Communities across America face a profound responsibility: honoring service members, police officers, firefighters, and first responders who made the ultimate sacrifice protecting others. These fallen heroes deserve recognition that preserves their legacies, educates future generations, and provides solace to families processing unimaginable loss. Yet traditional memorial approaches—bronze plaques, granite walls, and physical monuments—impose severe limitations on how comprehensively institutions can honor those who gave everything in service.
Space constraints force painful decisions about which fallen heroes receive recognition when memorial walls fill completely. Fixed inscriptions prevent adding newly discovered information or correcting historical inaccuracies without expensive replacement. Static displays offer minimal context beyond names and dates, failing to capture the complete lives, service records, and personal stories that made these individuals so impactful to their communities. Most significantly, physical memorials restrict access to those who can visit in person, excluding distant family members, researchers, and citizens seeking connection with local heroes.
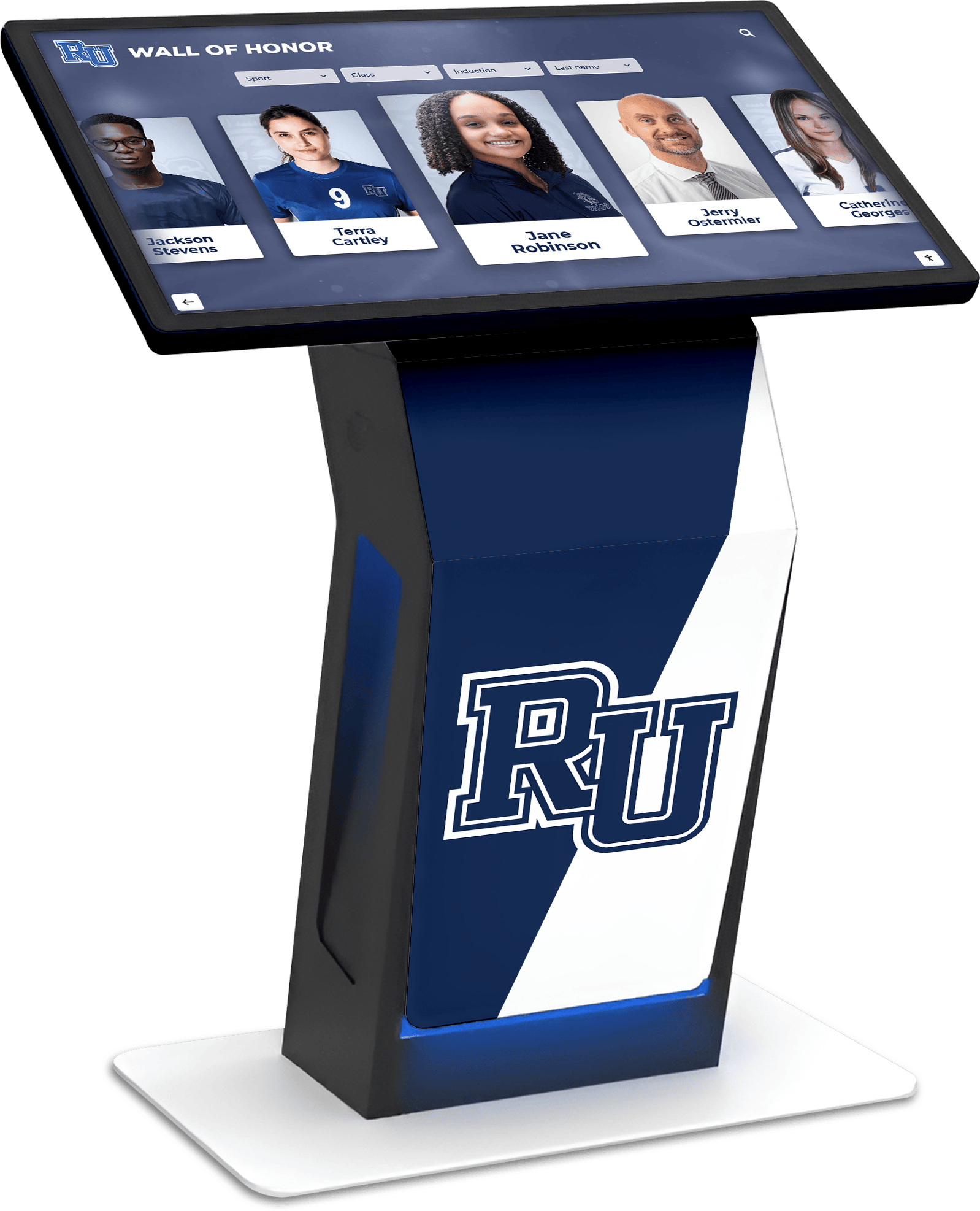
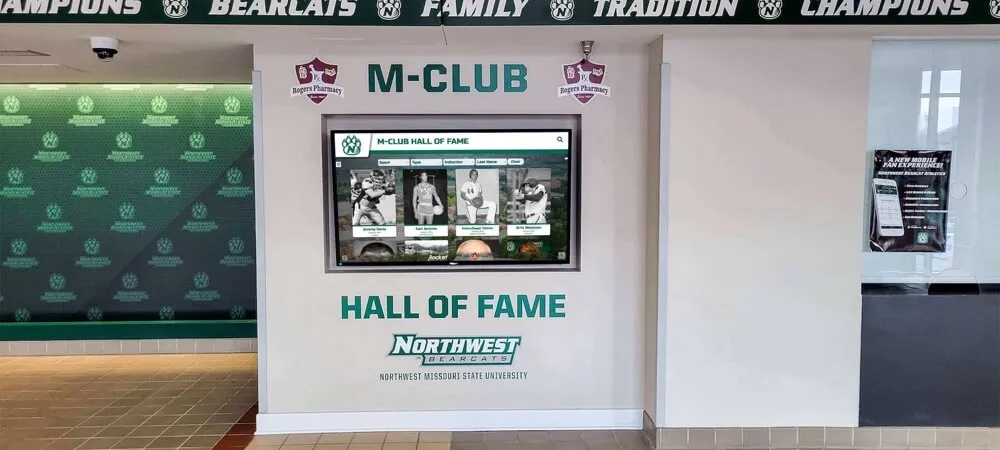
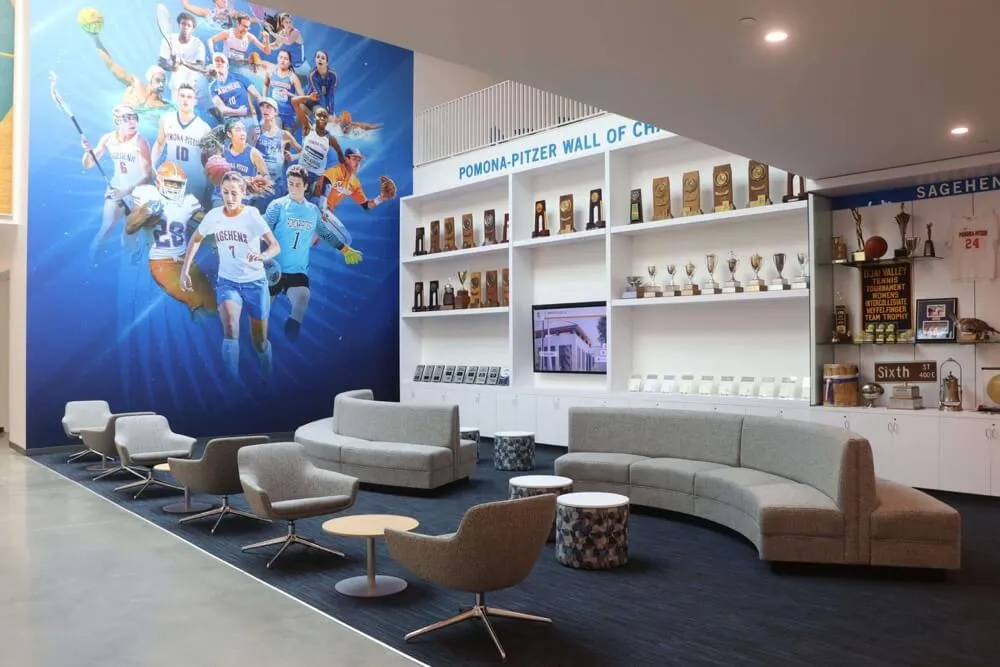
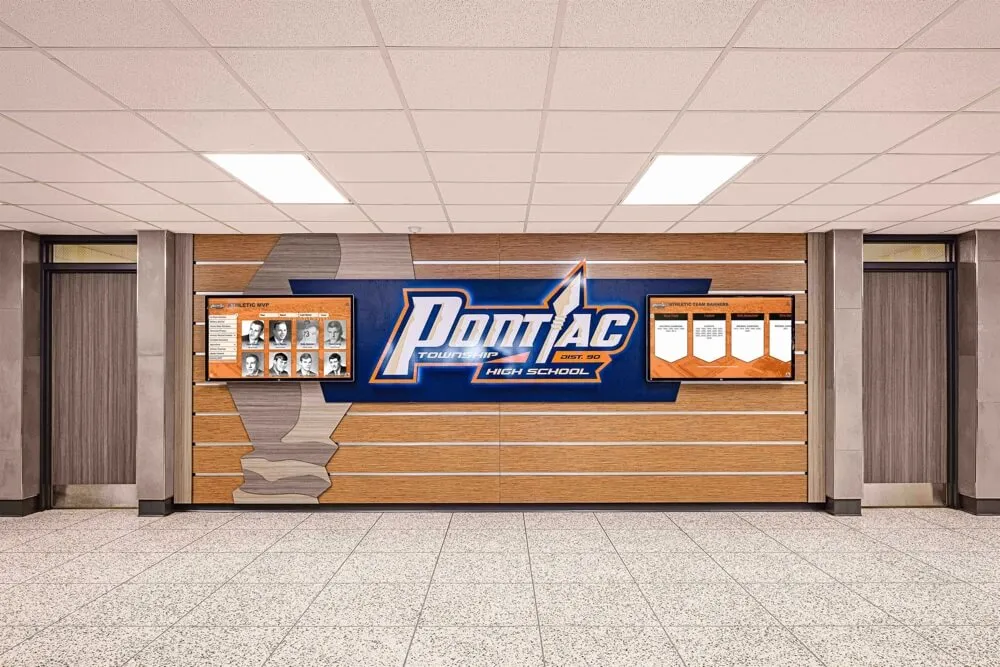
Modern fallen heroes touchscreen displays fundamentally transform memorial recognition by eliminating virtually every limitation inherent in traditional approaches while maintaining—and often enhancing—the appropriate dignity and reverence these solemn tributes require. Interactive digital systems accommodate unlimited honorees without space constraints, support rich multimedia storytelling impossible with engraved plaques, enable instant updates preserving historical accuracy, and provide worldwide accessibility ensuring families anywhere can connect with loved ones’ legacies.
Why Digital Memorial Displays Matter for Fallen Heroes
Fallen heroes memorial displays serve vital functions extending well beyond simple commemoration. They preserve institutional memory documenting those whose sacrifice shaped community history and safety. They provide comfort to families, colleagues, and citizens by demonstrating that heroes' contributions remain valued and remembered. They educate current and future generations about the real human costs of public service. Most importantly, they fulfill a moral obligation to honor those who gave their lives protecting others.
