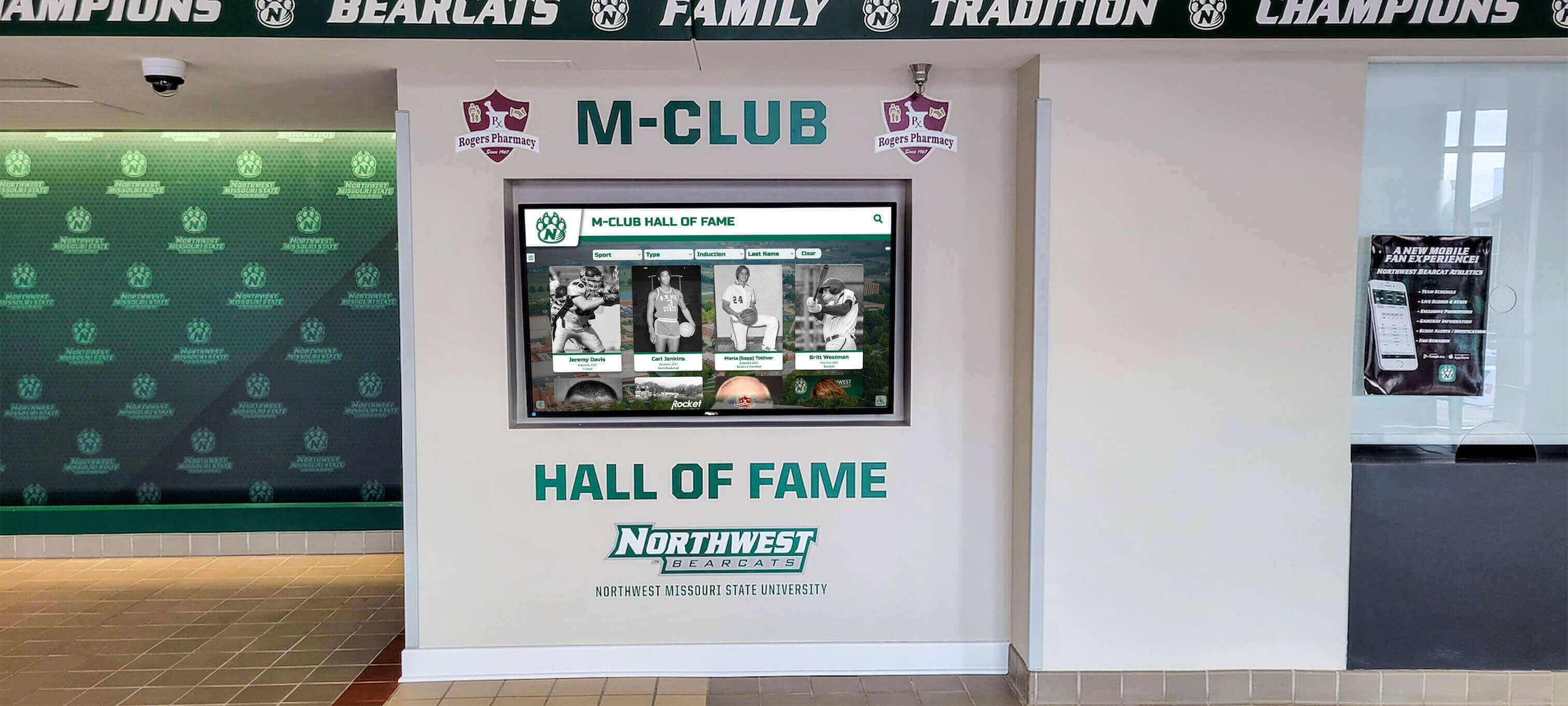
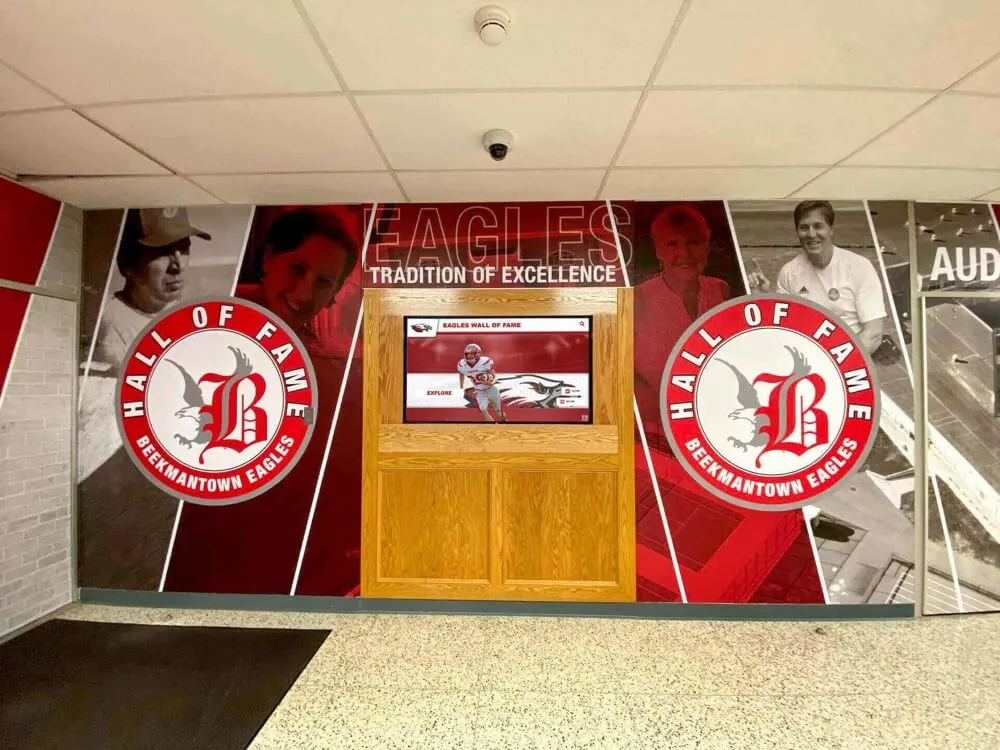
Schools establishing or refining athletic hall of fame programs face a fundamental challenge: creating selection criteria that balance inclusive celebration with meaningful standards. Set the bar too high, and deserving athletes go unrecognized. Set it too low, and hall of fame status loses significance. The most successful programs establish clear, transparent criteria that earn community respect while acknowledging the full spectrum of athletic excellence across sports, eras, and competitive contexts.
