Alumni halls of fame represent one of the most powerful tools educational institutions possess for honoring distinguished graduates, inspiring current students, and strengthening community bonds. Yet many schools, universities, and organizations struggle with where to begin when creating a recognition program that balances tradition with modern capabilities, honors diverse achievements appropriately, and remains sustainable across decades.
The challenge extends beyond simply deciding who to recognize. Creating an effective alumni hall of fame requires thoughtful consideration of selection criteria that ensure fairness and credibility, display formats that engage contemporary audiences while maintaining dignity, content strategies that tell compelling stories rather than listing basic facts, implementation approaches that fit institutional resources and culture, and maintenance systems that keep recognition current and relevant long-term.
Why Creating an Alumni Hall of Fame Transforms Your Institution
A well-designed alumni hall of fame delivers measurable benefits across multiple institutional priorities. Recognition programs inspire current students by showcasing tangible examples of excellence, strengthen alumni engagement and giving by honoring achievements publicly, preserve institutional history documenting remarkable graduates and their contributions, enhance recruitment by demonstrating educational quality and graduate success, and build community pride celebrating collective accomplishments across generations.
Modern solutions like those from Rocket Alumni Solutions make comprehensive recognition achievable even for institutions with limited resources, combining intuitive content management with professional presentation that honors inductees appropriately while engaging digital-native generations effectively.
Understanding the Purpose and Impact of Alumni Halls of Fame
Before diving into implementation details, institutions must clearly articulate why they’re creating recognition programs and what outcomes they hope to achieve. This foundational work shapes every subsequent decision about criteria, format, content, and operations.
Core Objectives That Drive Successful Programs
Alumni halls of fame serve multiple interconnected purposes that reinforce institutional mission and values.
Student Inspiration Through Role Models: Recognition walls create visible proof that excellence leads to remarkable outcomes. When students see alumni who share similar backgrounds, interests, or challenges achieving extraordinary success, abstract possibilities become concrete realities. A first-generation college student discovers graduates who overcame similar obstacles. An aspiring entrepreneur explores alumni who founded successful companies. An athlete sees professionals who balanced sports with academic excellence. These personalized connections inspire far more effectively than generic motivational messaging.

Alumni Engagement and Philanthropic Support: Recognition directly influences graduate behavior toward their alma mater. Research consistently shows that recognized alumni give more frequently and generously than unrecognized peers. Recognition creates psychological investment in institutional success, demonstrates that the institution values and remembers individual contributions, provides social proof encouraging philanthropic participation, and generates positive emotional associations strengthening lifelong connections. Institutions implementing comprehensive hall of fame programs commonly report 20-35% increases in alumni giving participation within two years of launch.
Historical Preservation and Institutional Memory: Recognition programs function as living archives documenting institutional evolution, excellence traditions, and remarkable individuals who shaped organizational character. Detailed alumni profiles capture career accomplishments, personal reflections, historical context, and institutional impact for permanent preservation accessible to future generations. Without systematic documentation, extraordinary graduates and their stories often disappear as collective memory fades over time.
Recruitment and Reputation Enhancement: Prospective students, families, and community members evaluate institutions partially through demonstrated graduate success. Comprehensive recognition provides tangible evidence of educational quality during campus tours and recruitment events. Families see graduates achieving remarkable success, reinforcing confidence in the institution. Prospective students envision themselves among future inductees, creating aspirational identification with excellence. Media coverage of inductee achievements credits educational foundations, enhancing institutional reputation locally and nationally.
Measuring Success: Defining Clear Outcomes
Effective programs establish measurable goals informing design decisions and enabling ongoing evaluation.
Quantifiable Metrics might include the number of alumni recognized annually with targets for diverse achievement representation, alumni giving increases measured through participation rates and average gift sizes, website traffic to recognition pages indicating engagement levels, event attendance at induction ceremonies and homecoming activities, and social media engagement reflecting recognition visibility and shareability.
Qualitative Indicators complement numerical data through student surveys measuring inspirational impact and career awareness, alumni feedback about recognition experiences and program appreciation, faculty observations of how recognition integrates with curriculum and student conversations, and community perception shifts regarding institutional quality and graduate accomplishments.
Resources on best ways to connect with alumni demonstrate how recognition programs serve as foundations for broader engagement initiatives creating ongoing institutional value beyond initial honorific purposes.
Establishing Selection Criteria and Nomination Processes
Credibility and perceived fairness represent essential elements of successful recognition programs. Clear, transparent selection standards ensure that halls of fame honor genuine achievement while maintaining community trust.
Defining What Warrants Recognition
Comprehensive criteria frameworks consider multiple achievement dimensions creating opportunities for diverse recognition.

Professional Accomplishment: Career achievement demonstrating exceptional success in chosen fields through leadership positions of significant influence, major contributions advancing professions or industries, recognition by professional peers and organizations, sustained excellence over extended careers, or innovation creating lasting impact. Criteria should remain broad enough to honor diverse career paths—educators making profound differences in students’ lives deserve recognition alongside entrepreneurs building successful businesses or researchers making scientific breakthroughs.
Community Impact and Service: Sustained civic engagement and philanthropic contributions through volunteer leadership improving communities, charitable giving supporting important causes, advocacy advancing social justice or public welfare, mentorship helping others achieve success, or initiatives addressing community challenges. Community service recognition ensures halls of fame celebrate values beyond professional achievement, demonstrating that institutional education produces graduates committed to making communities better.
Character and Values Alignment: Demonstration of integrity, ethical leadership, and embodiment of institutional values throughout careers and personal lives. Recognition programs honor not just achievement but how individuals achieved success—with honesty, compassion, resilience, and commitment to principles. This emphasis on character ensures inductees serve as worthy role models for current students beyond accomplishment alone.
