provides frameworks for ensuring equitable access to recognition across all student populations.
Managing Annual Recognition Volume Growth
As programs mature, cumulative recognition grows potentially overwhelming display capacity and making individual inductees less visible.
Sustainable Growth Management: For digital systems, leverage unlimited capacity accommodating unlimited growth without space constraints. Implement sophisticated search and filtering enabling easy discovery despite large databases. Use featured content rotation ensuring all inductees receive visibility over time rather than just recent additions. Create historical browsing tools enabling exploration by era or decade. For physical displays, implement rolling windows showing recent recognition (last 10-20 years) with comprehensive digital archives providing permanent recognition for all historical inductees. Understanding digital hall of fame implementation helps schools plan for sustainable long-term growth.
Securing Ongoing Resources and Institutional Commitment
Initial enthusiasm often fades without sustained resource allocation and administrative commitment across leadership changes.
Sustainability Strategies: Integrate program management into permanent staff role descriptions preventing dependence on temporary champions, secure multi-year budget commitments rather than annual fundraising or discretionary allocations, demonstrate measurable value through engagement analytics and achievement impact data justifying continued investment, connect recognition to multiple institutional priorities (recruitment, retention, culture, pride) making it difficult to eliminate, and document all processes enabling continuity across staff transitions. Programs viewed as institutional infrastructure rather than optional initiatives maintain support across leadership changes and budget challenges.
Conclusion: Building Academic Recognition That Inspires Excellence
Hall of Achievement programs represent strategic investments in academic culture, student motivation, and institutional identity. When thoughtfully designed and consistently maintained, these recognition systems honor exceptional intellectual accomplishment while communicating clearly that schools value academic excellence as highly as any other achievement domain.
The most successful programs share common characteristics including clear criteria ensuring fairness and credibility, compelling content honoring achievements through complete stories rather than minimal information, accessible discovery enabling easy exploration of recognition by students and families, ongoing maintenance keeping recognition current and accurate, strategic integration with recruitment, culture-building, and engagement initiatives, and continuous improvement based on analytics and stakeholder feedback.

For schools beginning academic recognition programs or modernizing existing systems, starting with solid foundations—well-defined selection standards, structured nomination processes, realistic resource planning, and appropriate technology choices—sets the stage for long-term success. Schools can launch with manageable initial installations featuring recent distinguished graduates, then systematically expand historical coverage and enhance functionality over time as resources allow and program value becomes evident.
Digital recognition solutions like those from Rocket Alumni Solutions provide particular advantages for institutions seeking flexibility, comprehensive storytelling capabilities, and cost-effective long-term management. Unlimited capacity accommodates all distinguished students without space constraints, rich multimedia tells compelling stories honoring achievements appropriately, instant updates eliminate physical modification costs and delays, remote accessibility extends engagement beyond campus visitors, analytics demonstrate program value while informing optimization, and continuous expandability ensures recognition systems remain relevant across decades.
Beyond immediate recognition purposes, effective Hall of Achievement programs create lasting benefits including inspiring current students through tangible academic role models, building school pride in intellectual excellence and educational quality, preserving institutional history documenting remarkable students and their accomplishments, supporting recruitment through demonstrated academic outcomes and culture, balancing comprehensive recognition across athletics, academics, and arts, and motivating sustained academic effort by showing achievement leads to permanent acknowledgment.
Every exceptional student deserves recognition honoring their academic achievements appropriately. Every school deserves comprehensive tools celebrating intellectual excellence while building culture valuing achievement. Modern Hall of Achievement programs—whether traditional, digital, or hybrid—make these aspirations achievable for educational institutions committed to comprehensive recognition supporting student success and institutional excellence.
Ready to create a Hall of Achievement program that honors academic excellence while inspiring current students toward higher achievement? Explore how Rocket Alumni Solutions delivers comprehensive recognition platforms designed specifically for schools seeking to celebrate scholastic accomplishment without space limitations or technical complexity, making world-class recognition accessible for institutions of all sizes.