Modern recognition solutions like Rocket Alumni Solutions enable communities, military installations, police departments, fire stations, and civic institutions to create comprehensive, dignified memorial programs that overcome traditional limitations while maintaining appropriate reverence for honoring fallen heroes.
Understanding Fallen Heroes Memorial Recognition
When service members and first responders make the ultimate sacrifice, their communities face distinct recognition challenges requiring exceptional sensitivity, historical accuracy, and sustained institutional commitment across decades or even centuries of accumulated loss.
The Scale of Sacrifice Across Service Communities
Every branch of military service, law enforcement, firefighting, emergency medical response, and related protective professions accumulates fallen heroes deserving memorial recognition. The cumulative toll creates memorial programs of significant scale even for smaller communities.
A mid-sized police department might have lost dozens of officers in line-of-duty deaths spanning its history. A metropolitan fire department may memorialize hundreds of firefighters killed across generations. Military installations honor thousands of service members from multiple conflicts, peacetime training accidents, and overseas deployments. Veterans organizations memorialize community members across all service branches and conflict eras.
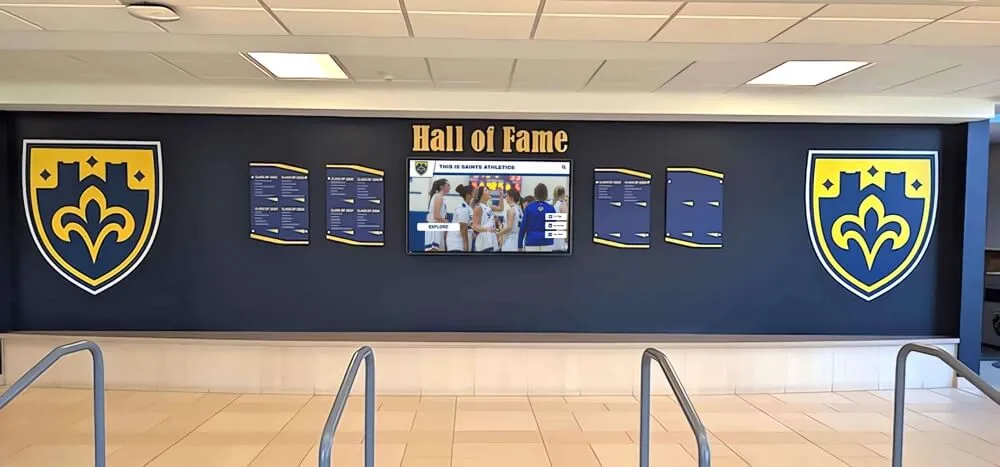

This scale creates fundamental challenges for traditional physical memorials. When wall space accommodates only limited plaques or inscriptions, institutions must make impossible decisions about whose sacrifice receives prominent recognition. The inevitable selectivity creates memorial programs where some heroes receive substantial acknowledgment while others who also gave their lives in service remain less visible or entirely unrecognized.
Categories of Fallen Heroes Deserving Recognition
Comprehensive memorial programs must address diverse service populations sacrificing their lives in different contexts and circumstances.
Combat Deaths and Hostile Action: Military service members killed in combat operations, police officers killed in confrontations or while preventing crimes, firefighters who die in structure fires or rescue operations, and first responders killed during emergency responses represent line-of-duty deaths directly resulting from the inherent dangers these professions face.