Athletic directors and administrators developing hall of fame criteria must address practical questions: What achievement thresholds separate hall of fame excellence from general recognition? How do selection standards account for different competitive contexts—small school versus large school, individual sports versus team sports, championship eras versus rebuilding periods? Should criteria emphasize raw athletic performance, character and leadership, post-athletic success, or balanced combinations? Most critically, how do schools create selection processes perceived as fair by stakeholders who naturally advocate for specific candidates or sports?
Building Credible Hall of Fame Programs
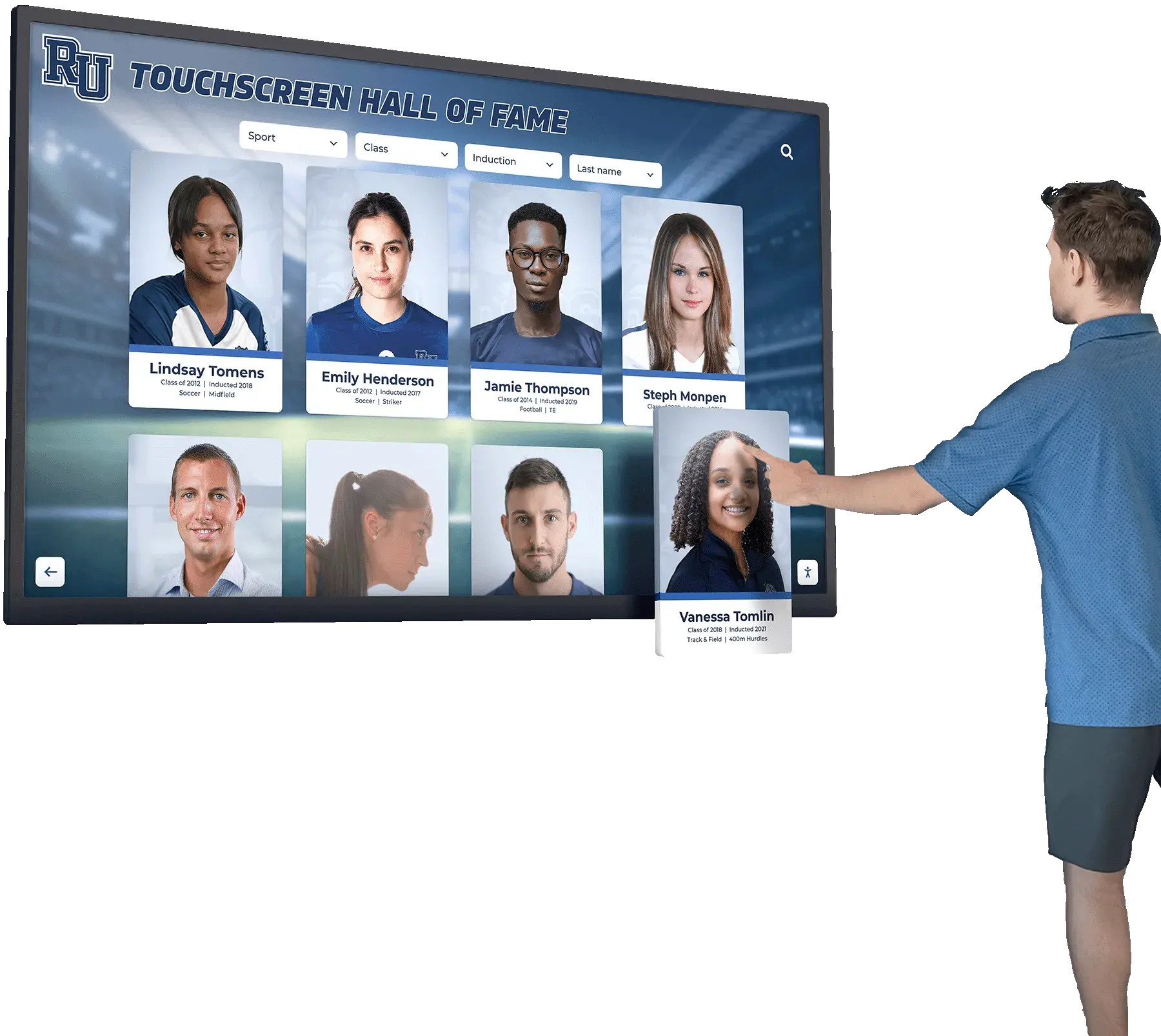
Effective hall of fame criteria accomplish multiple objectives simultaneously: they establish clear achievement thresholds that make induction meaningful, create transparent selection processes that build community confidence, accommodate diverse excellence across sports and eras, honor character alongside athletic performance, and remain adaptable as programs evolve while maintaining consistency. Modern digital hall of fame systems like Rocket Alumni Solutions enable schools to recognize unlimited inductees across comprehensive categories without space constraints forcing difficult exclusions, while providing engaging displays that showcase the criteria-driven selection excellence representing institutional values.