Alumni Support and Engagement: While not requiring that all inductees demonstrate ongoing institutional involvement, many programs value continued connection through mentorship programs, financial support, speaking engagements, or other contributions strengthening school communities. This criterion recognizes that some distinguished graduates maintain strong connections while others pursue remarkable careers with limited capacity for ongoing engagement—both merit recognition though involvement adds additional value.
Time-Since-Graduation Requirements: Most programs establish minimum periods between graduation and eligibility—commonly 10-15 years—allowing sufficient time for career establishment and achievement documentation. This requirement ensures recognition goes to sustained accomplishment rather than early promise, though some programs create special categories for recent graduates demonstrating extraordinary early achievement warranting acknowledgment.
Creating Transparent Nomination Systems
Effective nomination processes balance accessibility with thoroughness ensuring broad community participation while maintaining selection quality.
Open Nomination Periods: Annual or biennial windows when anyone can submit nominations—alumni, faculty, staff, students, community members—democratize the process beyond closed selection committees. Accessible online nomination forms request essential information including nominee background, specific achievements warranting recognition, documentation or evidence supporting nomination, and nominator contact information for follow-up questions. Clear guidelines explain eligibility requirements, evaluation criteria, and submission deadlines ensuring nominators understand program parameters.
Structured Evaluation Protocols: Selection committees follow documented procedures ensuring consistent, fair assessment across all nominees. Standardized evaluation rubrics score nominees against established criteria providing objective comparison frameworks. Background research verifies and expands nomination information through professional profile reviews, media coverage searches, and reference conversations with colleagues or community members who can speak to achievements. Multiple committee members independently evaluate each nominee reducing individual bias while diverse committee composition ensures varied perspectives inform decisions.