These deaths typically receive immediate recognition through department ceremonies, media coverage, and community observances. Yet permanent memorial recognition ensuring long-term remembrance requires systematic programs preserving these heroes’ legacies beyond initial grief responses.
Training Accidents and Operational Deaths: Military personnel killed during training exercises, police officers who die in vehicle accidents responding to emergencies, firefighters lost in apparatus crashes, and first responders succumbing to environmental hazards during operations constitute line-of-duty deaths that deserve equal recognition despite occurring outside direct hostile action.
Medical and Service-Connected Deaths: Veterans who succumb to combat injuries after returning home, first responders who die from occupational illnesses like cancer directly attributed to service exposures, and military members whose deaths connect to service-related conditions require thoughtful memorial approaches acknowledging these delayed but service-connected sacrifices.
Understanding how communities recognize different types of service helps memorial programs develop inclusive approaches honoring all fallen heroes appropriately regardless of death circumstances.
The Unique Emotional Weight of Fallen Heroes Recognition
Unlike recognizing athletic achievements, academic honors, or professional accomplishments, fallen heroes memorials intersect with ongoing grief, community trauma, and profound loss. These programs require exceptional sensitivity to families processing unimaginable tragedy, colleagues who witnessed sacrifice firsthand, and communities forever changed by heroes’ deaths.
Families seek memorial recognition honoring complete lives—not just service records but personal qualities, relationships with colleagues, passions beyond duty, and values guiding their dedication to protecting others. Colleagues desire tributes acknowledging the professional bonds, shared dangers, and deep friendships that define service communities. Citizens want memorials demonstrating sustained commitment to remembering those who made their safety and freedom possible.

Effective fallen heroes memorials must accommodate these varied perspectives while maintaining institutional appropriateness and managing finite resources. They should provide families opportunities to contribute memories and materials without becoming dependent on family initiative or resources. They need to capture personal dimensions that made heroes memorable without crossing boundaries into overly intimate revelation. Most importantly, they must demonstrate sustained institutional commitment to remembering heroes rather than brief observances quickly forgotten.
Traditional Memorial Approaches and Their Limitations
Physical memorials have served communities honorably for generations, but their inherent constraints increasingly limit comprehensive recognition as the number of fallen heroes grows.
Bronze Plaques and Engraved Walls
Traditional memorial walls feature engraved bronze plaques, granite inscriptions, or carved names permanently fixed to physical structures. These dignified tributes communicate institutional commitment and provide tangible places families can visit and touch.
Cost Considerations: Each memorial plaque costs $200-$800 for materials, engraving, and professional installation. Comprehensive programs recognizing dozens or hundreds of fallen heroes quickly become prohibitively expensive. A memorial honoring 100 line-of-duty deaths could cost $20,000-$80,000 in plaques alone before facility construction, architectural design, landscaping, or ongoing maintenance expenses.
Space Limitations: Physical wall space fills permanently. When memorial capacity exhausts available space, institutions face three equally problematic options: stop adding fallen heroes to memorials (unacceptable), replace existing memorials with smaller plaques accommodating more names (diminishes individual recognition), or construct expensive facility expansions (often financially impossible).
Many police departments, fire stations, and military installations face this exact predicament—memorial walls filled to capacity with more fallen heroes deserving recognition but no physical space remaining.
Information Constraints: Engraved plaques accommodate minimal information—typically name, rank, years of service, and date of death. This brevity prevents comprehensive storytelling about heroes’ complete lives, service records, personal qualities, and lasting community impact. A plaque reading “Officer Michael Chen, 1985-2019, EOW 7/14/2019” provides bare facts but misses the dedicated investigator who solved cold cases, the youth mentor who coached Little League, the colleague whose humor lifted spirits during difficult shifts, and the father whose sacrifice left three children without their parent.
Update Impossibility: Physical engravings cannot be edited. When historical research discovers inaccuracies, when families provide additional information, or when service records require correction, physical plaques must be entirely replaced at significant expense. This inflexibility means many traditional memorials contain factual errors that persist indefinitely because correction costs prove prohibitive.
Physical Memorial Walls and Monuments
Dedicated memorial structures—granite walls resembling the Vietnam Veterans Memorial, memorial gardens with individual monuments, or commemorative buildings—represent substantial institutional investments creating permanent recognition spaces.
These installations communicate profound respect and permanent commitment to remembering fallen heroes. Their physical presence creates sacred community spaces where ceremonies occur, families gather, and citizens contemplate sacrifice. For many communities, physical memorials constitute essential civic infrastructure deserving protection and preservation.
However, even the most impressive physical memorials face the same fundamental constraints as smaller plaques: space eventually fills, information remains fixed, updates require reconstruction, and access depends on physical presence.

The Digital Revolution in Fallen Heroes Memorial Recognition
Modern touchscreen display technology fundamentally transforms fallen heroes recognition by eliminating traditional limitations while preserving—and enhancing—appropriate memorial dignity and reverence.
Unlimited Memorial Capacity
Digital platforms accommodate unlimited fallen heroes without space constraints. Police departments can memorialize every line-of-duty death since department founding. Fire stations can honor every firefighter lost across generations. Military installations can recognize thousands of service members without ever “running out of room.” Veterans organizations can create comprehensive memorials including every community member who served and sacrificed.
This unlimited capacity enables truly equitable recognition where every fallen hero receives appropriate commemoration regardless of when they served, how famous they became, which conflict claimed their life, or how actively families advocate for inclusion. No institution ever faces impossible decisions about which heroes deserve limited memorial space because digital capacity remains functionally infinite.
According to the U.S. Department of Justice, more than 23,000 law enforcement officers have died in the line of duty throughout U.S. history. A comprehensive physical memorial honoring every fallen officer would require massive facility construction. Digital memorials accommodate this complete recognition within systems deployable in any police station regardless of physical space availability.
Rich Multimedia Storytelling
Traditional plaques restrict content to bare facts. Digital memorials support comprehensive content impossible with physical engravings:
Detailed Biographical Narratives: Comprehensive profiles (800-1500+ words) documenting complete lives and service records including family background and path to service, training and early career experiences, major assignments and unit histories, specific operations or cases they handled, awards, commendations, and decorations received, personal qualities that made them exemplary service members, colleague and commander testimonials, community involvement and volunteer activities, and lasting influence on their departments and communities.
Professional Photography and Portraits: Multiple photographs provide temporal depth showing heroes at different career stages—academy graduation photos capturing youthful dedication, on-duty images during active service, formal portraits in dress uniforms, candid shots revealing personality and character, and photographs with colleagues, family, or during service activities demonstrating relationships and context.
Service Records and Citations: Document complete service histories including deployment records and operational assignments, awards and decorations with full citation text, training certifications and specialized qualifications, promotion history and rank progression, unit assignments throughout careers, and official commendations from commanders and civic leaders.
Multimedia Elements: Video tributes from memorial services, audio recordings of eulogies or remembrances, scanned newspaper articles covering their service, historical documents related to their sacrifice, and ceremony footage from dedication events.
This multimedia richness creates emotional connections with fallen heroes that simple engraved names cannot achieve. Current service members discover inspiring stories about predecessors who worked the same beats, flew the same missions, or fought the same fires decades earlier. Families find profound comfort in comprehensive tributes capturing loved ones’ complete lives and service impact. Historians and researchers access detailed information supporting institutional history scholarship and service genealogy research.