Core Athletic Hall of Fame Eligibility Requirements
Before evaluating athletic achievement, schools must establish foundational eligibility requirements that define the candidate pool and prevent premature recognition.
Waiting Period Requirements
Nearly every credible hall of fame implements mandatory waiting periods between athletic career completion and eligibility for induction. These temporal buffers serve critical purposes in maintaining selection quality and program credibility.
Five-Year Minimum Standard: The most common approach requires five years between graduation or final athletic participation and hall of fame eligibility. This timeframe provides sufficient distance to evaluate achievements objectively, ensures athletic success reflected sustained excellence rather than temporary circumstances, and allows observation of whether high school or college success translated into continued athletic or personal achievement. The five-year standard balances timely recognition against premature inductions that might later appear questionable.
Ten-Year Standards for Perspective: Programs prioritizing historical perspective sometimes implement ten-year waiting periods, particularly for athlete categories. This extended timeframe reveals whether candidates maintained character standards after athletic careers ended, demonstrates whether achievements remain significant viewed across broader program history, and prevents recency bias where recent athletes receive disproportionate consideration versus historical figures whose accomplishments may be undervalued.

Veteran or Historical Categories: Some comprehensive programs create special categories with longer waiting periods—twenty-five or fifty years—specifically recognizing pioneers whose contributions might otherwise be forgotten as collective memory fades. These veteran categories honor athletes who competed when programs were less developed, resources were scarce, or opportunities were limited, applying modified achievement standards that acknowledge competitive context.
Posthumous Recognition Exceptions: Most programs waive waiting periods for deceased individuals, enabling timely recognition of athletes whose careers ended tragically. Immediate posthumous induction demonstrates institutional compassion while honoring individuals who can no longer personally experience recognition.
Participant Affiliation Requirements
Clear participation requirements prevent confusion about who qualifies for hall of fame consideration based on institutional affiliation and competitive representation.
Graduation Status Debates: Programs must decide whether hall of fame eligibility requires formal graduation. Requiring diplomas or degrees limits recognition to those who completed educational programs, reinforcing academic mission alignment. However, strict graduation requirements might exclude talented athletes who left school early for professional opportunities, transferred for various legitimate reasons, or faced personal circumstances preventing degree completion despite significant athletic contributions during attendance.
Most programs establish baseline attendance requirements—typically requiring minimum years of participation or enrollment—while remaining flexible about formal graduation status, particularly for athletes whose departures related to extraordinary athletic opportunities rather than academic failure or disciplinary issues.
Transfer Student Considerations: Schools must establish policies for athletes who transferred into or out of institutions. Common approaches include requiring specific minimum seasons competed, with transfers who participated only briefly generally excluded from consideration. Some programs create special recognition categories for transfer athletes who made significant but shorter contributions, acknowledging their impact while distinguishing their shorter tenure from four-year participants.
Multi-Sport Athlete Evaluation: Criteria should clarify how multi-sport athletes are evaluated—whether each sport generates separate candidacy, athletic contributions are viewed holistically, or achievements must meet thresholds in at least one sport for consideration. Clear multi-sport policies prevent confusion and ensure comprehensive evaluation of diverse athletic contributions.
Understanding comprehensive approaches to academic recognition programs provides frameworks applicable to athletic hall of fame eligibility structures.
Athletic Achievement Criteria and Performance Standards
Once baseline eligibility is established, programs must define what athletic accomplishments merit hall of fame recognition—the heart of credible selection criteria.
Quantifiable Achievement Thresholds
Objective performance benchmarks reduce selection subjectivity while creating transparent standards candidates and stakeholders can understand clearly.
Championship Participation and Team Success: Team achievement represents the most universally applicable standard across sports:
- Conference Championships: Athletes on teams winning conference titles demonstrated sustained excellence against peer competition
- State Tournament Qualification: Reaching state tournaments in any capacity indicates exceptional performance relative to comprehensive competitive fields
- State Championship Participation: Athletes on state championship teams achieved ultimate competitive success at their level
- National Recognition: Participation in national championships, invitational events, or representative teams signals excellence transcending regional competition
Defining precisely what level of championship participation triggers hall of fame consideration—whether simple qualification suffices or only championship wins count—significantly affects selection standards and volumes.