Transparent Communication: Programs maintain credibility through clear communication about processes and decisions. Public documentation of selection criteria and nomination procedures allows community understanding of recognition standards. Nominees receive notification of committee decisions with unsuccessful candidates informed respectfully. Recognition of all nominees (not just inductees) through published lists honors nomination itself as meaningful acknowledgment even when selection committees determine inductees don’t meet current induction thresholds.
Insights on high school alumni hall of fame displays provide frameworks for creating selection processes that community members respect and trust as fair, comprehensive, and consistent with institutional values.
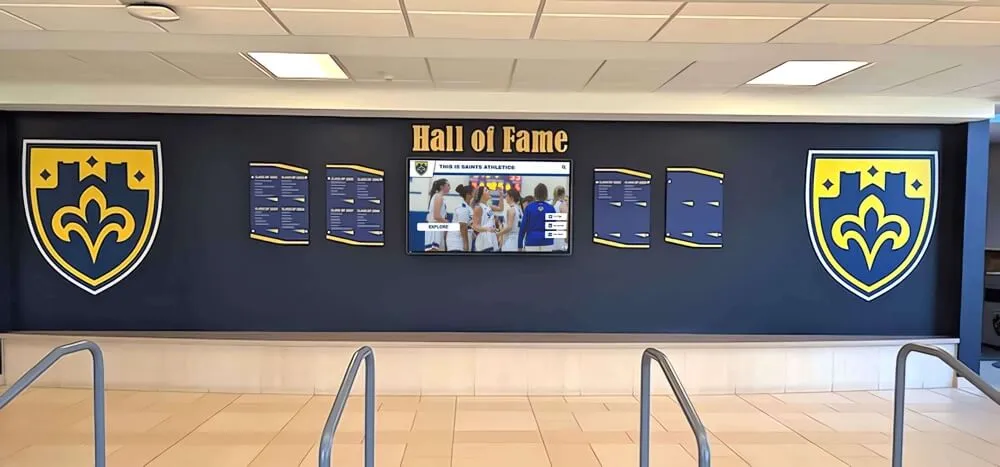
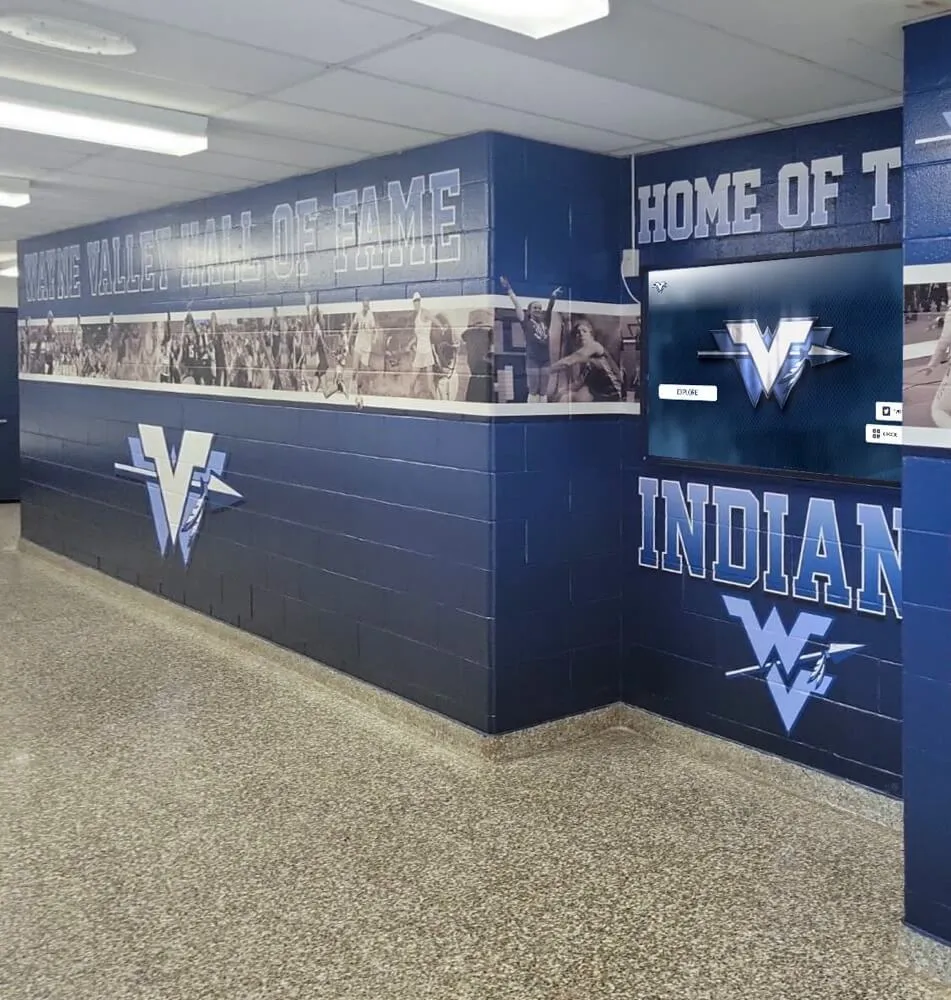
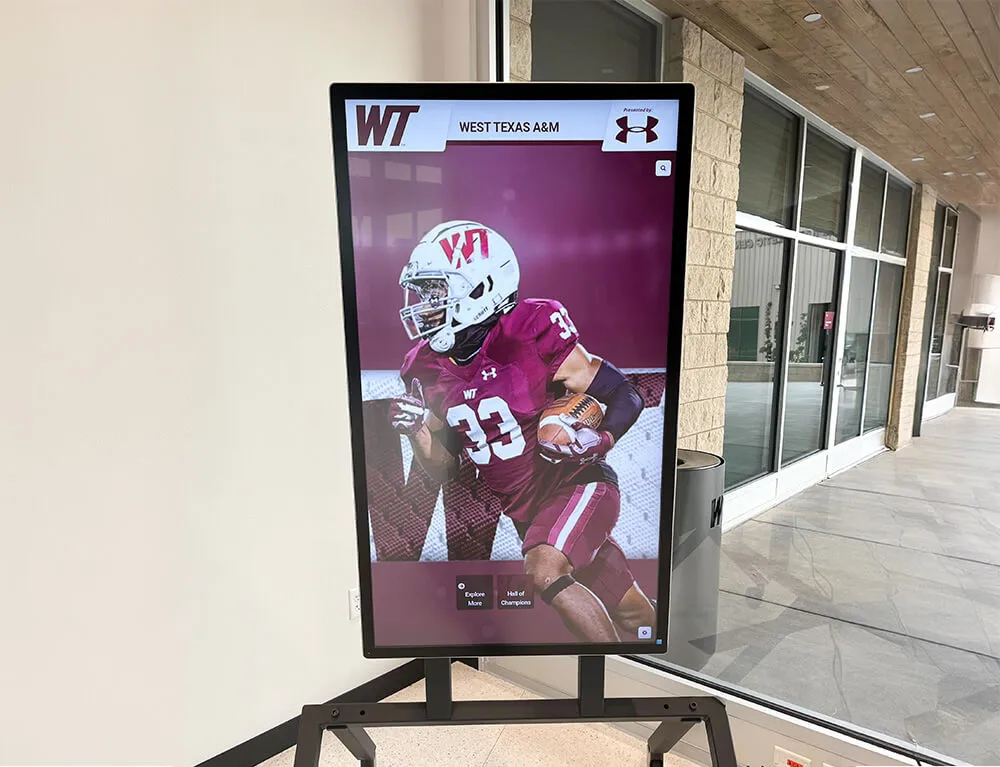
Choosing Display Formats: Traditional, Digital, or Hybrid Approaches
Display format selection significantly impacts recognition effectiveness, maintenance requirements, flexibility, and long-term sustainability. Understanding available options helps institutions make informed decisions aligned with objectives, resources, and culture.
Traditional Physical Recognition
Classic display formats maintain symbolic permanence and familiar aesthetics that some institutions and stakeholders value highly.
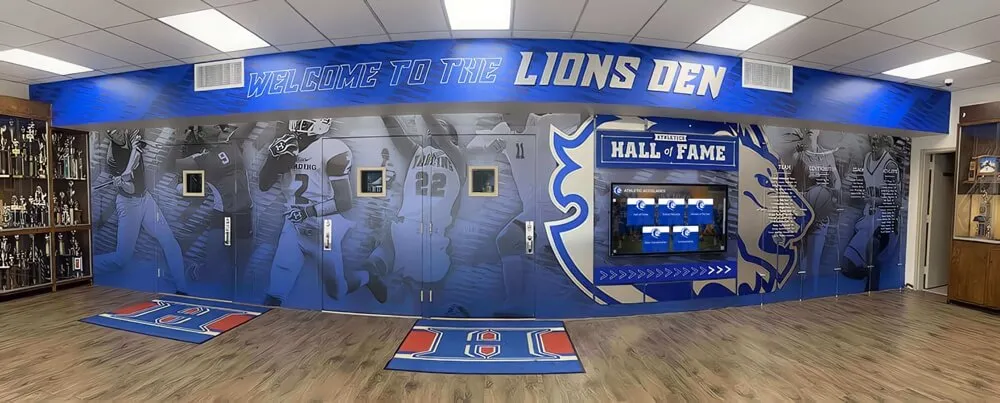
Engraved Plaques and Name Boards: Metal or wooden plaques mounted on dedicated walls provide formal, permanent recognition with tangible presence. These traditional formats communicate seriousness and respect through physical craftsmanship. However, plaques consume wall space rapidly—each inductee requires dedicated area meaning recognition capacity remains finite. Once available space fills, institutions face difficult choices about expanding displays, rotating recognition, or limiting future inductions. Per-inductee costs typically range from $200-$500 including design, production, and professional installation.
Photo Display Boards: Mounted photographs with accompanying biographical text provide superior recognition to name-only plaques through visual identification and expanded information. Custom millwork installations cost $1,500-$5,000 depending on size and materials. Photos create personal connections helping viewers identify with inductees. However, photographs fade over time requiring periodic replacement, frames need maintenance, and updating displays involves physical labor removing old materials and installing new components.