Solutions like Rocket Alumni Solutions’ digital recognition platforms specialize in creating these rich, multimedia memorial experiences that honor fallen heroes with depth and dignity their legacies deserve while maintaining appropriate solemnity and respect.
Instant Content Updates and Corrections
Digital systems enable immediate additions or corrections through cloud-based content management interfaces requiring no technical expertise. When families discover additional photographs years after initial profile creation, adding them takes minutes. When researchers uncover forgotten service details, updating memorial content involves simple text edits. When official records correct historical inaccuracies, changes happen immediately without physical plaque replacement costs.
The U.S. Army Special Operations Command implemented a digital memorial wall spanning 41 feet that is LED, multi-display, and interactive, where users can find their loved ones with a touch of their fingertip. Up to three individuals can interact with the wall simultaneously, searching by name, unit, operation, year, or location. This system enables immediate updates as new information emerges about fallen soldiers, ensuring historical accuracy while honoring sacrifice appropriately.
This update flexibility proves especially valuable for fallen heroes memorial programs where information frequently emerges long after initial memorial creation. A family member might share previously unknown service stories. A military historian might discover documentation of forgotten operations. A colleague might provide photographs thought lost. Digital platforms welcome these continuous memorial enhancements, making tributes progressively richer over time while maintaining perfect accuracy.
Powerful Search and Discovery Capabilities
Interactive fallen heroes memorials enable visitors to explore service members through sophisticated search capabilities:
Name Search: Find specific fallen heroes instantly by entering their name, eliminating the need to visually scan hundreds or thousands of names on physical walls.
Service Branch Filtering: Browse fallen heroes by military branch (Army, Navy, Marines, Air Force, Coast Guard), by first responder discipline (police, fire, EMS), or by specific department or unit.
Conflict and Era Exploration: Discover heroes from particular conflicts (Vietnam, Desert Storm, Iraq, Afghanistan) or time periods spanning institutional history from founding to present.
Geographic Connections: Filter by hometown, deployment location, or operational area connecting heroes to specific communities or regions.
Award and Decoration Filters: Identify service members who received specific honors like Medal of Honor, Silver Star, Purple Heart, or department-specific valor awards.
Circumstance of Death: Search by how heroes died (combat action, training accident, line-of-duty death types) when appropriate for research or educational purposes.
Full-Text Search: Locate heroes mentioned in biographical narratives, service citations, or testimonials even if users don’t know their names.
These discovery tools create engagement impossible with physical memorials where finding specific individuals requires visually scanning every inscription. Digital search makes memorial programs useful research resources while honoring memory through active community exploration and discovery.
Resources on implementing effective digital memorial walls provide frameworks applicable specifically to fallen heroes recognition programs.
Global Accessibility Through Online Platforms
Physical memorials can only be viewed by those visiting in person, limiting who can engage with fallen heroes recognition. Digital memorial platforms extend access worldwide through web-based systems complementing physical installations.

Online accessibility proves particularly meaningful for fallen heroes memorials where service members’ and first responders’ influence extends far beyond immediate communities. Military families frequently relocate, meaning fallen service members’ relatives may live thousands of miles from installation memorials. Police officers’ children who grew up elsewhere deserve access to their parents’ recognition. Fire department alumni scattered nationally want connection with fallen colleagues.
Digital platforms enable a widow in California to access comprehensive tributes honoring her husband killed in Afghanistan and memorialized at Fort Bragg, a son in Texas to explore his father’s police service memorialized in New York, and researchers anywhere to access fallen heroes information supporting historical scholarship or genealogical research.
This global reach transforms memorials from location-dependent displays into living tributes accessible to anyone with internet connection—dramatically expanding memorial impact while honoring fallen heroes appropriately across wider communities they served and protected.
Creating Comprehensive Fallen Heroes Touchscreen Display Programs
Implementing meaningful memorial recognition requires systematic planning addressing historical research, content development, family engagement, technology selection, and long-term sustainability.
Establishing Memorial Criteria and Inclusion Standards
The foundation of any fallen heroes memorial involves transparent criteria determining whose sacrifice receives recognition and what distinguishes various recognition levels.
Line-of-Duty Death Definitions: Clearly define which deaths qualify as line-of-duty for recognition purposes including deaths during direct combat or emergency operations, training accidents occurring during official duty, vehicle accidents during emergency response, occupational illness directly attributed to service exposure, and post-service deaths from combat injuries or service-connected conditions.
Published definitions prevent confusion while ensuring consistent application across different circumstances and time periods. For first responder memorials, criteria often reference official line-of-duty death determination processes established by organizations like the National Law Enforcement Officers Memorial Fund or National Fallen Firefighters Foundation.
Service Requirements: Some memorials recognize all fallen heroes regardless of service length, while others establish minimum service requirements (typically one year) to qualify for inclusion. These decisions depend on institutional priorities and memorial program purposes.
Comprehensive vs. Selective Approaches: Organizations must choose between comprehensive memorials honoring all eligible fallen heroes or selective recognition limited to those meeting higher standards of valor, sacrifice under extraordinary circumstances, or particular recognition thresholds.
Most fallen heroes memorials adopt comprehensive approaches honoring all who meet basic line-of-duty death criteria, reflecting the principle that all who sacrifice their lives in service deserve equal recognition regardless of death circumstances, media coverage received, or family advocacy.
Historical Research and Information Gathering
Rich memorial content requires systematic information gathering from multiple sources, documenting both service records and personal qualities that made heroes impactful to their communities.
Official Service Records: Begin with personnel files, service records, and administrative documentation. Human resources maintains hiring dates, position histories, training records, and employment timelines. Unit commanders preserve assignment details, operational histories, award documentation, and performance records. Department historians hold historical photographs, ceremony programs, newspaper clippings, and institutional publications documenting service careers.
Incident Reports and After-Action Reviews: Official documentation surrounding line-of-duty deaths provides factual details about circumstances, locations, and contexts of heroes’ sacrifices. These records ensure memorial accuracy while honoring the specific events that claimed heroes’ lives.
Family Contributions: Families possess irreplaceable information about fallen heroes including personal photographs spanning entire lives, childhood and family background stories, personal letters or journals reflecting their motivations for service, military or department memorabilia and uniforms, documentation of community service and volunteer activities, perspectives on values and principles guiding their service commitment, and memories of personal qualities and characteristics beyond official records.