Individual Honors and All-Star Recognition: Individual awards and selections provide clear achievement markers:
- All-Conference Selections: Multiple years earning all-conference honors demonstrates sustained excellence
- All-State Recognition: State-level all-star selection indicates elite performance within comprehensive competitive context
- All-American Status: National recognition represents highest individual competitive achievement
- Player of Year Awards: Conference, district, or state player recognition signals exceptional individual excellence
- Academic All-Conference/State: Combined academic-athletic recognition demonstrates balanced excellence
Programs establishing specific thresholds—requiring All-State selection, multiple All-Conference honors, or comparable achievement levels—create transparent standards while acknowledging that threshold determination significantly affects selectivity.
Statistical Records and Performance Milestones: Quantifiable performance achievements provide objective criteria particularly valuable in sports with comprehensive statistics:
- School Records: Holding career or single-season records in major statistical categories demonstrates exceptional performance relative to program history
- Statistical Milestones: Achieving notable career totals (1,000 points in basketball, specific yardage thresholds in football) represents sustained excellence
- Multiple Record Categories: Athletes holding records across multiple statistical measures demonstrated comprehensive excellence
- Records Longevity: Records standing for extended periods indicate exceptional performance transcending eras
Statistical thresholds prove most applicable in heavily quantified sports like track, swimming, basketball, football, baseball, and soccer. Sports with limited statistical documentation require greater emphasis on championships, honors, and qualitative evaluation.
Post-High School Athletic Success: Continued athletic achievement after high school or college provides additional validation:
- College Athletic Participation: Competing at any college level indicates talent recognized beyond single institution
- NCAA Division I Participation: Division I competition represents elite college athletics
- Professional Opportunities: Any professional sports participation—major leagues, minor leagues, international professional leagues—validates exceptional talent
- Olympic or International Competition: Representing nations internationally signals world-class excellence
Post-secondary success confirms high school or college achievements reflected genuine excellence rather than temporary competitive advantages. However, requiring post-institutional success risks excluding many deserving athletes who excelled athletically but chose non-athletic career paths.
Competitive Context Adjustments
Fair hall of fame criteria acknowledge that identical achievements may represent different excellence levels depending on competitive circumstances.
School Size and Classification Considerations: Athletic achievement significance varies dramatically by school competitive classification:
Large schools competing in highest state classifications face deeper talent pools, more competitive conferences, and more challenging paths to championships. Small schools in lower classifications compete against more limited fields. Recognizing this reality, some programs establish classification-adjusted thresholds—requiring more stringent achievement standards for larger school athletes while acknowledging smaller school excellence within their competitive context.
Alternative approaches create separate hall of fame categories by era or classification, enabling recognition of small-school stars without direct comparison to large-school athletes who faced objectively different competitive landscapes.
Era and Historical Context: Achievement significance changes across decades as programs develop, sports evolve, and competitive landscapes shift:
Athletes who pioneered programs when resources were limited and competition was developing deserve credit for building foundations, even if raw performance metrics appear modest compared to modern athletes benefiting from established programs, superior facilities, professional coaching, and comprehensive training.
Some programs implement era categories—recognizing “Pioneer Era” (first decades), “Development Era” (program growth), and “Modern Era” (current)—with adjusted criteria acknowledging different competitive realities across institutional history.

Sport-Specific Considerations: Different sports require individualized achievement thresholds reflecting their unique competitive structures:
Team sports like football and basketball may emphasize championship success and statistical achievement. Individual sports like track, swimming, cross country, wrestling, and tennis focus more heavily on individual championships, qualifying for state meets, and competitive placements. Less competitive or newer sports might require adjusted standards acknowledging limited competitive depth compared to flagship programs.
Some schools establish sport-specific achievement matrices, defining what constitutes hall of fame excellence within each sport’s unique context rather than applying uniform standards that inadvertently favor certain competitive structures.
Resources on teacher recognition programs demonstrate principles of context-appropriate recognition applicable across different achievement domains.
Character, Leadership, and Non-Performance Criteria
Athletic excellence alone proves insufficient for comprehensive hall of fame evaluation. Character and leadership components ensure recognition celebrates individuals representing institutional values.
Sportsmanship and Character Standards
Hall of fame recognition should honor athletes who competed with integrity, demonstrating values institutions wish to celebrate and model for current students.
Defining Character Requirements: Programs establish character standards through explicit criteria:
- Ejection or Disciplinary History: Some programs automatically disqualify candidates with serious disciplinary violations during athletic careers
- Academic Eligibility Maintenance: Requiring sustained academic eligibility demonstrates balanced student-athlete commitment
- Respect for Officials and Opponents: Sportsmanship expectations emphasize fair play and competitive integrity
- Team Citizenship: Positive teammate relationships and constructive team contribution demonstrate character
- Conduct Standard Violations: Post-career behavior may affect candidacy, particularly serious legal or ethical violations
Character as Disqualifier versus Evaluation Factor: Programs choose between treating character as absolute disqualifying standard—where violations automatically eliminate candidacy regardless of athletic excellence—or as significant factor within holistic evaluation where exceptional athletic achievement might outweigh minor character concerns.
Most programs implement hybrid approaches: serious character violations (violence, major criminal activity, flagrant sportsmanship failures) disqualify candidates absolutely, while minor or ambiguous situations receive case-by-case evaluation weighing complete context.
Post-Athletic Conduct Considerations: Schools must decide whether post-athletic behavior affects hall of fame standing. Some programs evaluate only conduct during athletic careers, viewing hall of fame recognition as acknowledging historical athletic achievement regardless of subsequent life choices. Others consider complete character, potentially excluding or even removing inductees whose post-career conduct contradicts institutional values.