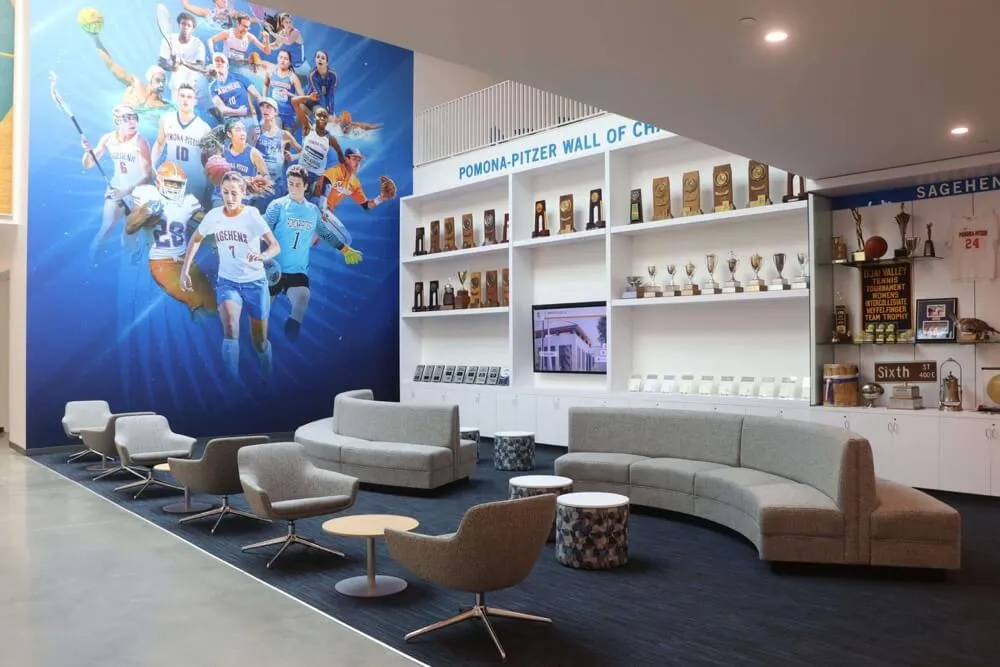
Trophy Cases: Glass-enclosed cases displaying awards, memorabilia, and three-dimensional artifacts create impressive recognition particularly for athletic achievements. Trophy cases typically cost $3,000-$15,000 depending on size and customization. The ability to showcase actual trophies, jerseys, or accomplishment artifacts adds authenticity and visual interest. Space limitations remain significant—cases hold finite items and require valuable floor space. Adding recognition means removing existing items creating difficult prioritization decisions.
Advantages and Limitations Summary: Physical recognition offers tangible permanence, familiar formats aligned with traditions, no technology learning curves, zero ongoing software costs, and strong sentimental value for traditionalists. Limitations include finite capacity forcing selection competition, high per-inductee costs, time-consuming physical updates, limited information beyond basics, no search or interactivity, and geographic restriction to campus visitors only.
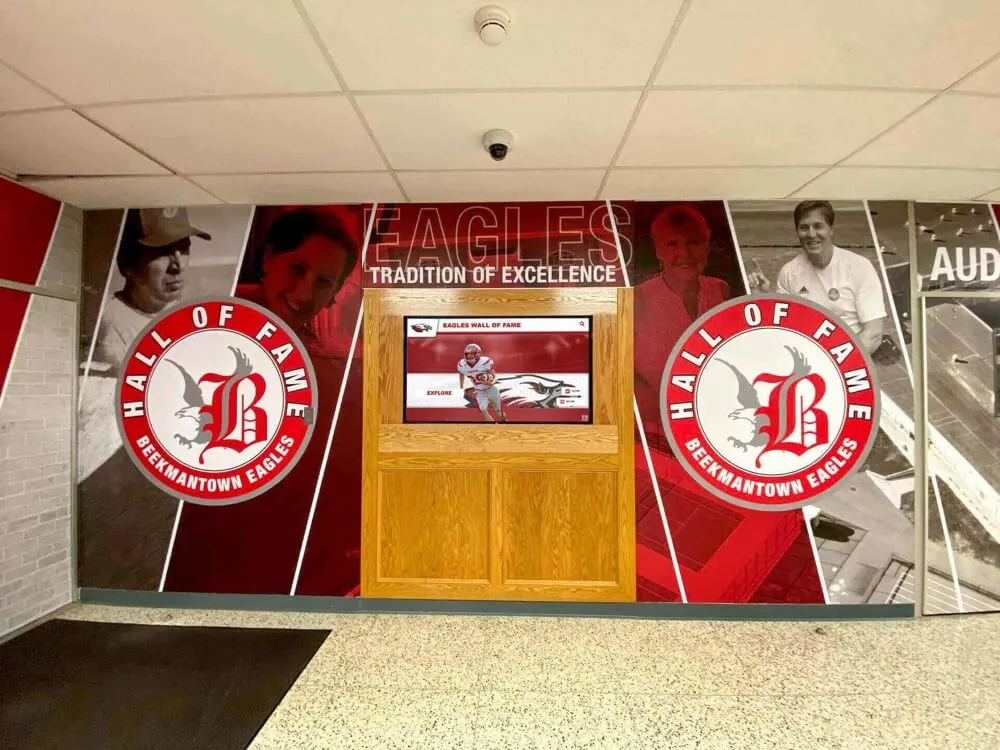
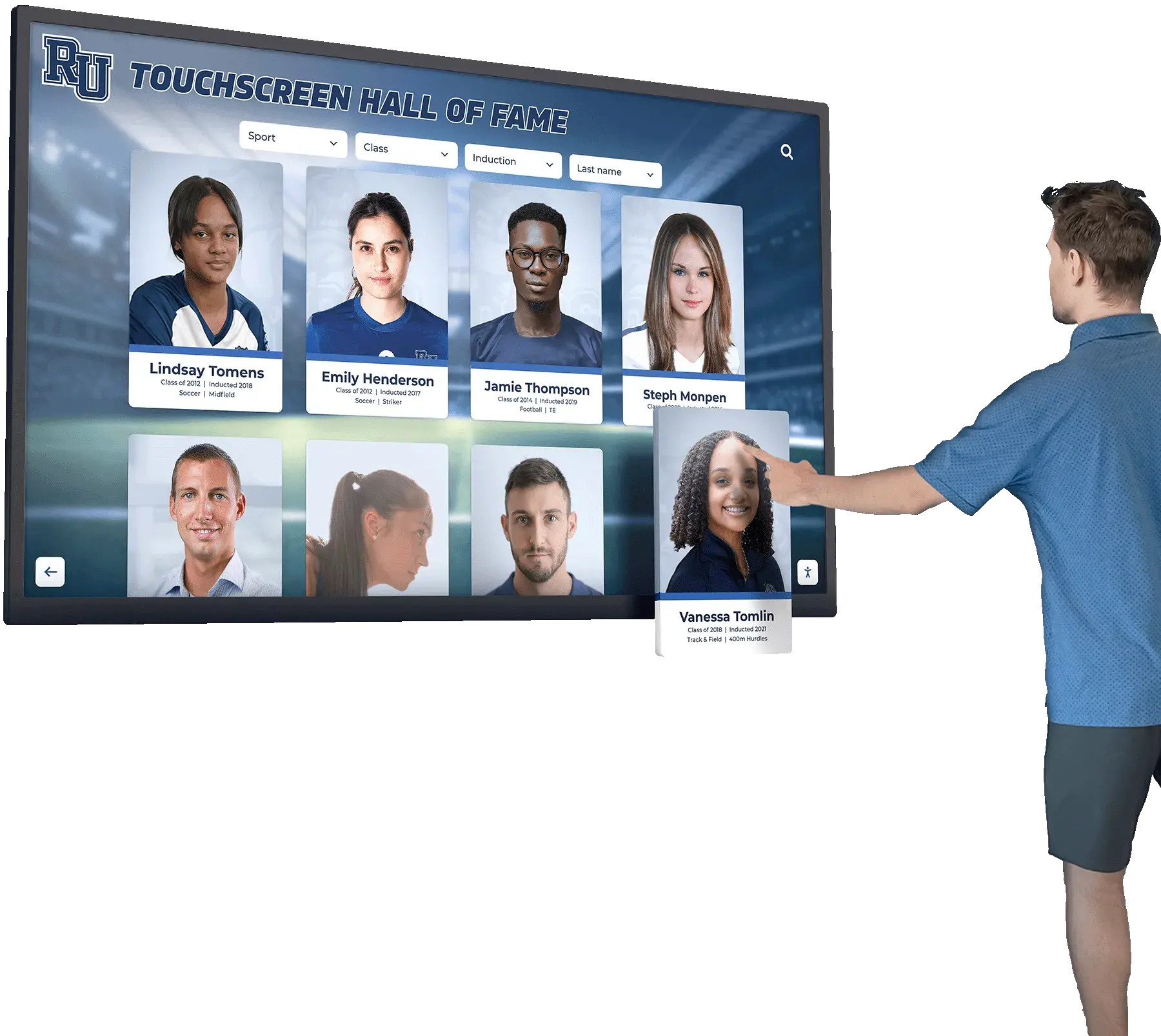
Digital Interactive Recognition Systems
Modern technology addresses every limitation of traditional approaches while introducing capabilities impossible with physical-only displays.
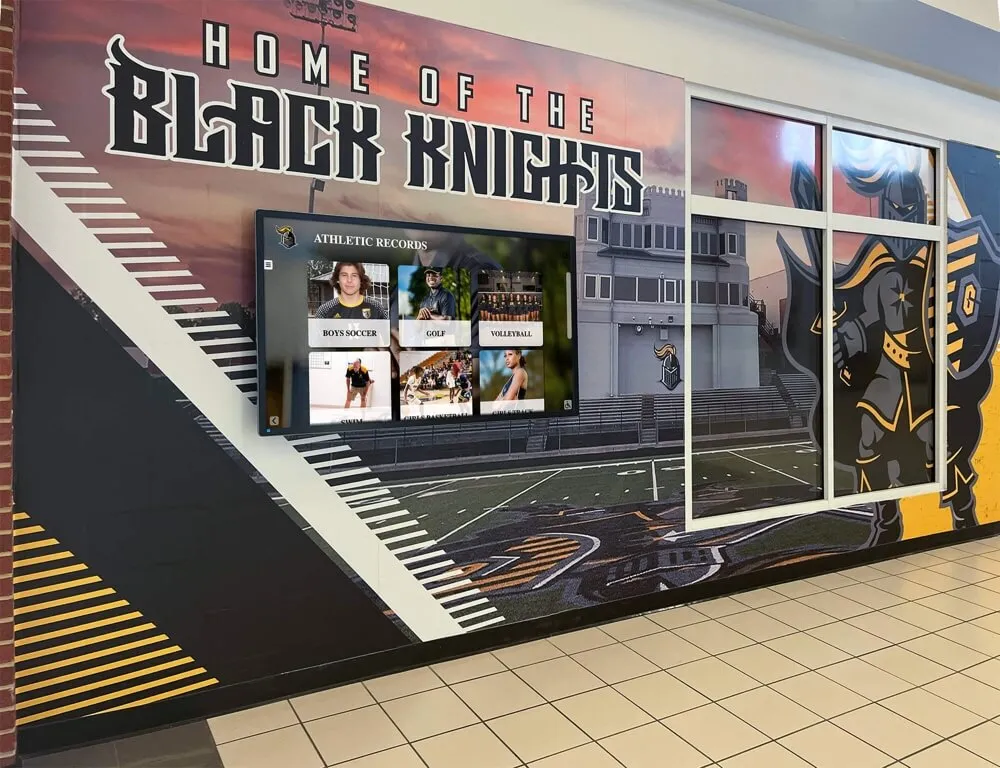
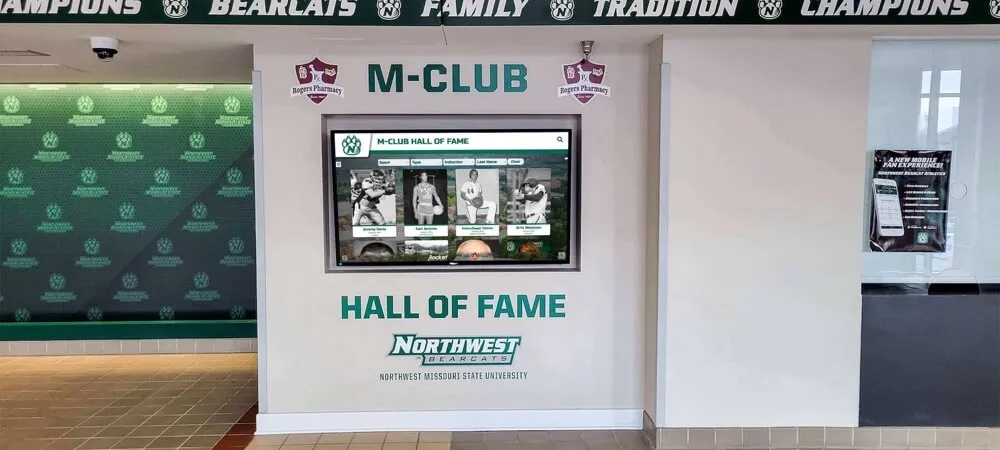
Unlimited Recognition Capacity: Digital systems accommodate hundreds or thousands of alumni profiles without physical space constraints. A single touchscreen display provides access to comprehensive recognition limited only by content development rather than wall space. This unlimited capacity means every distinguished graduate receives appropriate recognition regardless of when they graduated or how many others have been honored. Schools never face decisions about removing recognition to make room for new inductees.
Rich Multimedia Storytelling: Digital profiles support extensive content including professional photography, video interviews and messages, audio clips sharing reflections, photo galleries documenting careers, achievement documentation through certificates or awards, news coverage featuring accomplishments, and detailed biographical narratives. This multimedia capability creates engaging, comprehensive recognition far exceeding what physical plaques can communicate.