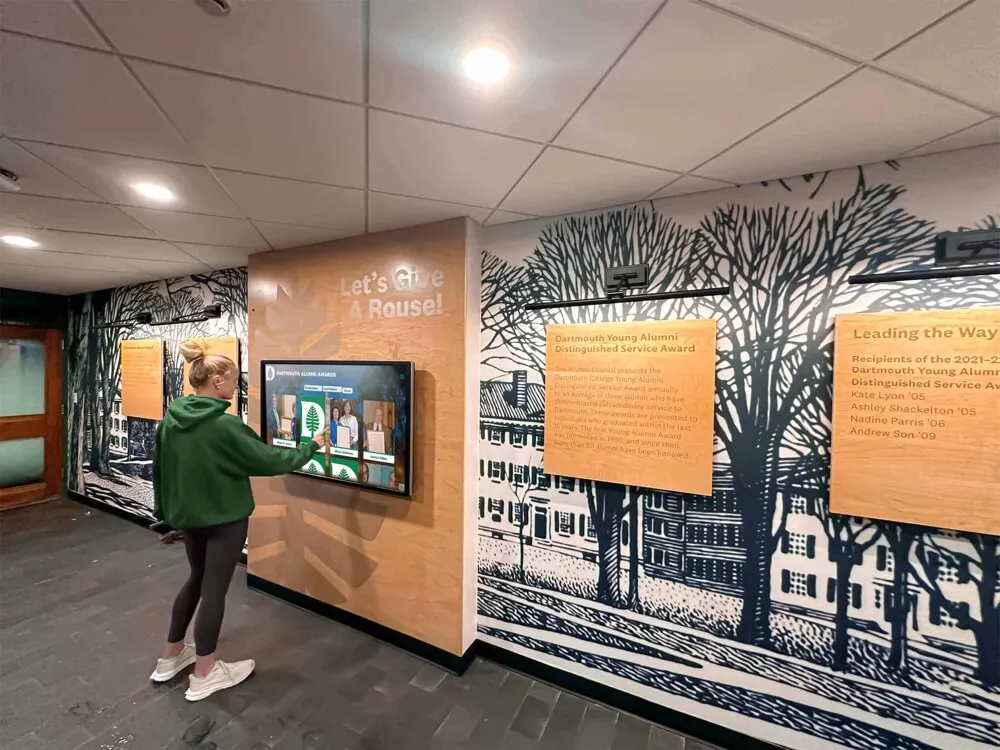

Thoughtful outreach to families yields memorial content far richer than official records alone provide. Invitations to contribute should emphasize that participation remains optional while expressing genuine interest in preserving complete portraits honoring loved ones appropriately.
Colleague Testimonials: Fellow service members offer authentic perspectives on fallen heroes’ service and character including operational excellence and professional skills, leadership and mentorship they provided to junior members, personal characteristics that made them valued colleagues, specific examples of bravery or dedication, and lasting influence on unit culture or institutional values.
Systematic colleague surveys, unit reunions, and memorial service recordings generate testimonial content that brings profiles to life beyond biographical facts and service credentials.
Media Coverage and Historical Research: Local newspapers, military publications, department newsletters, and online archives often contain detailed coverage of line-of-duty deaths, memorial services, biographical information, and community responses. Professional researchers or department historians can compile these dispersed materials into comprehensive historical records.
Creating Memorial Content That Honors Complete Lives
Quality fallen heroes memorial content balances official service documentation with personal storytelling that captures why these individuals mattered to families, colleagues, and communities they protected.
Biographical Narratives: Comprehensive profiles (800-1500 words for digital platforms) should describe family background and early life, motivation for entering military or first responder service, training experiences and early assignments, career progression and key operational experiences, specific incidents demonstrating courage or dedication, awards, decorations, and commendations received, service philosophy and professional values, personal interests and community involvement, family life and relationships, circumstances of their line-of-duty death, memorial services and community response, and lasting legacy and ongoing influence.
Visual Documentation: Multiple photographs spanning entire lives create powerful emotional connections including childhood photos showing their beginnings, training graduation photos from academy or boot camp, on-duty photographs during active service, formal portraits in dress uniforms, deployment or operational photos, candid images revealing personality, and family photographs showing personal relationships.
For comprehensive approaches to memorial recognition, resources on honoring deceased community members provide frameworks applicable to fallen heroes programs despite focusing on different populations.
Service Record Documentation: Present complete service histories in accessible formats including chronological assignment timelines, deployment records with locations and dates, promotion history showing rank progression, specialized training and certifications, unit assignments and commanding officers, awards and decorations with full citations, notable operations or cases they worked, and recognition from commanders and community leaders.
Personal Testimonials and Remembrances: First-person accounts from those who knew fallen heroes create authentic emotional connections including family members describing their character, colleagues sharing operational experiences, commanders explaining their leadership impact, community members expressing gratitude for service, and friends offering personal memories revealing who they were beyond uniforms.
Technology Selection and Implementation
Successful fallen heroes touchscreen display programs require careful technology selection addressing hardware, software, installation, and ongoing support.
Display Hardware Selection: Choose commercial-grade touchscreen displays specifically designed for high-traffic public environments rather than consumer televisions lacking durability for institutional use. Typical specifications include 55-75 inch screens (larger for primary memorial installations), commercial displays rated for 16-24 hour daily operation, multi-touch capacitive touchscreens supporting simultaneous users, anti-glare screens readable in varied lighting conditions, and robust mounting systems supporting display weight securely.
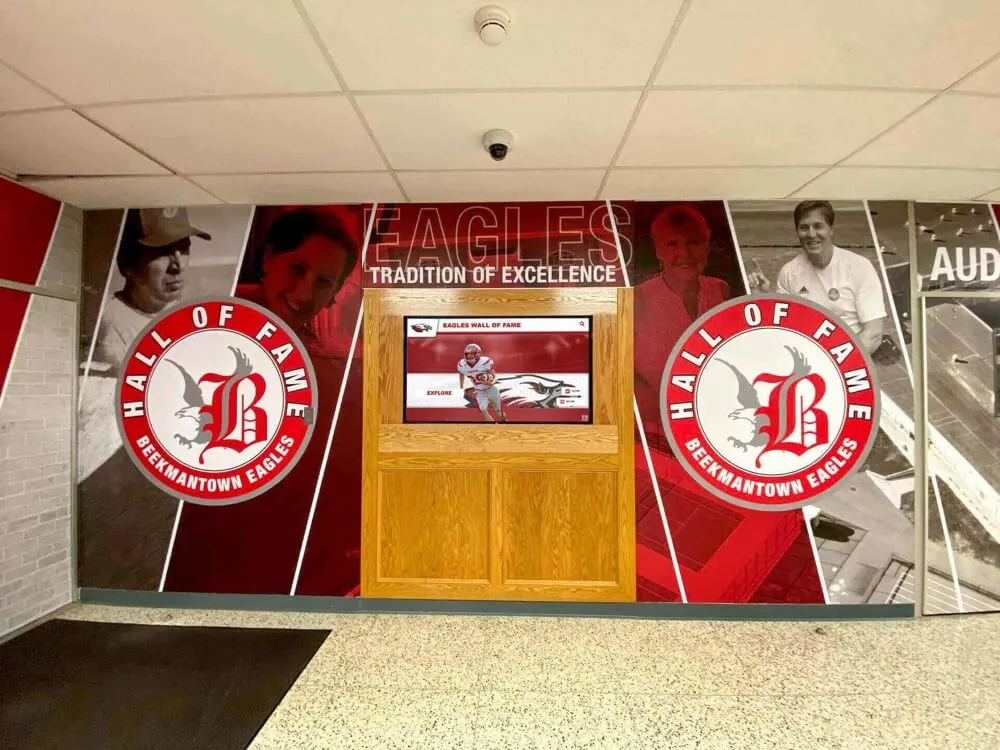
Kiosk and Enclosure Options: For maximum protection and professional presentation, many installations use purpose-built memorial kiosks. The Massachusetts Fallen Heroes Memorial uses an Advanced Kiosks tribute kiosk with a 43-inch touchscreen in a wall-mounted configuration that provides a clean, simple installation appropriate for self-service and immersive memorial experiences.
Kiosk enclosures protect sensitive electronics from environmental damage, prevent unauthorized access to internal components, integrate cable management for clean presentation, provide secure mounting for permanent installations, and create cohesive branded appearance reflecting institutional identity.