Clear policies established proactively—before controversial situations arise—prevent accusations of ad hoc decision-making targeting specific individuals.
Leadership and Impact Evaluation
Beyond individual performance, hall of fame criteria may recognize leadership contributions that elevated teams and programs.
Captaincy and Team Leadership: Formal team captain designation or informal leadership roles demonstrate respect from teammates and coaches. Multiple-year captains signal sustained leadership impact worth recognizing alongside athletic achievement.
Mentorship and Development: Athletes who developed younger teammates, improved program culture, or demonstrated selfless commitment to collective success over individual statistics exemplify leadership deserving recognition even when raw performance metrics might fall slightly below typical thresholds.
Program Ambassadorship: Representing programs with distinction in community, media interactions, and public settings demonstrates character and leadership extending beyond competitive venues.

Overcoming Adversity Narratives: Athletes who demonstrated resilience overcoming injuries, personal challenges, academic struggles, or other obstacles while maintaining athletic excellence often inspire current athletes in ways pure athletic dominance cannot. Selection criteria acknowledging perseverance alongside performance enable recognition of complete athletic journeys.
Post-Athletic Contributions and Alumni Engagement
Some programs explicitly recognize post-career contributions when evaluating hall of fame candidates, while others limit evaluation strictly to athletic careers.
Alumni Program Support: Former athletes who remain engaged—mentoring current athletes, attending events, supporting fundraising, promoting programs—demonstrate lasting commitment that some selection committees view as enhancement to hall of fame candidacy.
Professional Achievement: Significant post-athletic career success in any field indicates the character, work ethic, and excellence that athletic programs aim to develop, potentially factoring into holistic candidate evaluation.
Community Leadership: Civic engagement, charitable work, and community service demonstrate values schools wish to associate with hall of fame recognition.
Programs must carefully balance post-athletic considerations against risks of favoring well-connected or locally prominent alumni over equally deserving athletes who moved away or chose private lives. Clear criteria establishing how alumni contributions factor into selection—whether as supplementary consideration or significant evaluation component—maintain fairness while acknowledging some programs value ongoing institutional connection.
Hall of Fame Categories Beyond Athletes
Comprehensive hall of fame programs extend recognition beyond individual athletes to honor coaches, contributors, teams, and special achievement categories.
Coaching and Staff Inductee Criteria
Coaches who built programs, developed talent, and shaped student-athletes deserve recognition alongside the players they mentored.
Head Coach Achievement Thresholds: Coaching induction criteria typically emphasize:
- Career Win Totals: Reaching specific victory milestones demonstrates sustained competitive success
- Championship Success: Conference championships, state tournament appearances, or state titles represent ultimate coaching achievement
- Program Building: Elevating programs to unprecedented competitive levels deserves recognition even absent championships
- Coaching Longevity: Long-tenured coaches demonstrating sustained commitment to institutions earn appreciation
- Player Development: Producing college athletes, all-state performers, or championship contributors demonstrates coaching excellence
- Coaching Honors: Conference or state coach of year recognition validates peer acknowledgment
Assistant Coach and Staff Recognition: Some comprehensive programs recognize exceptional assistant coaches, athletic trainers, strength coaches, or equipment managers whose behind-the-scenes contributions enabled athletic success. These categories acknowledge that championships require comprehensive team efforts beyond head coaching and athlete performance alone.
Understanding approaches to athletic director responsibilities illuminates leadership contributions deserving hall of fame consideration.
Team Induction Criteria
Historic teams achieving exceptional collective success merit recognition celebrating shared achievement and team chemistry that exceeded individual talent.
Championship Team Recognition: State championship teams represent the highest collective achievement, with many programs automatically inducting all state champions. Conference championship teams or state tournament qualifiers may also receive team induction depending on program history and championship frequency.
Undefeated or Historic Season Teams: Teams completing perfect seasons or achieving extraordinary records (like 30+ victories in basketball) demonstrated rare collective excellence even if championship success eluded them.
Program Milestone Teams: Teams achieving program firsts—first conference title, first state tournament appearance, first victory over traditional rival—hold special historical significance potentially meriting team induction even without championship success.

Team Selection Timing: Programs must establish when team induction occurs—whether immediately following achievement or subject to the same waiting periods as individual athletes. Immediate team recognition capitalizes on contemporary interest and enables team member participation while relationships and memories remain fresh. Delayed recognition ensures historical perspective but may miss opportunities for team reunions and collective celebration.
Contributor and Builder Categories
Individuals who never competed or coached but enabled athletic excellence through other contributions merit recognition in comprehensive hall of fame programs.
Facility Benefactor Recognition: Major donors whose philanthropy built athletic facilities, funded equipment, or enabled program enhancements made tangible contributions often acknowledged through contributor categories.
Long-Service Administrative Recognition: Athletic directors, principals, or administrators whose leadership elevated athletic programs, secured resources, or advocated for athletics over extended periods contributed significantly to comprehensive athletic excellence.
Program Founder Recognition: Individuals who established specific sports programs, created athletic departments, or initiated athletic traditions deserve acknowledgment for pioneering contributions that enabled all subsequent achievement.