Instant Content Updates: Adding new inductees or updating existing profiles requires no physical changes—just content management system updates. This eliminates lead times for plaque production, installation scheduling, or physical mounting. Updates take hours rather than weeks and cost dramatically less than physical modifications. Digital systems also enable content refinements addressing errors or adding new information as alumni careers progress.
Interactive Discovery Features: Robust search enables finding specific alumni instantly by name, graduation year, achievement category, career field, or geographic location. Browsing tools allow chronological exploration, category filtering, featured content rotation, and related profile suggestions. These discovery capabilities encourage extended exploration—visitors spend more time engaging with recognition content discovering alumni connections they wouldn’t find in static displays.
Remote Accessibility: Web integration extends recognition beyond physical campus locations allowing alumni worldwide to view their recognition, families to share achievements with distant relatives, prospective students to explore graduate success before visiting campus, and donors to see recognition from anywhere. This expanded accessibility multiplies engagement exponentially beyond in-person visitors to physical displays.
Engagement Analytics: Digital systems generate valuable data revealing which profiles generate most interest, popular search terms showing how visitors discover content, session duration indicating engagement depth, and demographic information about who accesses recognition. These insights inform content development, promotional strategies, and program optimization impossible with traditional displays.
Long-Term Cost Advantages: While digital systems require higher initial investment ($8,000-$18,000 for commercial touchscreen hardware plus $3,000-$6,000 for software setup), long-term costs prove dramatically lower than continuously adding physical recognition. For institutions recognizing 10-15 alumni annually, digital approaches typically achieve cost parity with traditional methods within 5-7 years while delivering vastly superior functionality. Most significantly, increased giving that effective recognition generates often covers entire investment within first two years.