Software Platform Requirements: Evaluate memorial software based on intuitive content management enabling staff without technical backgrounds to add fallen heroes, update information, and maintain accuracy independently. Essential capabilities include cloud-based systems accessible through standard web browsers, template-based design maintaining professional presentation, multimedia support for photos, videos, and documents, powerful search and filtering tools, web-based access complementing physical displays, mobile-responsive design for smartphone access, and analytics tracking engagement and usage patterns.
Purpose-built memorial platforms from providers like Rocket Alumni Solutions offer specialized features specifically designed for fallen heroes recognition rather than generic digital signage systems requiring extensive customization.
Strategic Installation Placement: Identify locations where touchscreen displays maximize visibility and access while maintaining appropriate solemnity. Ideal placements include main entrance lobbies where all visitors naturally pass, memorial rooms or chapels dedicated to reflection, headquarters buildings with high personnel traffic, training facilities where new service members learn institutional history, and community areas where public access supports educational missions.
Consider sight lines, lighting conditions, ADA accessibility requirements, network connectivity availability, and power infrastructure when evaluating potential installation locations.
Network and Infrastructure Requirements: Ensure adequate technical infrastructure supports reliable operation including wired ethernet connections (preferred over WiFi for reliability), adequate electrical power meeting display requirements, proper cable management maintaining professional aesthetics, climate control maintaining equipment operating temperatures, and security measures protecting expensive installations.
Work with facilities and IT departments during planning phases addressing infrastructure needs before hardware arrival prevents implementation delays and ensures proper professional installation.
Special Memorial Recognition Considerations
Fallen heroes programs often must address specific populations or circumstances requiring particular approaches reflecting unique contexts surrounding their sacrifice.
Military Service Member Memorials
Military installations and veterans organizations face distinctive challenges honoring fallen service members across multiple conflicts, peacetime eras, and diverse circumstances.
Multi-Conflict Recognition: Comprehensive military memorials often span multiple wars and conflicts—World War II, Korea, Vietnam, Desert Storm, Afghanistan, Iraq, and ongoing operations. Organize content enabling exploration by specific conflicts while maintaining unified memorial recognizing all sacrifice equally regardless of which conflict claimed lives.
Branch-Specific Considerations: Each military branch maintains distinct traditions, terminology, rank structures, and award systems. Memorials honoring service members from multiple branches should respect these differences through appropriate service-specific language, correct insignia and rank representations, proper award and decoration nomenclature, and acknowledgment of branch-specific operational contexts.
Peacetime Training Deaths: Military service members die during training accidents, operational mishaps, and peacetime duties even during non-combat periods. These fallen heroes deserve equal recognition reflecting that service inherently involves sacrifice regardless of whether death occurs in active combat. Digital platforms ensure comprehensive recognition without artificial hierarchies suggesting combat deaths merit greater acknowledgment than training deaths.
Gold Star Families: Military memorials involving families of fallen service members require exceptional sensitivity to Gold Star family status and ongoing grief. Establish clear family engagement protocols including respectful initial contact procedures, opportunities to contribute memorial content, invitations to dedication ceremonies, and sustained communication demonstrating ongoing commitment to honoring loved ones.
The U.S. Air Force Memorial features interactive LCD displays where visitors can view names and profiles of Air Force veterans, demonstrating how major military memorials increasingly adopt digital technology for comprehensive recognition.
Law Enforcement Memorial Programs
Police departments and law enforcement agencies face unique challenges honoring officers killed in line-of-duty deaths occurring during diverse circumstances.

Diverse Death Circumstances: Law enforcement line-of-duty deaths include officers killed during confrontations, traffic fatalities during pursuits or emergency response, training accidents, terrorist attacks, and medical events directly attributed to service stress. Comprehensive memorials honor all these circumstances while maintaining appropriate sensitivity to different contexts surrounding officers’ deaths.
Privacy and Security Considerations: Some law enforcement operations involve ongoing investigations, classified intelligence, undercover work, or sensitive information requiring careful handling in public memorials. Coordinate memorial content with department legal counsel and intelligence sections ensuring memorial recognition doesn’t compromise operational security while appropriately honoring fallen officers’ service.
Community Trauma and Healing: High-profile officer deaths often traumatize entire communities beyond immediate law enforcement families. Memorial recognition serves broader healing purposes for communities processing violent loss of those sworn to protect them. Design memorial programs acknowledging this community dimension while maintaining primary focus on honoring fallen officers and supporting their families.
According to the National Law Enforcement Officers Memorial Fund, 23,785 law enforcement officers have died in the line of duty throughout U.S. history. Digital memorial technology makes comprehensive recognition of this massive sacrifice practically achievable where traditional physical memorials would prove prohibitively expensive and space-constrained.
Fire Service and First Responder Recognition
Fire departments, EMS organizations, and emergency services face particular memorial considerations reflecting their distinctive operational environments and service cultures.
LODD Circumstances Specific to Fire Service: Firefighter line-of-duty deaths include deaths during structure fires and rescue operations, cardiac events during emergency response (the leading cause of firefighter deaths), apparatus crashes during emergency response, training accidents, and cancer deaths attributed to occupational exposures. Comprehensive memorials address all these circumstances while acknowledging the particular cancer challenge confronting fire service through occupational carcinogen exposure.
Multi-Disciplinary Recognition: Modern fire departments increasingly provide integrated emergency services including fire suppression, emergency medical response, technical rescue, and hazardous materials operations. Fallen firefighter memorials should acknowledge this operational diversity honoring those who died during different types of emergency responses equally.
Volunteer vs. Career Distinctions: Many communities rely heavily on volunteer firefighters who sacrifice their lives providing emergency response despite not being full-time career firefighters. Memorial programs must honor volunteer sacrifice equally with career firefighters, recognizing that dedication to protecting communities transcends employment status.
The National Fallen Firefighters Memorial honors firefighters who died in the line of duty, with names added annually during memorial services. Local fire department memorials can mirror this comprehensive approach through digital platforms accommodating unlimited recognition.
Multi-Agency and Community-Wide Memorials
Some communities create comprehensive fallen heroes memorials honoring all service members and first responders regardless of specific agency, branch, or service type.
Inclusive Recognition Philosophy: Community-wide memorials demonstrate that municipalities value all who sacrificed protecting others equally—military service members, police officers, firefighters, EMS personnel, corrections officers, and other protective service members. This inclusive approach reflects community gratitude transcending organizational boundaries.
Organizational Coordination: Multi-agency memorials require collaboration among multiple institutions including military veterans organizations, police departments and sheriff’s offices, fire departments and fire districts, emergency medical services, municipal governments, and community memorial foundations or committees.
Establish clear governance structures, content approval processes, and institutional responsibilities ensuring sustained commitment across all participating organizations.
Diverse Content Standards: Different agencies maintain different record-keeping practices, service documentation, and available information about fallen members. Develop flexible content standards accommodating these variations while maintaining consistent memorial quality across all honorees regardless of which organization they served.
Educational Programming and Community Engagement
Fallen heroes memorials serve vital educational functions beyond individual commemoration. Thoughtful programming maximizes memorial impact while supporting institutional missions and community healing.
School and Youth Group Programs

Educational visits to fallen heroes memorials teach young people about sacrifice, service, citizenship, and history through personal stories that textbooks cannot convey.
Curriculum Integration: Develop teaching resources connecting memorial content to curriculum standards including history lessons about conflicts represented in memorials, civics education about public service and citizenship, character education highlighting heroism and sacrifice, and social studies examining how communities honor those who protect them.