Community and Booster Recognition: Long-serving booster club leaders, volunteer coordinators, or community advocates who dedicated significant time and energy supporting athletic programs may receive contributor recognition acknowledging that championships require community ecosystem support beyond institutional resources alone.
Resources on donor recognition strategies provide frameworks for acknowledging non-athletic contributions in hall of fame contexts.
Nomination and Selection Process Structures
Even with clear criteria, credible hall of fame programs require structured nomination processes and transparent selection procedures that build community confidence.
Nomination System Design
Effective nomination processes balance accessibility—ensuring all worthy candidates receive consideration—with manageability—preventing overwhelming administrative burden from excessive low-quality nominations.
Open Nomination Systems: Programs accepting nominations from any source—alumni, current students, parents, coaches, community members—demonstrate democratic inclusivity. Open systems surface worthy candidates selection committees might overlook, engage broader communities in recognition awareness, and create transparency reducing perceptions of insider control.
However, open nominations generate higher administrative workload processing applications, require public education about eligibility criteria preventing inappropriate submissions, and may produce numerous unqualified nominations consuming committee review time without advancing selection quality.
Committee-Only Nominations: Restricting nomination authority to designated selection committee members ensures thorough candidate vetting, reduces administrative burden, and maintains quality control over nomination pools. Critics argue committee-only systems create insider control, reduce community engagement, and risk overlooking worthy candidates lacking direct committee connections.
Hybrid Nomination Approaches: Many programs implement compromise solutions: open nomination systems with administrative pre-screening where athletic staff verify basic eligibility before forwarding candidates to selection committees. This approach maintains open accessibility while ensuring committees evaluate only qualified candidates meeting baseline standards.
Nomination Application Requirements
Standardized nomination forms ensure consistent information for candidate evaluation while documenting achievements systematically.
Essential Application Components:
- Biographical Information: Full name, years of attendance/competition, graduation year, contact information if available
- Athletic Participation Details: Sports competed, positions played, years of participation, jersey numbers
- Achievement Documentation: Championships won, honors received, statistical records, all-conference or all-state selections
- Impact Statement: Written narrative explaining why candidate merits hall of fame induction beyond raw data
- Supporting Materials: Photos, news clippings, game programs, video links, statistical sheets, or other documentation
- Nominator Information: Name and relationship to candidate demonstrating nomination legitimacy
Clear submission deadlines with adequate preparation windows balance giving nominators sufficient time against preventing year-round rolling submissions creating unsustainable administrative burden.

Selection Committee Composition and Function
Committee structure significantly affects selection credibility, decision quality, and stakeholder confidence in process fairness.
Balanced Committee Representation: Effective committees include diverse perspectives while maintaining manageable size:
- Athletic Administration: Athletic directors provide institutional knowledge and program context
- Coaching Staff: Current or former coaches understand competitive standards and athletic excellence markers
- Alumni Representatives: Former athletes offer peer perspective and historical program knowledge
- Community Members: External representatives provide outside viewpoint and credibility
- Faculty or Administrative Representation: Non-athletic school personnel ensure alignment with institutional values
- Booster Club Leadership: Supporter representatives acknowledge community stakeholder interests
Committee size typically ranges from seven to fifteen members—large enough for diverse perspectives but small enough for substantive discussion and decision-making efficiency.
Recusal and Conflict Management: Clear policies maintaining selection integrity:
- Committee members must recuse themselves from voting on relatives, former teammates, or individuals with significant personal relationships
- Professional relationships (coaches evaluating former players) receive explicit policy guidance—some programs require recusal, others permit participation
- Recent graduates or immediate family members of current staff typically deemed ineligible for committee service
- Documented recusals create transparency and accountability demonstrating process integrity
Evaluation and Voting Procedures: Committees implement various decision-making approaches:
Quantitative Scoring Systems: Some programs assign numerical ratings across defined criteria—athletic achievement (40%), championships (20%), honors (15%), leadership (15%), character (10%)—with aggregate scores determining recommendations. Quantitative approaches provide perceived objectivity, enable clear ranking of candidates, and create documentation for decision justification.
Holistic Discussion Processes: Other committees prefer qualitative deliberation without numerical scoring, believing athletic excellence resists pure quantification and that nuanced discussion better captures unique circumstances and context. Holistic approaches enable flexible evaluation but may appear more subjective to stakeholders questioning selection decisions.
Voting Thresholds: Programs establish specific approval requirements—simple majority, two-thirds supermajority, or unanimous consent—balancing efficiency against selectivity. Higher thresholds create more exclusive recognition by requiring broader agreement but may exclude deserving candidates lacking universal support.
Annual Induction Quotas and Frequency
Administrative decisions about how many inductees to recognize annually and how often to hold inductions significantly shape hall of fame character.
Fixed Annual Class Sizes: Many programs induct specific numbers annually—commonly three to six individuals across all categories—ensuring consistent recognition rhythm, predictable ceremony planning, and guaranteed momentum maintaining program visibility.
Fixed quotas prevent years without inductees that might undermine program continuity while avoiding excessively large classes that dilute recognition significance. However, strict quotas may force excluding deserving candidates to meet numerical caps or inducting marginally qualified individuals to reach minimums.