Understanding digital hall of fame benefits helps institutions evaluate whether modern technology aligns with recognition objectives and community expectations while delivering measurable returns on investment.
Hybrid Implementation Models
Many successful programs combine selective traditional recognition with comprehensive digital systems, balancing symbolic permanence with practical functionality.
Strategic Hybrid Approaches might include maintaining signature physical displays for highest-profile inductees (major donors, national achievers, hall of fame founding members), adding digital touchscreens providing unlimited capacity for comprehensive recognition, integrating QR codes on physical plaques linking to expanded digital profiles, and ensuring web accessibility for remote alumni regardless of physical display format. This balanced strategy honors tradition while solving practical limitations through modern technology, often satisfying stakeholders preferring physical permanence while enabling comprehensive recognition digital systems make possible.
Designing Compelling Content That Honors and Engages
Display format matters less than content quality. The most sophisticated technology or beautifully crafted physical installation fails if content doesn’t honor inductees appropriately while engaging audiences effectively.
Essential Profile Elements
Comprehensive alumni profiles should include specific information creating complete pictures of achievements and journeys.
Educational Foundation: High school or undergraduate years documenting when alumni attended, activities and organizations in which they participated, sports played or arts pursued, academic honors received, leadership positions held, and teachers or mentors who influenced their paths. This institutional connection helps current students see themselves in inductees’ early years while honoring formative educational experiences.
Career Progression: Professional path documentation showing first positions after graduation, career advancement and major transitions, leadership roles and accomplishments, companies or organizations where they worked, industries or fields in which they excelled, and innovations or contributions advancing their professions. Career narratives demonstrate that success develops through persistent effort over time rather than overnight transformation.