Provide teacher guides, student worksheets, and discussion questions enabling educators to integrate memorial visits into structured learning experiences rather than treating visits as isolated field trips disconnected from classroom instruction.
Interactive Scavenger Hunts: Design age-appropriate memorial exploration activities guiding students to discover specific fallen heroes, search for heroes from particular time periods, locate service members with specific awards, and learn facts about conflicts or service contexts through self-directed touchscreen exploration.
Interactive approaches dramatically increase student engagement compared to passive lectures or reading. Students using interactive recognition displays typically engage for 5-10 minutes rather than the 30 seconds typical for static memorials, dramatically increasing educational impact.
Service Learning Connections: Connect memorial education to service learning programs where students contribute to memorial maintenance, research fallen heroes for profile development, coordinate memorial ceremonies, or develop digital content supporting ongoing memorial enhancement.
These hands-on experiences teach respect for fallen heroes while developing research skills, civic engagement, and appreciation for service careers.
Ceremony and Observance Integration
Annual memorial ceremonies provide structured occasions when communities gather to honor fallen heroes collectively while maintaining individual recognition for those lost during particular years.
Memorial Day and Remembrance Observances: Major national observances provide natural occasions for fallen heroes memorial ceremonies including Memorial Day (honoring all military fallen), Peace Officers Memorial Day (May 15), National Fallen Firefighters Memorial Day (First Sunday in October), and Patriot Day (September 11).
Incorporate touchscreen memorial displays into ceremony programming as visual backdrops displaying fallen heroes’ photographs during observances, interactive stations where attendees explore specific heroes’ stories, and live displays highlighting those being honored during particular ceremonies.
Anniversary Observations: Many families and organizations observe anniversaries of specific line-of-duty deaths through annual ceremonies, fundraising events, or community gatherings. Digital memorials enable highlighting specific fallen heroes on their death anniversaries through automated rotation features or manual content spotlighting.
New Inductee Ceremonies: When fallen heroes are added to memorials—typically annually for recent deaths after official investigations conclude—formal induction ceremonies provide appropriate occasions for families, colleagues, and communities to gather. Live touchscreen demonstrations during ceremonies show families how their loved ones are permanently memorialized and accessible to future generations.
Research and Genealogy Support
Comprehensive fallen heroes memorials serve as valuable research resources supporting historical scholarship, genealogical research, and institutional history documentation.
Academic Research Access: Historians studying military history, law enforcement evolution, fire service development, or community responses to tragedy benefit from accessible fallen heroes information. Digital platforms enable researchers to systematically explore memorial data including trends in line-of-duty deaths across time periods, geographic patterns in service sacrifice, demographic characteristics of fallen heroes, and operational contexts surrounding deaths.
Provide appropriate data export capabilities, citation information, and permissions enabling ethical academic research while maintaining memorial dignity and family privacy.
Family Genealogy: Descendants of fallen heroes—often several generations removed from original sacrifice—increasingly seek information about ancestors’ service and deaths. Digital memorials with robust search capabilities enable genealogical research connecting families to their service heritage.
Consider providing dedicated family access enabling descendants to claim relationships to fallen heroes, request additional information from institutional archives, and contribute family-held materials enriching memorial content.
Institutional History Documentation: Fallen heroes memorials constitute institutional historical records documenting service organizations’ evolution, operational contexts across different eras, leadership and personnel development, and cumulative sacrifice defining organizational culture.
Understanding best practices for preserving institutional history helps memorial programs develop sustainable documentation approaches serving historical research needs.
Technical Considerations and Best Practices
Successful fallen heroes touchscreen display programs require attention to technical details ensuring reliable operation, professional presentation, and appropriate memorial dignity.
Content Management and Workflow

Role-Based Access Control: Memorial content management systems should implement appropriate security including administrator access for full system configuration, editor access for adding and modifying fallen heroes profiles, reviewer access for family members or committee verification, and public access with appropriate view-only permissions.
This tiered approach maintains content integrity while enabling appropriate stakeholders to contribute without requiring technical expertise or compromising system security.
Content Approval Workflows: Establish clear processes ensuring memorial content receives appropriate review before publication including family review and approval for new profiles, administrative verification of service facts and dates, sensitive content evaluation for privacy or security concerns, and final publication authorization from designated officials.
Formal workflows prevent premature publication of unverified information while ensuring families have opportunities to contribute and review content honoring their loved ones.
Version Control and Audit Trails: Professional memorial systems maintain complete histories of content changes including who made modifications and when, what specific changes occurred, ability to revert to previous versions if necessary, and documentation supporting content accuracy and institutional accountability.
These capabilities prove particularly important for memorials where historical accuracy carries profound significance and errors require immediate correction.
Accessibility and Inclusive Design
Fallen heroes memorials must remain accessible to all community members regardless of physical abilities, ensuring that disability never prevents citizens from honoring those who protected them.
ADA Compliance: Touchscreen displays must meet Americans with Disabilities Act requirements including installation heights enabling wheelchair users to reach screens comfortably, clear floor space allowing wheelchair maneuvering, color contrast meeting readability standards, and text sizes supporting visitors with visual impairments.
Work with ADA compliance specialists during installation planning ensuring memorial accessibility for all visitors.
Assistive Technology Integration: Advanced memorial systems may integrate assistive technologies including screen reader compatibility for blind or low-vision visitors, closed captioning for video content, adjustable text sizes and color schemes, and audio descriptions for visual content.
Multi-Language Support: Communities with significant non-English speaking populations should consider multi-language memorial interfaces enabling all residents to explore fallen heroes recognition regardless of primary language. Cloud-based translation services increasingly make multi-language support practical even for smaller programs.
Security and Durability
Memorial displays operate in public spaces requiring protection against vandalism, environmental damage, and unauthorized access while remaining accessible for legitimate memorial purposes.
Physical Security: Protect expensive touchscreen hardware through tamper-resistant mounting systems, security enclosures with locked access panels, anti-theft hardware preventing display removal, and location selection in monitored or secured areas when possible.
Balance security requirements against memorial accessibility—overly restrictive security measures that limit public access undermine memorial purposes.
Environmental Protection: Ensure displays withstand environmental conditions in installation locations including temperature control maintaining equipment operating ranges, protection from moisture in outdoor or semi-outdoor locations, anti-glare screens remaining readable in varied lighting conditions, and dust protection in industrial or high-particulate environments.
Cybersecurity: Protect digital memorial content and systems through regular software security updates, network security isolating display systems from vulnerable infrastructure, regular backup procedures protecting against data loss, and access controls preventing unauthorized content modification.
Work with institutional IT security professionals ensuring memorial systems meet organizational cybersecurity standards while maintaining operational accessibility.
Funding Fallen Heroes Memorial Programs
Comprehensive memorial programs require sustained financial resources for initial implementation, ongoing content development, technology maintenance, and long-term sustainability.
Initial Implementation Costs
Hardware Investment: Touchscreen displays, kiosks, mounting systems, and installation represent the largest initial expenses. Budget $5,000-$15,000 per display depending on size, enclosure requirements, and installation complexity. A comprehensive memorial with 2-3 displays might require $15,000-$40,000 in hardware investment.
Software Licensing: Purpose-built memorial software typically involves initial setup fees ($1,000-$5,000) and ongoing licensing ($500-$3,000 annually) depending on system complexity, number of displays, and service levels. Cloud-based platforms with included hosting, backups, and technical support provide more predictable costs than self-hosted solutions requiring internal IT resources.