Variable Class Sizes: Alternative approaches induct all candidates meeting thresholds regardless of number, avoiding artificial limitations excluding worthy recognition or forcing inappropriate selections. Variable classes adapt naturally to candidate quality—larger inaugural classes building recognition volume, smaller classes in years with fewer qualifying candidates.
Induction Frequency: While most programs hold annual inductions, some smaller institutions conduct ceremonies every two or three years. Less frequent inductions accumulate larger candidate pools ensuring substantial classes worthy of significant ceremony investment, reduce administrative burden on smaller staffs, and create special occasion significance.
However, extended cycles mean longer delays between achievement and recognition, risk losing opportunities for inductee participation as time passes, and may reduce sustained program visibility.
Understanding frameworks for trophy display case selection helps contextualize physical recognition alongside systematic selection processes.
Addressing Common Hall of Fame Criteria Challenges
Even thoughtfully designed criteria face predictable implementation challenges requiring proactive solutions.
Challenge: Sport Equity and Balance
Selection patterns may inadvertently favor high-profile sports like football and basketball over less visible programs, creating perception of biased recognition.
Solutions: Monitor induction distribution across sports identifying disproportionate patterns. Establish minimum quotas ensuring each sport receives regular recognition. Create sport-specific achievement matrices defining excellence within each competitive context. Consider rotating sport-focused induction years guaranteeing comprehensive attention. Track demographic patterns ensuring equitable gender representation across men’s and women’s sports.
Challenge: Recency Bias
Recent athletes may receive disproportionate consideration versus historical figures whose accomplishments fade from collective memory despite equal or superior achievement.
Solutions: Implement robust nomination systems actively soliciting historical candidate recommendations. Assign committee members specific responsibility for researching and championing historical candidates. Create separate “veteran” or “historical” categories with dedicated induction slots. Conduct periodic historical reviews systematically evaluating prior eras for overlooked candidates. Document selection rationale enabling future review ensuring historical athletes received fair evaluation relative to contemporary standards.

Challenge: Incomplete Historical Documentation
Many schools discover incomplete records when researching deserving historical athletes, complicating evaluation and recognition.
Solutions: Acknowledge documentation gaps honestly while honoring athletes appropriately based on available information. Implement oral history projects capturing firsthand accounts from senior alumni before knowledge is permanently lost. Create community appeals asking alumni to contribute photos, clippings, and memories filling historical gaps. Accept that some inductees will have less complete profiles due to historical circumstances beyond current control. Consider adjusted standards for historical categories recognizing documentation limitations while preserving recognition opportunity.
Challenge: Controversial Candidate Situations
Occasionally qualified candidates have complicated personal histories—post-career legal troubles, character questions, or documented behavioral issues—creating selection dilemmas.
Solutions: Establish clear character standards proactively before controversial situations arise rather than creating ad hoc policies appearing targeted at individuals. Determine whether character violations occurred during or substantially after athletic careers, weighing relevance to athletic achievement recognition. Consider whether adequate time passed enabling redemption and changed behavior demonstrating character growth. Engage committees in confidential thorough deliberation respecting candidate privacy while ensuring principled decisions. Document decision reasoning for institutional memory preventing future inconsistent approaches. Accept that some decisions will receive criticism regardless of process thoroughness.
Challenge: Maintaining Selection Credibility
Hall of fame programs lose value if selection decisions appear arbitrary, political, or inconsistent with stated criteria.
Solutions: Publish clear criteria publicly on websites, nomination materials, and ceremony programs. Document selection committee composition and process transparency. Communicate selection rationale for inductees through ceremony programs and display content connecting recognition to specific criteria. Regularly review and refine criteria based on experience and stakeholder feedback while maintaining consistency across time. Invite periodic external review from peer institutions validating process integrity and suggesting improvements.
Resources examining best hall of fame tools provide context for systematic recognition program development.
Documenting and Publishing Hall of Fame Criteria
Transparent criteria communication builds stakeholder confidence while guiding nominations toward appropriate candidates.
Written Criteria Documentation
Comprehensive written criteria should address all major eligibility and selection considerations:
Eligibility Section: Clearly state who qualifies for consideration—graduation requirements, waiting periods, participation minimums, and affiliation standards.
Achievement Standards: Define specific thresholds for athletic performance, championships, honors, statistical records, and post-athletic success that constitute hall of fame-worthy excellence.
Character and Leadership Expectations: Articulate sportsmanship standards, leadership considerations, and how character factors into evaluation.
Category Descriptions: Explain all induction categories—athletes, coaches, contributors, teams—with category-specific criteria.
Selection Process Overview: Describe nomination procedures, committee composition and function, evaluation approach, and voting thresholds.
Timeline and Deadlines: Specify annual nomination windows, committee deliberation schedule, announcement timing, and ceremony dates.
Publishing and Accessibility
Criteria should be readily available to all stakeholders:
- Athletic Department Websites: Dedicated hall of fame pages with complete criteria, nomination forms, and current inductee information
- Nomination Materials: Forms and instructions including eligibility summaries and submission requirements
- Ceremony Programs: Published criteria in induction event materials demonstrating recognition basis
- Digital Displays: Criteria information integrated into interactive hall of fame installations educating viewers about selection standards
Wide criteria distribution ensures stakeholders understand recognition basis, reduces inappropriate nominations by clarifying standards, demonstrates process transparency building credibility, and enables informed community discussion about program values and priorities.