Notable Achievements: Specific accomplishments warranting recognition including awards and honors received, publications or creative works produced, patents or innovations developed, organizations founded or led, community initiatives launched, or recognition by professional peers. Concrete examples provide substance supporting general acclaim while giving audiences clear understanding of why individuals merit hall of fame induction.
Community and Service Impact: Civic engagement and philanthropic contributions through volunteer leadership, charitable giving, advocacy work, mentorship activities, board service, or community initiatives. Service recognition demonstrates that institutions value graduates who use success to benefit others and improve communities.

Personal Reflections: Inductees’ own words create authentic connections including reflections on how education shaped their success, memories of teachers or experiences that proved formative, advice for current students pursuing similar paths, messages about values or principles guiding their careers, and expressions of gratitude toward the institution. First-person narratives humanize achievements making inductees relatable rather than distant figures on pedestals.
Writing Principles for Engaging Recognition
Effective profile writing balances formality appropriate for honoring achievements with accessibility engaging diverse audiences.
Active Voice and Dynamic Language: Profiles should use action verbs and engaging syntax rather than passive, bureaucratic language. “Dr. Martinez pioneered innovative treatments revolutionizing patient care” engages more effectively than “treatments were developed.” Dynamic writing makes achievements come alive rather than reading like résumé bullet points.
Specific Examples Over Vague Praise: Rather than general statements like “distinguished career” or “remarkable contributions,” compelling profiles provide concrete details: “led team developing software used by 50 million people worldwide” or “volunteered 2,000 hours over 15 years mentoring at-risk youth.” Specific information gives audiences clear understanding of actual impact while demonstrating achievement depth.
Story Arcs Showing Journey: The most engaging profiles present narratives showing progression from student through career development. How did early interests connect to later success? What challenges did inductees overcome? How did experiences at the institution influence professional paths? Story structure creates emotional engagement helping audiences connect with inductees as real people rather than just impressive achievements.
Accessible Vocabulary: Profiles should avoid jargon or technical terminology making content inaccessible to general audiences. When technical terms prove necessary, brief explanations ensure understanding. Recognition serves students, families, and community members alongside subject matter experts—writing should engage all audiences effectively.
Consistent Length and Structure: While achievement levels vary, profiles should provide roughly equivalent recognition through similar length and structure. This consistency demonstrates equitable treatment while maintaining professional presentation standards. Establish word count guidelines (typically 300-500 words for primary profiles) ensuring neither excessive brevity nor verbose elaboration.
Resources on storytelling through digital recognition provide frameworks for developing compelling narratives that honor achievements authentically while inspiring and engaging audiences effectively.
Strategic Implementation: From Planning Through Launch
Successful recognition programs result from systematic planning addressing all dimensions of implementation from stakeholder engagement through ongoing operations.
Phase 1: Foundation and Planning
Comprehensive planning prevents common pitfalls while establishing strong program foundations.
Stakeholder Engagement: Involve diverse perspectives early ensuring broad support including alumni relations and advancement staff who understand graduate communities, athletic directors and coaches with insights on athletic achievement, academic administrators providing educational perspective, facilities and IT departments addressing technical implementation, student representatives offering contemporary viewpoints, and major donors or booster leadership with philanthropic interests. Early engagement identifies concerns, generates ideas, and builds ownership supporting long-term sustainability.
Objective Clarification: Clear goals inform all subsequent decisions about primary purposes (inspiration, engagement, giving, recruitment, preservation), target audiences (current students, alumni, prospective students, community members), success metrics for program evaluation, timeline parameters and milestone targets, and budget allocation across development, implementation, and operations. Document objectives providing shared reference points when making decisions or evaluating trade-offs.
Resource Assessment: Realistic evaluation of available resources prevents underinvestment or unsustainable commitments including budget for initial implementation and ongoing operations, staff capacity for content development and program management, physical space for displays and recognition events, technical infrastructure supporting digital systems if applicable, and timeline considering other institutional priorities and initiatives. Resource constraints don’t preclude recognition programs—they inform appropriate scale and phasing enabling success within realistic parameters.
Phase 2: Content Development Strategy
Systematic content planning ensures manageable, sustainable profile creation supporting program launch and ongoing growth.
Initial Recognition Pool: Rather than attempting comprehensive historical documentation immediately, strategic approaches begin with recent inductees for whom information is readily available and current students find most relevant, then systematically expand backward through decades as resources allow. Some programs launch with 20-30 recent inductees creating immediate impact while building content development processes, then add 10-15 historical profiles annually gradually expanding coverage.
Content Collection Processes: Establish efficient methods for gathering comprehensive information including archival research checking yearbooks, publications, and institutional records, direct alumni outreach requesting information and materials, professional photography sessions or video interviews when feasible, student project involvement in research and writing when appropriate, and quality control review ensuring accuracy and consistency. Document processes enabling multiple people to contribute efficiently while maintaining professional standards.
Sustainable Annual Cycles: Create predictable rhythms for ongoing recognition including nomination periods accepting community submissions, selection committee meetings evaluating candidates, inductee notification and acceptance, profile development coordinating with new inductees, and induction ceremonies or announcements celebrating new recognition. Regular cycles ensure programs maintain momentum rather than sporadic activity followed by long dormant periods.

Guidance on content planning for digital hall of fame provides practical frameworks for sustainable profile development avoiding burnout while maintaining quality standards supporting effective recognition.
Phase 3: Technology and Display Selection
For institutions choosing digital recognition, careful technology evaluation ensures platforms serve objectives effectively while fitting resources and capabilities.
Essential Evaluation Criteria include content management ease for non-technical staff updating information, user interface intuitiveness ensuring accessibility for all ages and abilities, total cost of ownership including hardware, software, support, and updates, vendor reputation and support quality based on references and track record, scalability supporting future expansion without platform changes, and integration capabilities connecting with existing systems when valuable.