Content Development: Historical research, profile writing, photograph scanning and processing, family outreach, and initial content population require significant labor. Budget for dedicated project coordination (100-300 hours depending on memorial scope), content writing and editing, graphic design for visual elements, and historical research for comprehensive programs.
Many organizations use combinations of paid staff time, volunteer contributions, and contracted specialists for content development.
Ongoing Operational Expenses
Annual Software Licensing: Cloud-based platforms require ongoing licensing fees covering hosting infrastructure, technical support, software updates and security patches, and backup services protecting memorial content.
Technology Maintenance: Hardware requires periodic maintenance including display calibration and cleaning, touchscreen recalibration, replacement of worn components, and eventual full display replacement (typically 5-10 year lifecycles).

Content Updates: Adding fallen heroes as line-of-duty deaths occur, updating existing profiles with new information, correcting historical inaccuracies, and enhancing content with family contributions require sustained staff attention or contracted services.
Ceremony and Program Costs: Annual memorial services, family outreach, educational programming, and community engagement involve ongoing expenses supporting memorial program vitality beyond basic technology operation.
Funding Strategies and Revenue Sources
Municipal Operating Budgets: For police, fire, and municipal memorials, integration into departmental operating budgets provides most sustainable funding. Position memorials as essential institutional infrastructure serving departmental missions, community relations, and historical documentation—not optional programs vulnerable to budget cuts.
Veterans Organizations and Foundations: Military memorials often receive support from veterans organizations including American Legion, Veterans of Foreign Wars, Marine Corps League, service-specific associations, and community veterans foundations. These organizations frequently prioritize memorial projects supporting their core missions.
Philanthropic and Community Fundraising: Many fallen heroes memorials receive significant community financial support through individual donor campaigns, corporate sponsorships from businesses valuing public service, memorial fundraising events, naming opportunities for major donors, and planned giving programs through bequests.
Digital memorial platforms can integrate fundraising capabilities directly into memorial displays, creating natural giving moments when visitors feel moved by heroes’ stories and motivated to support ongoing memorial programs. Understanding how digital recognition supports advancement goals helps development professionals leverage memorials for sustainable fundraising.
Grant Funding: Numerous grant programs support fallen heroes memorial development including Assistance to Firefighters Grants (AFG), Department of Justice grants for law enforcement programs, state and federal historic preservation grants, community development block grants, and private foundation grants supporting veterans and public safety initiatives.
Work with institutional grant writers to identify relevant opportunities and develop competitive proposals positioning memorials as community assets deserving external support.
The Future of Fallen Heroes Memorial Recognition
Memorial technology continues evolving, bringing new capabilities transforming how communities honor service members and first responders while maintaining appropriate dignity and respect.
Enhanced Interactivity and Personalization
Emerging memorial technologies enable increasingly sophisticated experiences tailored to individual visitors’ interests and connections.
Biometric and ID Integration: Future systems might recognize authorized users when they approach displays, automatically highlighting fallen heroes they knew personally, served alongside, or share family connections with. This personalization creates immediate emotional engagement while respecting privacy through opt-in authorization.
Augmented Reality Experiences: AR applications may soon enable visitors to use smartphones to trigger additional digital content when viewing physical memorial elements, virtually “place” fallen heroes in their operational contexts through historical AR overlays, and experience immersive storytelling bringing service records to life through interactive 3D environments.
Virtual Reality Memorial Tours: VR technology promises complete memorial experiences accessible from anywhere globally including virtual walks through memorial installations for distant families, immersive storytelling experiences recreating fallen heroes’ service contexts, and virtual attendance at memorial ceremonies for those unable to travel.
While maintaining appropriate solemnity remains essential, thoughtful VR implementations could create powerful connections between current communities and historical heroes whose legacies deserve ongoing recognition.
Artificial Intelligence for Content Development
AI technologies may eventually assist fallen heroes memorial programs through automated research discovering published service information, official records, and historical documentation, interview transcription and summarization for oral history projects from colleagues and families, photograph organization and metadata generation identifying people, places, and dates, content translation enabling multilingual memorial access for diverse communities, and pattern recognition identifying gaps in memorial coverage requiring additional research.
Human oversight remains absolutely essential for maintaining appropriate tone, verifying accuracy, and ensuring ethical implementation, but AI tools could make comprehensive memorial programs more achievable for resource-constrained organizations.
Blockchain for Memorial Permanence
Distributed ledger technology offers potential solutions ensuring memorial content permanence even if individual organizations dissolve or technology platforms change. Blockchain systems could store memorial content across decentralized networks guaranteeing fallen heroes recognition survives organizational changes, document complete content histories preventing unauthorized alterations, enable family access to authoritative memorial records, and create permanent, tamper-proof service record documentation.
These applications remain emerging, but they address valid concerns about long-term memorial preservation as technology inevitably evolves and current platforms eventually become obsolete.
Honoring Those Who Gave Everything
Every service member and first responder who dies protecting others becomes part of permanent national story. Death doesn’t erase their sacrifice, end their connection to communities they served, or diminish their place in history. Fallen heroes memorial programs formalize the moral obligation to remember these heroes, honor their families processing unimaginable loss, educate future generations about service and sacrifice, and ensure their legacies continue inspiring others long after grief fades into history.
Traditional bronze plaques and engraved memorial walls have served honorably when no alternatives existed, and they retain symbolic power many families value. But modern touchscreen display technology now enables memorial recognition transcending physical limitations through unlimited capacity honoring every fallen hero without space constraints, rich multimedia capturing complete lives rather than bare facts, accessible commemoration reaching distant families enabling global engagement, instant updates maintaining accuracy and completeness perpetually, and powerful discovery tools enabling personal connections with heroes’ stories and legacies.
For communities creating new memorial programs, military installations revitalizing existing recognition, police departments expanding capacity to honor more fallen officers comprehensively, fire departments memorializing decades of line-of-duty deaths, or veterans organizations preserving complete service histories, solutions like Rocket Alumni Solutions provide specialized platforms designed specifically for fallen heroes memorial purposes—combining unlimited capacity with comprehensive storytelling, dignified presentation with accessible operation, and powerful technology with appropriate reverence for honoring those who gave everything protecting others.
Every fallen hero deserves remembrance. Every family deserves comfort knowing loved ones are honored appropriately and permanently. Every generation deserves connection with those who came before, understanding how previous service members shaped communities, influenced service cultures, and made ultimate sacrifices enabling the freedom and safety we enjoy today. Modern fallen heroes touchscreen display programs make these aspirations achievable—creating comprehensive, perpetual tributes that honor service and sacrifice with dignity, depth, and accessibility these legacies deserve while ensuring no hero is forgotten and no sacrifice goes unrecognized.
The service members and first responders who came before us gave courage, dedication, sacrifice, and ultimately their lives to protect institutions, communities, and citizens throughout their service. They deserve memorial recognition that gives everything back—preserving their memories, honoring their families, educating future generations about service excellence, and ensuring their contributions to community safety and national security remain visible, understood, and valued for as long as grateful communities endure. Modern memorial touchscreen display technology makes this perpetual commemoration possible, transforming how we honor fallen heroes while ensuring every service member and first responder who made the ultimate sacrifice receives the lasting tribute their life and legacy deserve.
Schedule a Zoom demo to explore how digital recognition displays can honor your fallen heroes with the dignity and comprehensiveness their sacrifice deserves.