Periodic Criteria Review and Refinement
Hall of fame criteria should not remain static indefinitely. Periodic review ensures standards remain appropriate as programs evolve:
Review Frequency: Many programs conduct comprehensive criteria reviews every five to ten years or when significant program changes occur—competitive reclassification, new sports additions, facility transformations.
Review Process: Effective reviews engage diverse stakeholders including current committee members, athletic administration, coaches, recent and historical alumni, and community representatives. Structured feedback mechanisms identify criteria strengths and weaknesses while proposing specific refinements.
Balanced Evolution: Criteria refinement should balance consistency—avoiding constant changes that undermine selection stability—with adaptation ensuring standards remain relevant. Modifications should strengthen fairness and clarity while maintaining recognition program integrity rather than lowering standards to accommodate specific candidates.
Modern Display Solutions Supporting Comprehensive Criteria
Well-designed criteria create large inductee volumes as programs recognize excellence across sports, eras, and categories. Traditional physical displays struggle accommodating unlimited growth, while modern digital systems eliminate capacity constraints.
Digital Hall of Fame Display Advantages
Interactive digital recognition systems overcome traditional limitations while providing enhanced capabilities:
Unlimited Capacity: Digital displays accommodate hundreds or thousands of inductees without space constraints. As selection criteria identify deserving candidates across comprehensive categories, displays scale infinitely unlike physical plaques facing wall space limitations.
Category Organization: Digital systems organize inductees by sport, era, achievement type, or custom categories aligning with selection criteria. Visitors easily navigate to specific recognition types, search by name or year, filter by achievement category, and explore comprehensive program history systematically.
Rich Achievement Documentation: Digital profiles showcase complete candidate information that justified induction—career statistics, championships won, honors received, leadership contributions, character demonstrations, and multimedia content bringing achievements to life through photos, videos, and detailed narratives impossible with physical plaques.
Easy Updates: Adding new inductees, correcting historical information, or enhancing profiles requires simple content updates rather than physical plaque production and installation. This ease encourages comprehensive recognition across diverse criteria rather than selective limitation forced by physical constraints.
Remote Accessibility: Web-integrated digital systems extend hall of fame access beyond physical facility locations, enabling alumni anywhere to explore recognition, prospective students to research program tradition, and community members to appreciate athletic excellence regardless of facility visit capacity.
Solutions like Rocket Alumni Solutions provide purpose-built platforms designed specifically for educational athletic recognition, delivering intuitive content management requiring no technical expertise while creating engaging displays that showcase criteria-driven excellence across unlimited inductee volume.
Understanding digital recognition display options helps programs select appropriate systems supporting comprehensive recognition aligned with thoughtful selection criteria.
Building Hall of Fame Programs That Honor True Excellence
The most successful athletic hall of fame programs share core characteristics: clear criteria applied consistently ensuring fairness and credibility, transparent selection processes building stakeholder confidence, comprehensive recognition acknowledging diverse excellence across sports and categories, balanced standards honoring athletic performance alongside character and leadership, and sustainable operations maintaining program vitality across leadership transitions and institutional changes.
When schools invest systematically in hall of fame criteria development, the benefits extend far beyond individual inductee recognition. Current athletes witness concrete excellence standards creating motivation and aspiration. Alumni communities see fair recognition of diverse contributions building inclusive engagement. Athletic programs demonstrate values and priorities through systematic celebration of excellence. Institutional culture strengthens around shared appreciation for achievement, character, and service. Historical preservation protects athletic heritage that otherwise disappears as collective memory fades across generations.

Effective hall of fame criteria accomplish what arbitrary recognition cannot: they create perceived fairness even among stakeholders disappointed by specific selections, maintain recognition significance preventing dilution through over-inclusion, build institutional confidence that recognition reflects genuine excellence, preserve flexibility accommodating evolving program circumstances, and demonstrate systematic thoughtfulness honoring achievement appropriately.
Ready to develop or refine your athletic hall of fame criteria and selection process? Begin by engaging diverse stakeholders in structured criteria development, research peer institution approaches identifying effective practices and common pitfalls, draft comprehensive written criteria addressing all major selection considerations, establish transparent nomination and selection processes with clear timelines, implement digital recognition systems supporting unlimited criteria-driven selection, and commit to periodic criteria review ensuring ongoing relevance and fairness.
Your athletic programs have produced generations of talented student-athletes, dedicated coaches, and passionate supporters whose achievements deserve recognition that honors genuine excellence while maintaining meaningful standards. Thoughtful hall of fame criteria ensure this recognition reflects institutional values, celebrates diverse contributions equitably, and preserves athletic heritage in ways that inspire current athletes toward their own pursuit of hall of fame-worthy excellence.
Athletic halls of fame represent more than retrospective recognition—they’re forward-looking investments in program culture, athlete motivation, and institutional tradition. When selection criteria balance inclusive celebration with meaningful standards through transparent processes managed consistently across time, schools create recognition programs that strengthen athletic communities while honoring everyone whose contributions genuinely merit the permanent acknowledgment that hall of fame status represents.
Explore digital hall of fame solutions that enable comprehensive recognition aligned with thoughtful selection criteria, supporting unlimited inductees across diverse categories while providing engaging displays that showcase the criteria-driven excellence representing your program’s highest values and most distinguished achievements.