Hardware Specifications: Commercial-grade displays rated for continuous operation (not consumer models), minimum 4K resolution for professional presentation, reliable multi-touch technology supporting intuitive gestures, appropriate screen size for viewing distance and available space (commonly 55"-75" for most installations), and secure mounting with professional cable management ensuring clean, safe installation.
Physical Placement Strategy: Location dramatically affects visibility and engagement through high-traffic areas maximizing exposure (main entrances, cafeterias, gymnasiums, student centers), contextually appropriate locations where alumni naturally gather, accessible positioning meeting ADA requirements, and environmental considerations including lighting avoiding glare, power and network connectivity, and appropriate ambient noise levels enabling comfortable interaction.
Phase 4: Launch and Ongoing Promotion
Strategic launches generate awareness while establishing engagement patterns supporting long-term success.
Soft Launch Testing: Limited release before full public launch identifies issues through inviting select stakeholders for early feedback, testing all functionality comprehensively, gathering usability insights from diverse users, making refinements based on feedback, and verifying analytics tracking works correctly. Soft launches prevent public problems while demonstrating responsiveness to stakeholder input.
Public Launch Events: Grand openings generate awareness and establish recognition importance through formal unveiling ceremonies creating memorable moments, recognition of inaugural or recent inductees celebrating achievements, invitations to recognized alumni and families honoring their presence, media engagement generating publicity coverage, and feature demonstrations encouraging exploration and interaction.
Sustained Promotion: Recognition requires ongoing visibility beyond initial launches including regular communications highlighting new additions, social media featuring individual alumni and their stories, integration with campus tours and student orientations, event-based promotion during reunions or homecoming, and publication features in alumni magazines or newsletters. Sustained promotion ensures recognition remains visible to continuously evolving audiences rather than initial excitement fading into background awareness.
Common Challenges and Proven Solutions
Institutions creating alumni halls of fame encounter predictable obstacles that experienced approaches address effectively.
Limited Historical Information
Many schools discover incomplete records for past alumni complicate comprehensive recognition attempts. Proven solutions include systematic archive research checking yearbooks, newspapers, facility plaques, and organizational records for documentation, alumni outreach campaigns requesting information from classmates or family members, transparent acknowledgment of gaps while inviting community assistance filling them, and phased implementation beginning with well-documented recent alumni while expanding historically as information becomes available. Understanding digitizing yearbooks helps institutions preserve and access historical information systematically.
Selection Controversy and Perceived Favoritism
Despite best intentions, selection decisions sometimes generate community concerns about fairness or favoritism. Prevention strategies include transparent criteria and processes documented publicly, diverse selection committees representing varied perspectives, written evaluation rubrics providing objective assessment frameworks, conflict of interest policies addressing committee member relationships with nominees, and decision documentation maintaining institutional memory about rationales. When concerns arise despite precautions, open communication addressing questions directly while maintaining confidentiality about deliberations typically resolves issues satisfactorily.
Maintaining Long-Term Momentum
Initial launch excitement often fades without strategic attention to sustained relevance and engagement. Sustainability approaches include regular content additions providing reasons for repeat visits, featured content rotation keeping displays fresh between major updates, event-based promotion creating periodic engagement spikes, integration with ongoing programs like reunions or giving campaigns, and continuous improvement based on analytics and feedback rather than “set and forget” approaches. Programs viewing recognition as ongoing commitment rather than one-time project achieve lasting impact and engagement.
Budget Constraints and Resource Limitations
Financial and staffing constraints affect implementation scope and timeline for many institutions. Practical strategies include phased investment deploying initial systems with expansion plans, creative funding through alumni contributions or corporate sponsorships, volunteer involvement for content research or quality assurance, purpose-built platforms minimizing technical complexity, and long-term cost analysis demonstrating digital systems achieve parity with ongoing physical recognition expenses. Many successful programs start modestly, demonstrate value, then expand as additional resources become available.
Conclusion: Building Recognition Programs That Endure
Creating an alumni hall of fame represents a significant investment in institutional culture, community engagement, and legacy preservation. When thoughtfully designed and consistently maintained, recognition programs deliver lasting benefits including inspiring current students through tangible role models, strengthening alumni engagement and philanthropic support, preserving institutional history for future generations, enhancing recruitment through demonstrated graduate success, and building community pride in collective achievements.
The most successful programs share common characteristics: clear criteria ensuring fairness and credibility, compelling content honoring achievements while engaging audiences, appropriate display formats balancing tradition with functionality, sustainable operations maintaining program vitality long-term, and strategic integration with advancement and engagement initiatives.
For institutions beginning recognition programs, starting with solid foundations sets the stage for long-term success. Well-defined selection standards create credibility. Structured nomination processes ensure community participation. Realistic resource planning enables sustainable operations. Manageable initial scope allows demonstration of value supporting expansion over time.
Modern digital recognition solutions like those from Rocket Alumni Solutions offer particular advantages for schools seeking comprehensive, flexible, cost-effective recognition. Unlimited capacity accommodates all distinguished graduates without space constraints. Rich multimedia tells compelling stories honoring achievements appropriately. Instant updates eliminate physical modification costs and delays. Remote accessibility extends engagement beyond campus visitors. The ability to continuously expand recognition while maintaining professional presentation makes interactive touchscreen systems increasingly popular for modern programs.
Beyond immediate recognition purposes, effective alumni halls of fame strengthen bonds connecting past, present, and future institutional community members. They demonstrate that institutions value excellence across diverse domains, inspire students to pursue their own paths to achievement, and create tangible connections between today’s students and accomplished graduates who once walked the same hallways.
Schools ready to create recognition programs can explore additional resources on alumni recognition walls, digital donor recognition displays, and measuring recognition ROI that maximize impact while creating manageable, sustainable programs honoring distinguished graduates for generations to come.